Exosome Lipidomics Service
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) present in a multitude of body fluids and cell culture supernatants. Most cell in organism can secret exosomes, which are diminutive vesicles characterized by a lipid bilayer with diameters ranging from 50 to 150 nm. The genesis of exosomes involves several stages: invagination of the plasma membrane, endosome formation, multivesicular bodies (MVBs) formation, and eventual extracellular release. Exosomes facilitate intercellular communication by transferring a complex array of molecules, including lipids, proteins, DNAs, RNAs, mRNAs, and miRNAs.
Exosomes are composed of proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and other metabolites. Lipids are crucial not only for the structure of exosomal membrane but also the formation and release of exosomes. A comprehensive understanding of the lipid constituents of exosomes is vital for elucidating biological property and therapeutic potentials of EVs. Exosome lipidomics can elucidate biogenesis and functional role of EVs, facilitate the identification of lipid-based biomarkers, and enhance our understanding of their roles in disease surveillance.
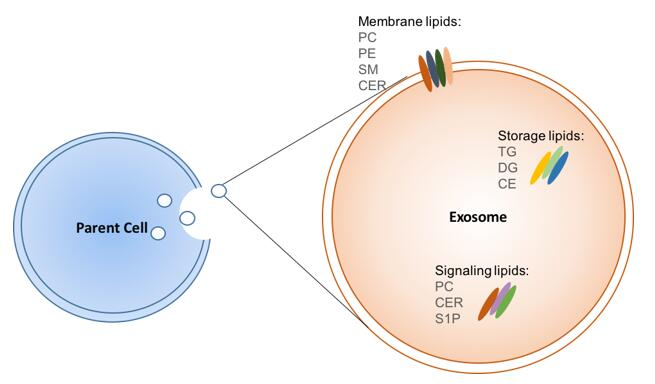
Javdani-Mallak, A. et al. Sci Total Environ. 2024.
Figure 1. Exosome Lipidomics Expertise
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs offers an integrated, one-stop solution for exosome lipidomics analysis, encompassing exosomal isolation, lipidomics analysis, data interpretation, and report production. This service is supported by a platform renowned for its stability, reproducibility, and sensitivity in the separation, characterization, identification, and quantification of exosomal components. Free project evaluation!
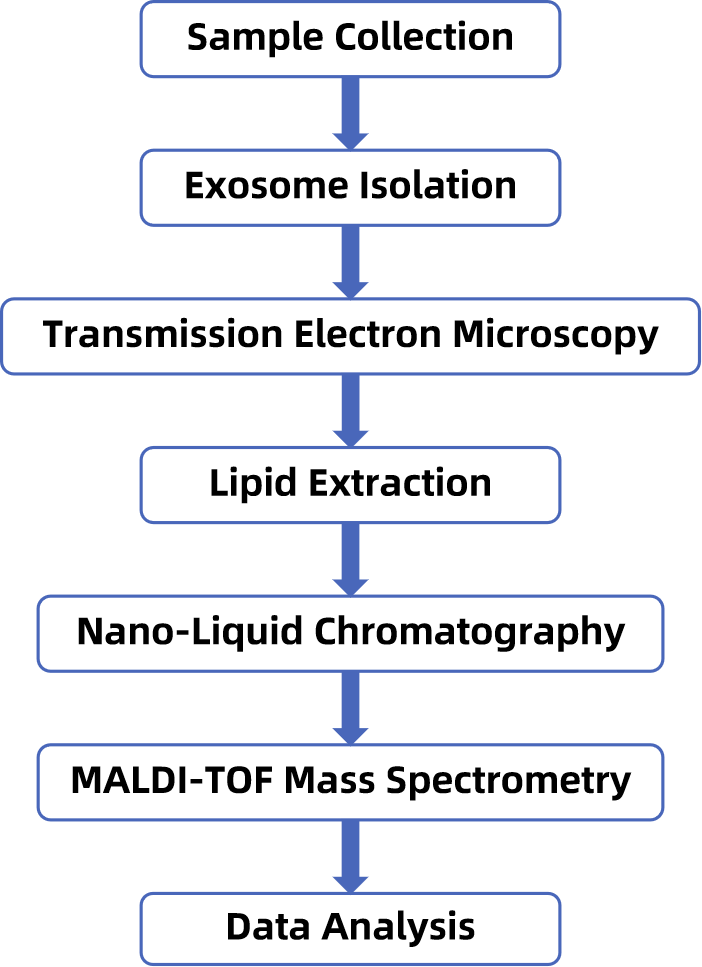
Analysis Workflow
Sample Submission Requirements
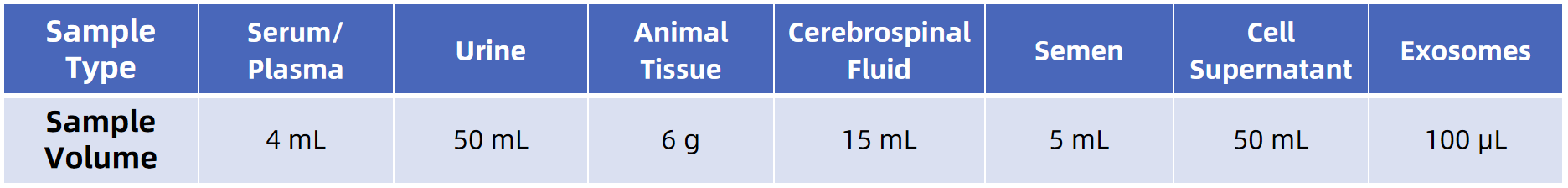
For more sample details, please consult our technical team.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Untargeted Lipidomics Analysis Service
How to order?







