Post-Translational Modifications Proteomics Service
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) are covalent and usually enzymatic modifications on proteins. Common PTMs include phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, glycosylation, and so on. These PTMs can cause huge influences on protein structure, distribution, and function, hence, increasing the complexity of proteome to a greater extent. Protein PTMs is generally analyzed by measuring the mass increased on the modified peptides. Since PTMs are generally present in very low abundance, specific enrichment procedures are required before PTMs identification. MtoZ Biolabs has established a powerful and professional Post-Translational Modifications Proteomics Service, which includes Thermo Fisher Q ExactiveHF and Orbitrap Fusion Lumos mass analyzer system, coupled with Nano-LC system. Our aim is to provide the most professional support for our clients' research.
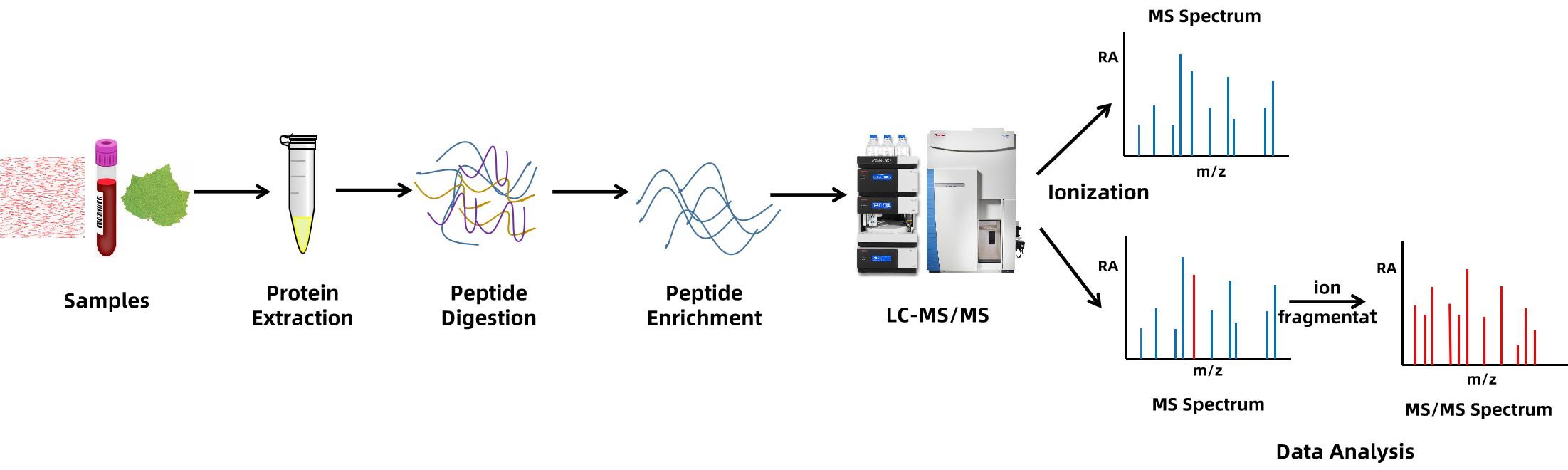
Analysis Workflow

PTMs Analysis Service Categories
MtoZ Biolabs provides protein phosphorylation analysis service with highly efficient phospho-peptides enrichment processing and Nano LC-MS/MS analysis. Coupled with SILAC/iTRAQ labeling, this service can be applied to large-scale phospho-proteomics analysis.
MtoZ Biolabs provides precise acetyl-proteomics analysis service using Nano LC-MS/MS. We also use CST acetylation-specific antibodies for acetyl-peptide enrichment, and 2-3 different enzymes for protein digestion to ensure full scan of acetyl-peptides.

MtoZ Biolabs offers protein ubiquitination identification and quantification service using high-resolution mass spectrometry analysis. We also use highly specific ubiquitin antibody for enrichment of low abundance ubiquitin-peptide.
MtoZ Biolabs utilizes the HCD/ETD mode of Orbitrap Fusion mass spectrometry for glycoprotein analysis. Coupled with Byonic software, we can accurately analyze N- and O-linked glycosylation sites and the corresponding glycogens.

