Lipidomics Analysis Service
Lipidomics is the study of the complete set of lipids in biological systems, aiming to understand their composition, structure, function, and dynamic changes under various physiological and pathological conditions. By utilizing advanced mass spectrometry techniques and bioinformatics tools, lipidomics enables the comprehensive identification, quantification, and characterization of lipid species, offering critical insights into cellular signaling, energy metabolism, and membrane dynamics. Lipidomics analysis workflow primarily consists of sample preparation, mass spectrometry (MS) data acquisition, and data processing. First, during sample preparation, biological samples are processed through steps such as the addition of internal standards, solvent extraction, and optional derivatization. Next, in the MS data acquisition phase, various ionization techniques (e.g., ESI, MALDI) are used, optionally combined with ion mobility spectrometry, followed by MS and MS/MS analysis to generate high-resolution lipid data. Finally, in the data processing stage, spectral data analysis and bioinformatics tools are employed for isotope correction, lipid species identification, quantification, pathway enrichment, and metabolic network analysis, ultimately yielding valuable outputs such as lipidomes, disease biomarkers, and therapeutic targets.
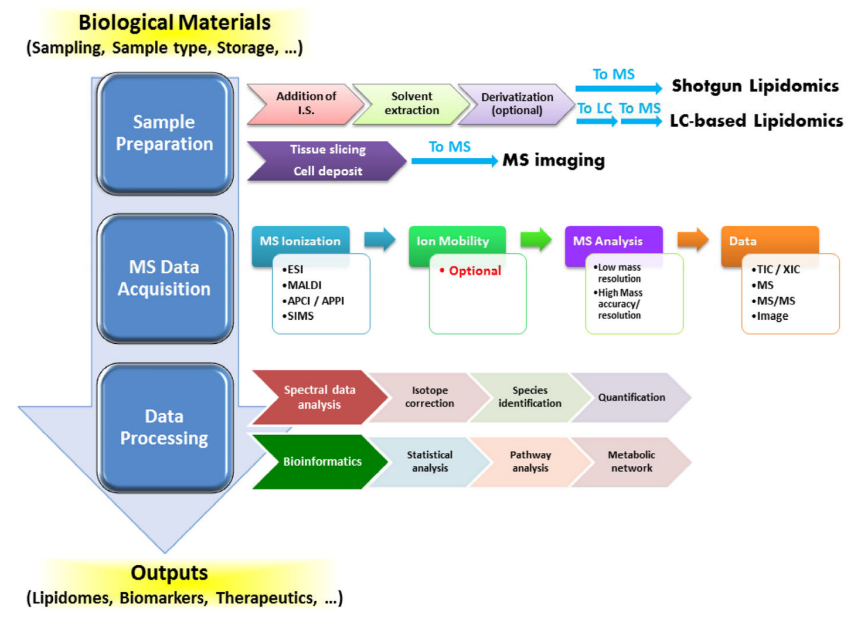
Yang, K. et al. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016.
Figure 1. A Typical Workflow of Lipidomic Analysis of Biological Samples
MtoZ Biolabs leverages advanced mass spectrometry platforms, including the Thermo Fisher Orbitrap Fusion Lumos and Q Exactive HF mass spectrometers, combined with the Nano-LC nanoliter liquid chromatography system, to deliver high-precision, high-throughput lipidomics analysis service that provides comprehensive insights into lipid composition, structure, and dynamics across diverse biological samples. Our team consists of experienced scientific experts proficient in various lipid extraction, separation, and quantitative analysis techniques, ensuring data accuracy and reproducibility. We utilize cutting-edge bioinformatics tools for in-depth data mining, providing comprehensive insights into lipid metabolic pathways and their regulatory mechanisms in biological processes. MtoZ Biolabs is dedicated to offering reliable lipidomics analysis service to research institutions and enterprises, supporting the investigation of disease mechanisms, the discovery of potential biomarkers, and the advancement of drug target development. If you are interested in our service, please contact us freely.
Service Advantages
1. Our lipidomics analysis service offers professional and customized experimental design to meet your research requirements.
