Metabolomics Analysis Service
- Precision Medicine
- Drug Discovery
- Pathological Research
- Biomarker Discovery
- Plant Physiology and Pathology Research
In the post-genomic era, metabolomics has become a cross-disciplinary field with the primary goal of quantitatively studying the diverse dynamic metabolite levels when an organism confront with external stimuli, pathophysiological changes, and genetic mutations. Established at the end of the 20th century by professor Jeremy Nicholson at Imperial College London, metabolomics has since expanded rapidly into various fields such as disease diagnosis, drug development, nutritional science, toxicology, environmental science, and botany, all of which are closely related to human health care.
Metabolomics technology now exceeds standard clinical chemistry techniques, accurately analyzing hundreds to thousands of metabolites. It provides detailed information of the metabolic phenotype, enabling precise medical research, including the characterization of metabolic disorders underlying diseases, discovery of new therapeutic targets, and identification of biomarkers for disease diagnosis or monitoring drug activity.
The most common metabolomics analysis methods are mass spectrometry (MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. MS techniques include LC-MS and GC-MS. The basic principle of MS involves ionizing sample components in an ion source, generating charged ions with different mass-to-charge (m/z) ratios, forming an ion beam under an accelerating electric field, and entering the mass analyzer. In the mass analyzer, electric and magnetic fields are used to achieve opposite speed dispersion, focusing the ions to obtain a mass spectrum. This determines their mass (m/z) and allows quantitative or semi-quantitative analysis based on the intensity of m/z. NMR is a spectroscopic technique based on the principle of nuclear energy absorption and re-emission caused by changes in an external magnetic field. NMR spectra can be used to quantify concentrations and characterize the chemical structures of metabolites.
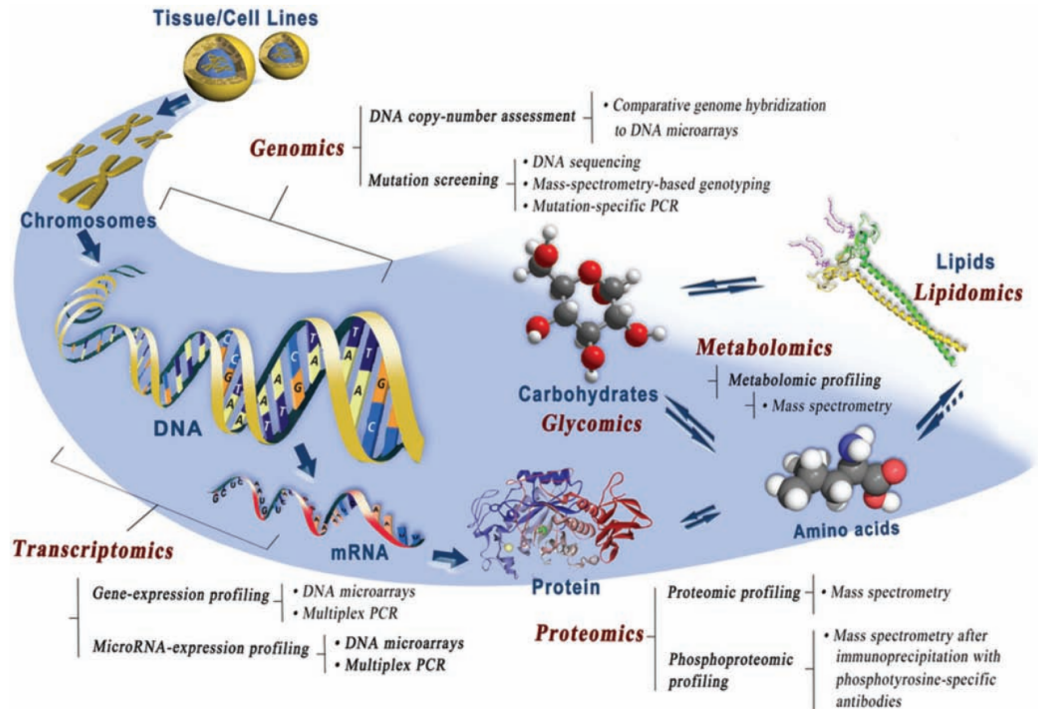
Wu, R. Q. et al. J Dent Res. 2011.
Figure 1. Technological Approaches Used in Different Omics
The choice of metabolomics technology depends primarily on the study's objectives and sample type. NMR requires minimal sample preparation, and the spectra generated have a linear relationship with compound concentrations. However, NMR's relatively low sensitivity usually only detects the most abundant species and fewer substances, with a long purification process limiting its widespread use. Conversely, MS, combined with effective sample preparation and chromatographic separation, offers high sensitivity and specificity, and a good dynamic range. This makes MS, especially high-resolution LC-MS, particularly suitable for both untargeted and targeted metabolomics. As long as a substance can be ionized and detected, it can be analyzed using LC-MS. Therefore, optimized sample preparation conditions, appropriate chromatographic mass spectrometry detection methods, and standardized operating procedures are crucial for successful metabolomics analysis. MtoZ Biolabs' comprehensive standard operating procedures (standard operating procedure, SOP) ensure reliable sample testing.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
1. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
It is commonly used for targeted analysis of water-soluble metabolites (requiring derivatization), some lipids, and organic acids.
2. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
LC-MS-based metabolomics includes untargeted metabolomics, targeted metabolomics, untargeted lipidomics, and targeted lipidomics. It is commonly used for targeted and untargeted analysis of water-soluble small molecules such as amino acids, sugars, alcohols, organic acids, amines, and TCA cycle intermediates, as well as large lipid molecules.
3. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR)
It is commonly used for substance identification and analysis of simple or purified samples.
Service Advantages
1. High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Platform
Leveraging high resolution mass spectrometry for data acquisition enables the differentiation of isomers and metabolites with similar molecular weights, significantly enhancing the reliability of metabolite identification.
2. Accurate Qualitative Results
Utilizing the "Four-Step Filtering Method" ensures higher precision in molecular mass matching, greatly improving qualitative accuracy.
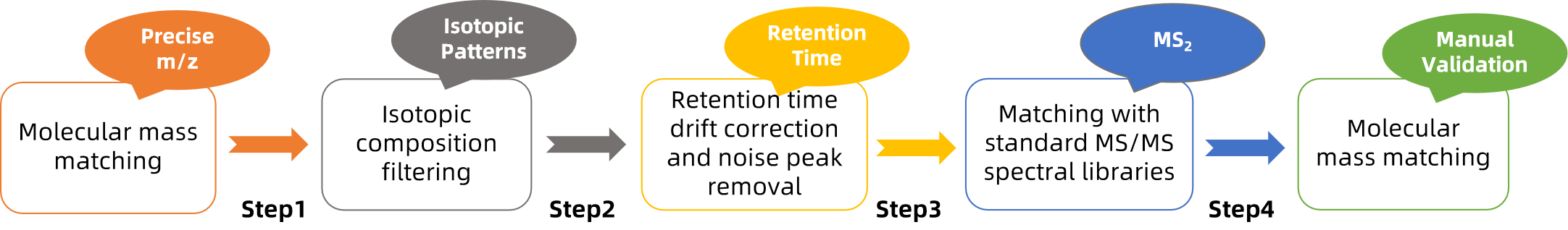
3. Stringent Quality Control
A comprehensive multi-tier quality control system is in place to ensure the highest standards in data quality management.
Sample Submission Requirements
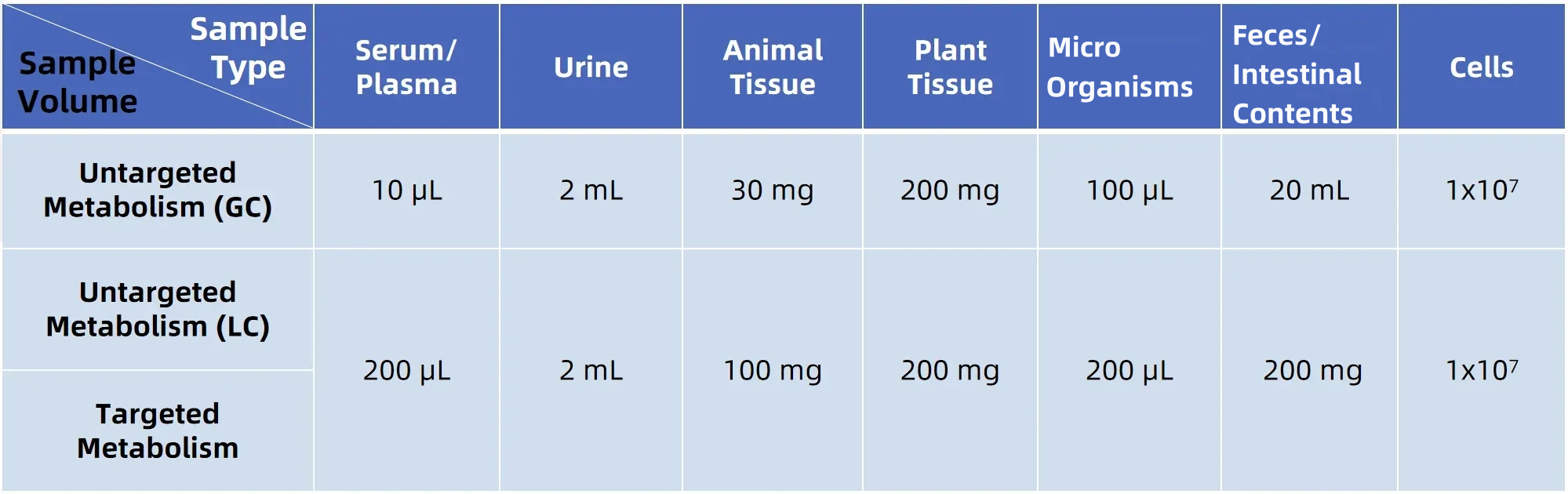
For more sample details, please consult our technical team.
Applications
FAQ
1. Which sample type is more suitable for metabolomics, serum or plasma?
Both serum and plasma are frequently used in metabolomics studies. While their detection capabilities are quite similar, the matrix effects differ significantly between the two and are not directly comparable. Therefore, it is crucial to use the same sample type consistently throughout a given project.
2. Can samples stored for several years still be used for metabolomics analysis?
The quality of the sample has a direct impact on the results of metabolomics studies. If the samples were collected following standardized protocols, promptly frozen after collection, and have not undergone any freeze-thaw cycles during storage, even those stored for several years, or over a decade, can still be viable for metabolomics analysis.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