MtoZ Biolabs provides disulfide bond analysis service at both single protein level and proteome level. We have optimized our sample preparation method to reduce the chance of in vitro disulfide bond exchange and maintain the native protein structure to the greatest extent.
MtoZ Biolabs has optimized our sample preparation protocols to obtain highly purified histones with the least effect to the modification, and ensures precise histone modification analysis using Nano LC-MS/MS.
*Note: We also provide custom analytical service to identify many other types of PTMs. For special requirement, please contact us for project discussion.
Sample Submission Requirements
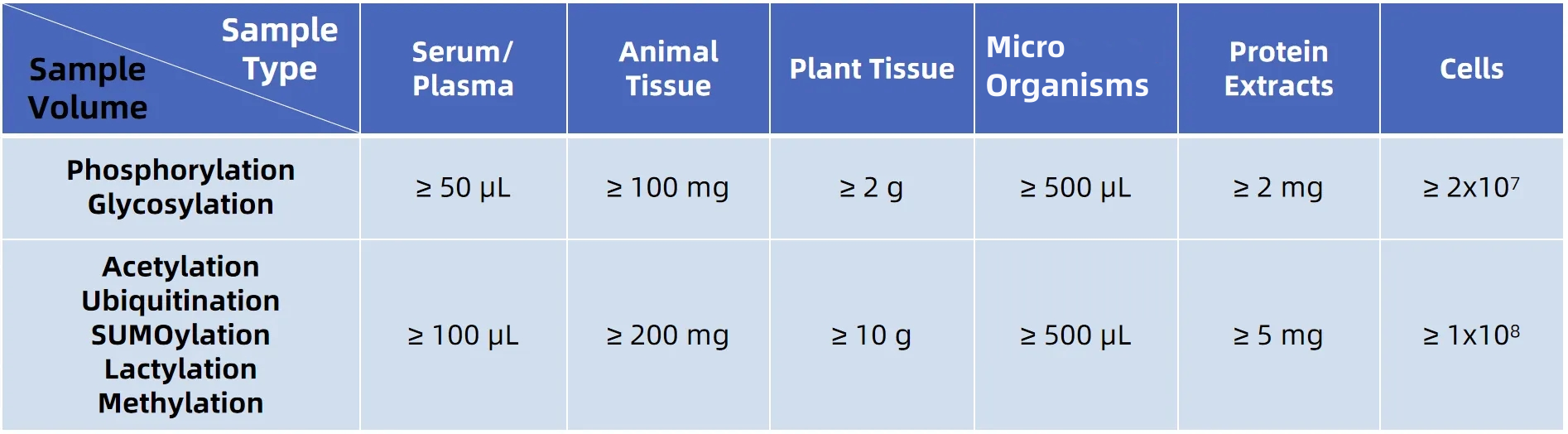
*Customers are welcome to contact us for detailed sample requirements before sending your samples.
Case Study
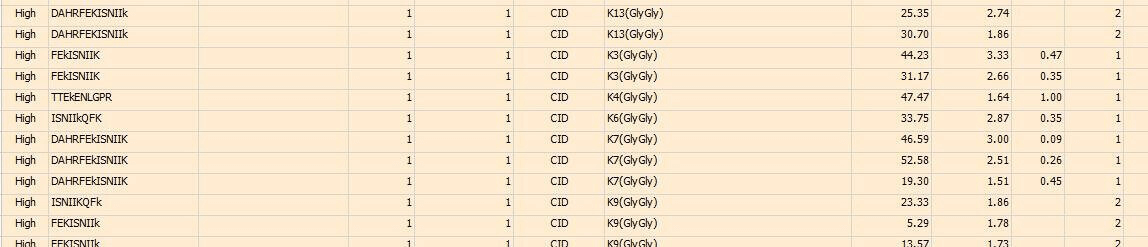
In this study, the ubiquitination modification sites of a Co-IP protein sample are analyzed. Part of the final analytical results is listed as below, showing the peptide sequences and identified ubiquitination sites respectively.
Deliverables
1. Experiment Procedures
2. Parameters of Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometer
3. MS Raw Data Files
4. Identification of Peptides with PTMs
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Quantitative Ubiquitinomics Service
Quantitative Phosphoproteomics Service
Quantitative Glycoproteomics Service
Protein Analysis
LC-MS Analysis of Pull-Down Proteins
Protein Sequencing
Protein Full-Length Sequencing
PTM Analysis
How to order?