2. Multiple choices of state-of-the-art analytical platforms for reaching a higher level both in depth and scope
3. Lower sample demand
4. Stringent quality control system covering the entire qnalytical processes, ensuring acquisition of high-quality data
5. Lipidomics analysis service in MtoZ Biolabs is compatible with a variety of types of samples, ranging from all Kinds of tissues and cell samples to body fluids, etc.
Case Study
1. Native MS-Guided Lipidomics to Define Endogenous Lipid Microenvironments of Eukaryotic Receptors and Transporters
This study introduces a comprehensive strategy combining Native MS and lipidomics to elucidate the interactions between mammalian membrane proteins and their endogenous lipid microenvironments. By employing Native MS, researchers can directly observe co-purified endogenous lipids within membrane protein complexes and determine the apparent affinity of specific lipids. Simultaneously, lipidomics enables qualitative and quantitative analysis of the bound lipids, including fatty acids, sterols, glycerolipids, phospholipids, and glycolipids. This method encompasses the entire workflow, from membrane protein sample preparation and native mass spectrometry data acquisition to lipidomics analysis, integrating multi-layered information to address experimental challenges. This strategy facilitates a deeper understanding of the structural and functional mechanisms underlying lipid-membrane protein interactions. Combining Native MS, the lipidomics analysis service enables qualitative and quantitative analysis of endogenous lipids bound to membrane proteins, meeting diverse research needs.
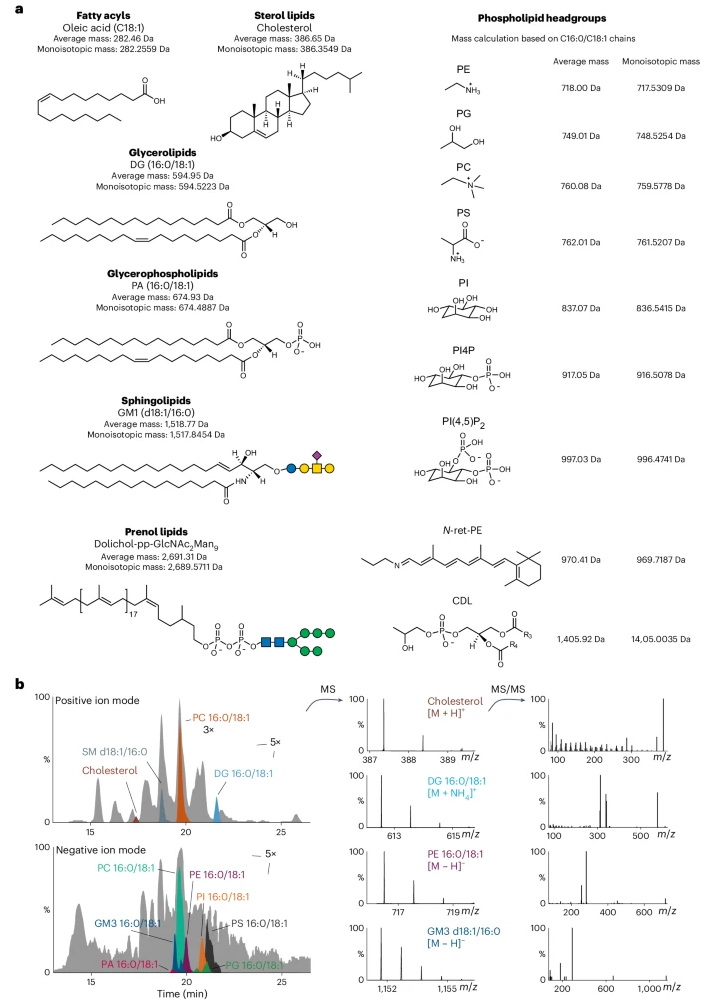
Wu, D. et al. Nat Protoc. 2024.
