16S/18S/ITS Amplicon Sequencing Service
Amplicon sequencing is a method that sequences specific lengths of PCR-amplified products or captured fragments, primarily using high-throughput sequencing technologies to target specific genetic materials within defined environments. Traditional methods often fail to isolate and clone most natural microbes, presenting significant challenges in qualitative and quantitative microbial analysis and diversity studies. Amplicon sequencing addresses these challenges by enabling precise qualitative and quantitative analyses of microbial content in samples, making it a vital tool in microbial diversity assessments.
16S rDNA and 18S rDNA are ribosomal DNAs found in bacteria and fungi, respectively, which contain multiple highly variable regions, whlie ITS represents the DNA sequence located between the small and large subunit rRNA genes across bacteria, fungi, and archaea. These target regions are chosen for their mix of evolutionary conservation and variability. The ease of PCR amplification, even from minimal DNA quantities, combined with the significant sequence variation even among closely related species, makes amplicon sequencing a preferred method in both taxonomy and molecular systematics.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
1. 16S rDNA Sequencing
This method targets the gene encoding 16S rRNA, found across all bacterial genomes. It is particularly useful for distinguishing between bacterial genera and is easily sequenced, making it extensively used for pathogen detection and identification. The variable regions of the 16S rRNA gene frequently aid in phylogenetic classification at the genus or species level.
2. 18S rDNA Sequencing
Targets the DNA encoding the ribosomal small subunit RNA in eukaryotes, with regions varying from conserved to highly variable. These differences are used to reflect phylogenetic relationships and interspecies variations, respectively. 18S rDNA is evolutionarily more conserved than ITS.
3. ITS Sequencing
In eukaryotes, the ITS region, the spacer between 18S and 28S rDNA, experiences less selective pressure and shows considerable variability. It serves as a moderately conserved area useful for taxonomic studies at or below the species level.
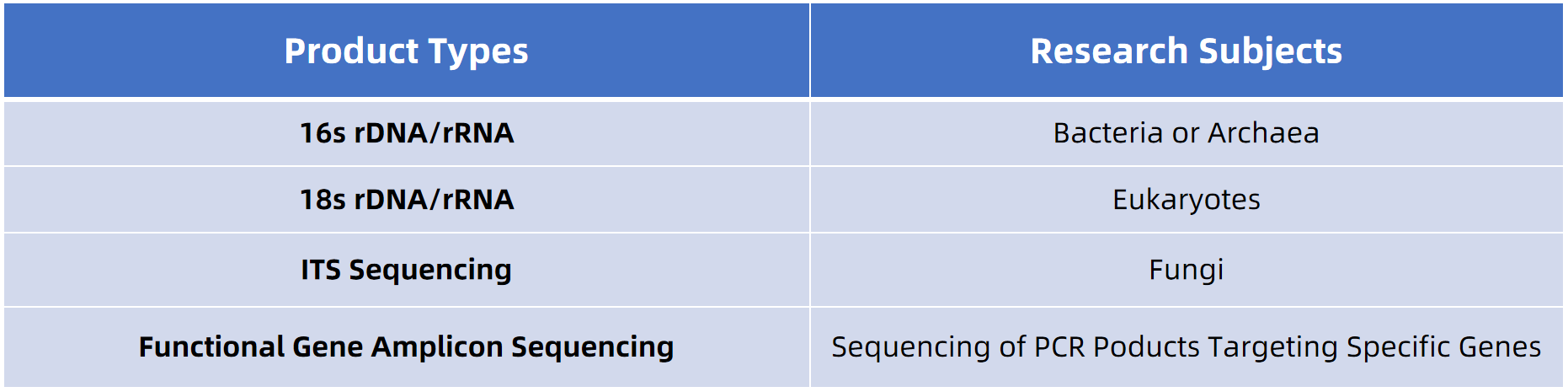
Figure 1. Amplicon Sequencing Research Subjects
Experimental Workflow

Analysis Workflow
![]()
Figure 2. Amplicon Sequencing Analysis Workflow
Technology Advantages
1. High Efficiency in Identification
This sequencing approach offers a rapid and accurate alternative to traditional methods such as cloning or culturing.
2. Dual-Region Detection
Allows flexibility in targeting one or several variable regions, facilitating longer reads and more accurate microbial analyses.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
Requires less sequencing depth compared to metagenomic sequencing, thus offering a higher cost-benefit ratio.
4. High Sensitivity
Enables the detection of microbes present in very low abundance.
Service Advantages
1. Experienced Technical Team
Offers comprehensive professional services from experimental design through sample testing to data analysis.
2. Streamlined Procedures
Minimizes unnecessary sample usage and time waste, ensuring faster turnaround times.
3. Customized Strategies
Employs varied extraction methods and sequencing strategies tailored to different sample sources to accommodate diverse environmental studies.
4. Integrated Multi-Omics Analysis
MtoZ Biolabs utilizes advanced platforms for proteomics and metabolomics, enhancing paper quality through comprehensive omic integration.
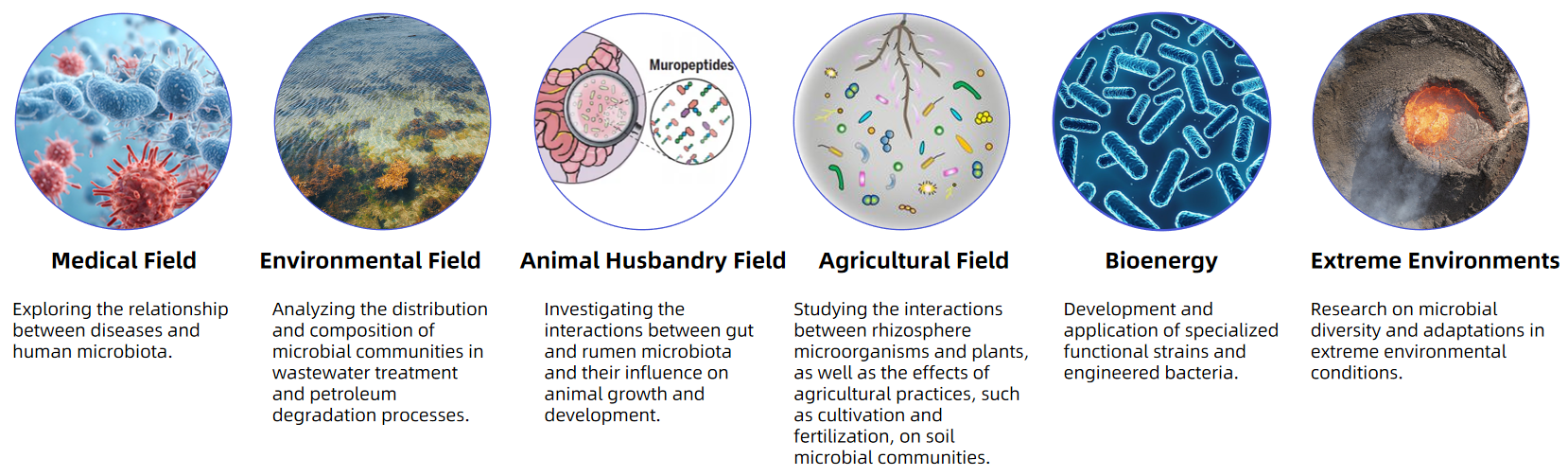
Applications
Sample Submission Requirements
Types of samples: Meta samples such as feces, soil, etc. or Meta DNA samples can be tested. For detailed requirements, please consult our technical staff.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Full-Length 16S/18S/ITS Sequencing Service
Integrative Metabolomics-16S rDNA Sequencing Analysis Service
How to order?