Figure 2. The Most Common Lipids Detected in MS-Based Lipidomics
2. Four-Dimensional Trapped Ion Mobility Spectrometry Lipidomics for High Throughput Clinical Profiling of Human Blood Samples
This study proposes a lipidomics approach based on four-dimensional (4D) trapped ion mobility spectrometry mass spectrometry for high-throughput analysis of lipidomes in human blood samples. The method integrates automated lipid extraction, four-dimensional feature selection (mass-to-charge ratio, retention time, collision cross-section, and fragmentation spectra), and strategies for reproducible and cross-validated quantification. Using trapped ion mobility mass spectrometry, researchers characterized the 4D features of 200 lipid standards and 493 lipids from reference plasma, establishing stringent criteria for lipid annotation. With this approach, 370 lipids were annotated in reference plasma, 364 lipids in serum, and 359 lipids were quantified using internal standards. Furthermore, the study demonstrates the high-throughput capability of 4D lipidomics in analyzing plasma, serum, whole blood, and venous and finger-prick dried blood spots, facilitating reliable characterization of individualized lipidome phenotypes. Utilizing advanced ion mobility spectrometry and high-throughput workflows, lipidomics analysis service can achieve accurate lipid annotation and reliable quantification across diverse biological samples, facilitating comprehensive lipidomic profiling for clinical and phenotypic studies.
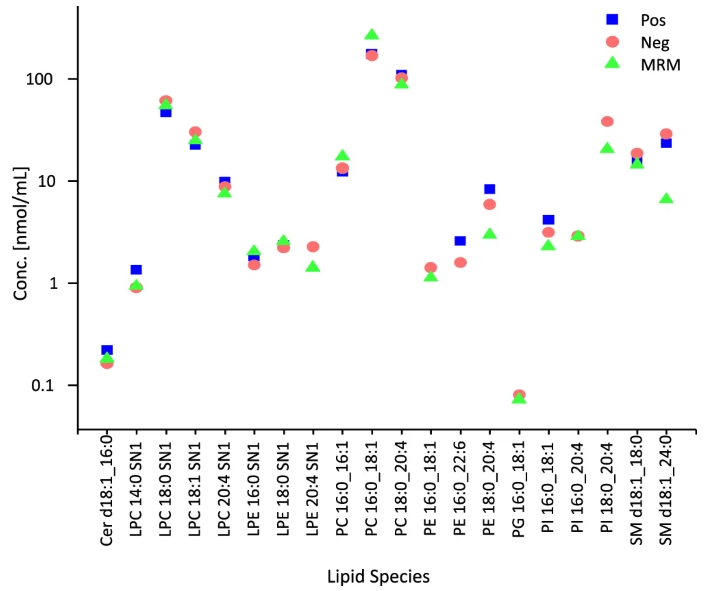
Lerner, R. et al. Nat Commun. 2023.
Figure 3. Comparison and Cross-Validation of Quantified Lipid Concentrations
Applications
1. Lipidomics Analysis Service for Studying Metabolism
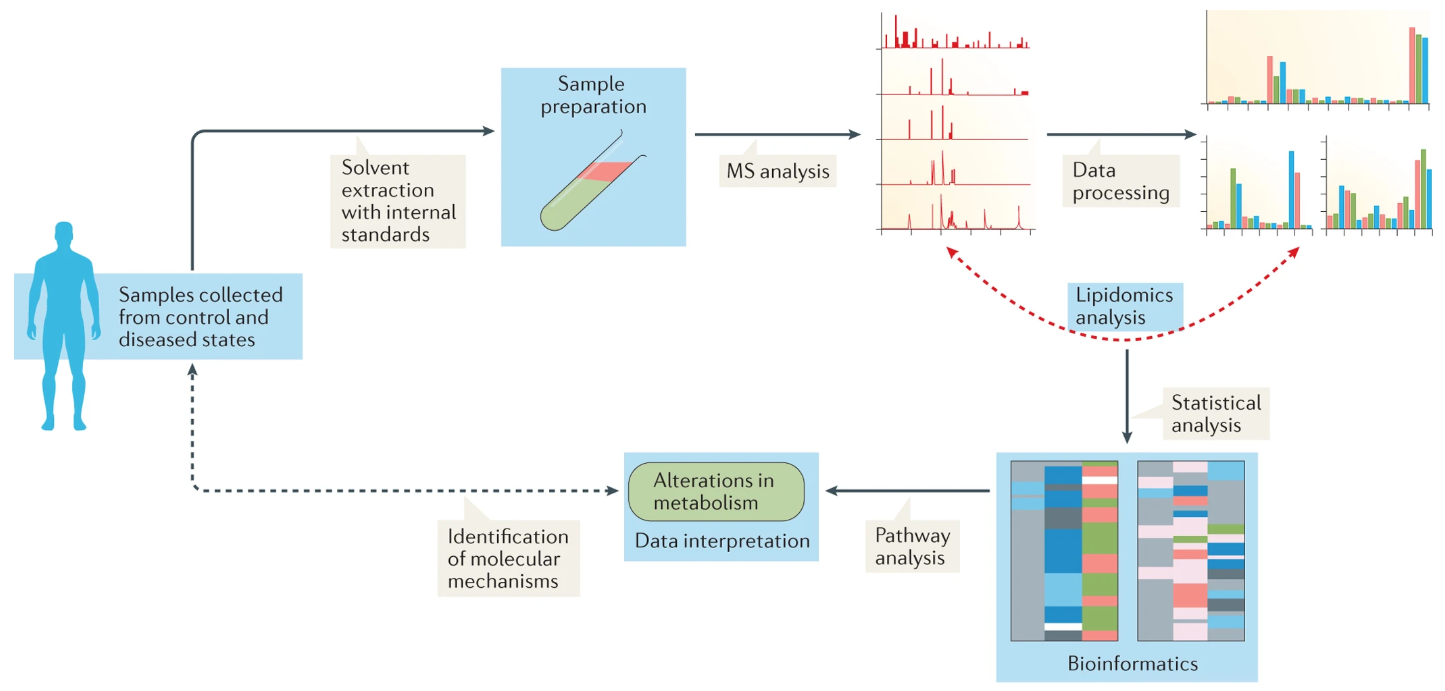
Han, X. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016.
Figure 4. Lipidomics for Studying Metabolism
2. Lipidomics Analysis Service in Biomarker Research
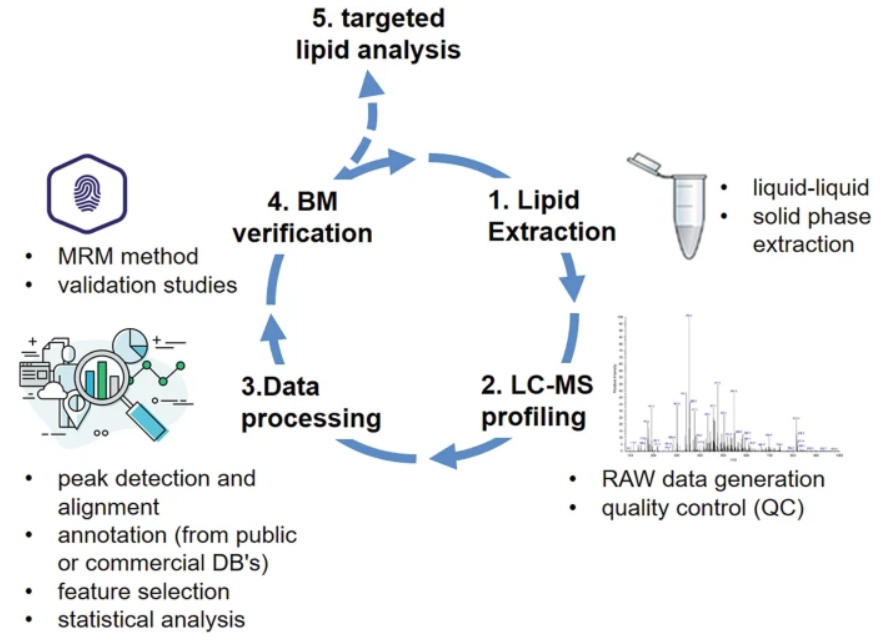
Hornemann, T. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022.
Figure 5. Lipidomics in Biomarker Research
3. Lipidomics Analysis Service in Drug Development
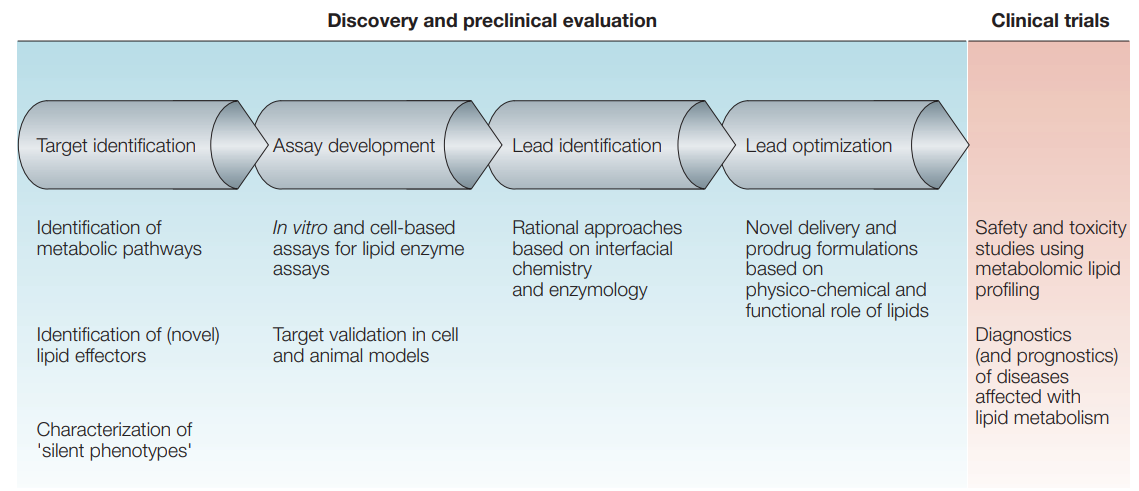
Wenk, MR. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005.
Figure 6. Lipidomics in Drug Development
Sample Submission Suggestions
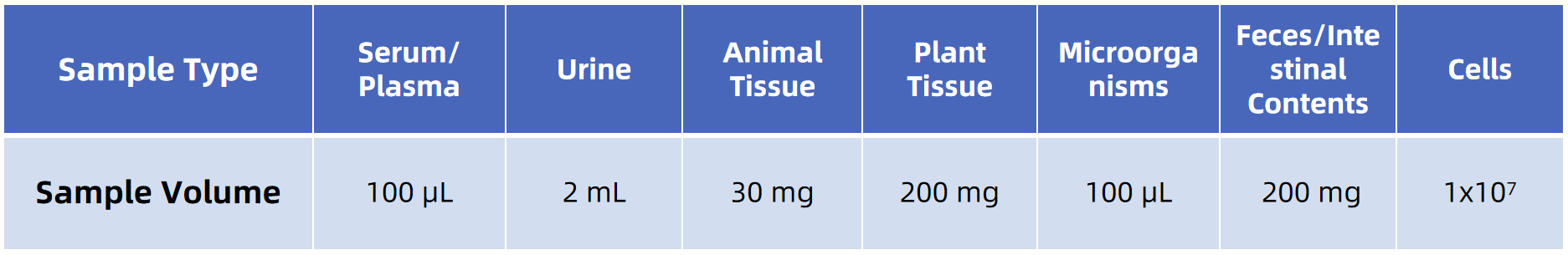
Note: We will perform testing experiments before we start official experiments. To ensure the most cost-effective and accurate analysis is provided, only qualified samples will proceed to the official analysis.
Deliverables
1. Experiment Procedures
2. Parameters of Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometer
3. MS Raw Data Files
4. MS Data Quality Checks
5. Metabolites Quantification Data
6. Bioinformatics Analysis (PCA, KEGG, etc)
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Untargeted Lipidomics Analysis Service
Targeted Lipidomics Analysis Service
Lipidomics MALDI Imaging Service
Metabolomics
Quantitative Proteomics
Protein Analysis
How to order?







