Mass Spectrometry Protein Sequencing Service
Mass Spectrometry Protein Sequencing is an advanced technique for addressing complex protein sequence analysis, capable of accurately identifying and interpreting the amino acid sequences of unknown proteins. Proteins function both inside and outside cells and are involved in nearly all biological processes. As the final executors of gene expression, they directly participate in various intricate activities such as cellular metabolism, signal transduction, and immune responses. Therefore, precise protein sequence analysis is not only central to fundamental biological research but also a critical step in precision medicine, early disease diagnosis, and new drug development. Although traditional protein analysis techniques, such as Western Blot and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), have played important roles in specific fields, their capacity to identify and characterize unknown proteins in complex samples remains limited.
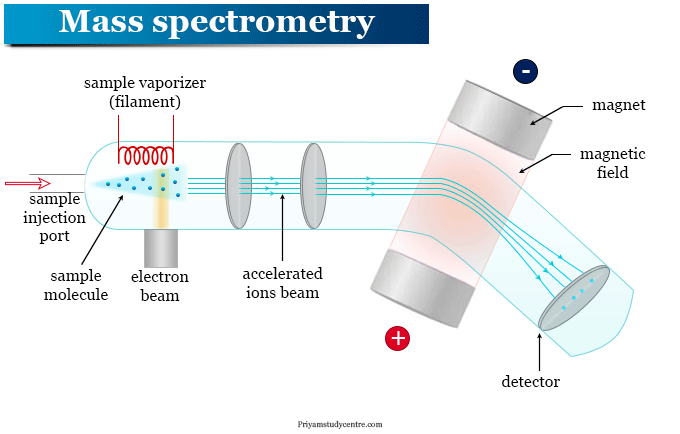
Source:https://www.priyamstudycentre.com/2022/02/mass-spectrometry.html
Principle of Mass Spectrometry
With the rapid development of mass spectrometry (MS) technology, Mass Spectrometry Protein Sequencing has become a core tool in proteomics research. As a high-sensitivity, high-resolution technology, mass spectrometry can reveal protein amino acid sequences and structural features by analyzing mass-to-charge ratios (m/z) and fragment information. Consequently, Mass Spectrometry Protein Sequencing Service have been widely applied to proteomics analyses of complex biological samples, providing strong support for disease research, drug development, and biomarker screening.
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
The core technology of the Mass Spectrometry Protein Sequencing Service is protein sequence decoding based on mass spectrometry analysis. By measuring the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of protein molecules and the fragment ions generated under high-energy collisions, mass spectrometry reveals the molecular structure and sequence of proteins. Relying on high-resolution liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS), tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS), and other techniques, MtoZ Biolabs’ Mass Spectrometry Protein Sequencing Service can comprehensively sequence proteins in complex samples, providing highly accurate amino acid sequence information. Whether it’s a purified single-protein sample or a complex biological sample, MtoZ Biolabs can offer customized services to help clients obtain the precise data they need.
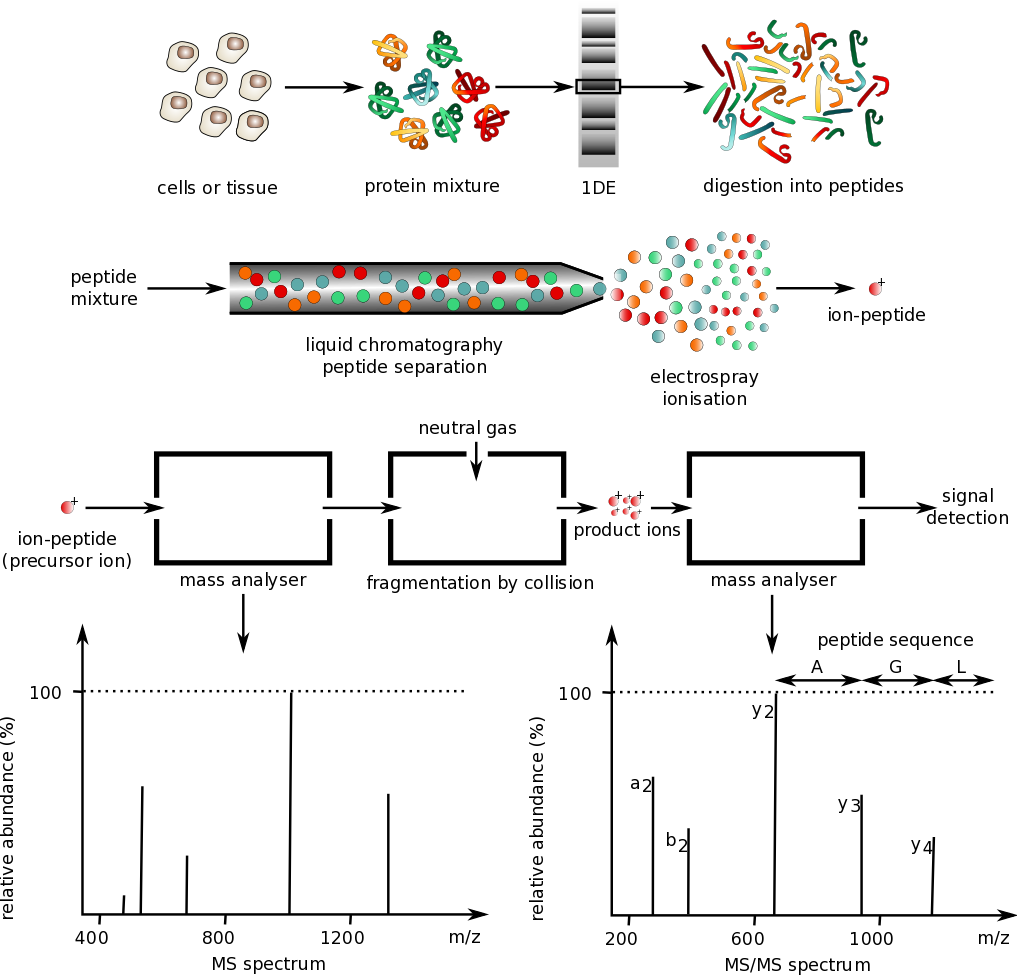
Service Advantages
1. High Sensitivity and High Resolution
Our Mass Spectrometry Protein Sequencing Service utilizes state-of-the-art instruments such as Orbitrap and Q-TOF mass spectrometers, enabling precise analysis of protein sequences in complex samples and delivering high-resolution mass data. This allows even low-abundance or trace proteins to be accurately measured, ensuring highly reliable results.
2. Diverse Sample Compatibility
This service supports various types of protein samples, including but not limited to single proteins, complexes, cell extracts, and tissue samples. Whether your sample is a simple purified protein or a complex biological mixture, we provide the appropriate pretreatment and analysis solutions to ensure experimental success.
3. Automated Data Analysis and Report Generation
Our analytical platform, integrated with advanced software tools, automates the processing of mass spectrometry data and accurately identifies protein sequences and their modifications. The final report provides detailed protein identification information, including amino acid sequence, molecular weight, sequence coverage, and other parameters, making subsequent functional research more convenient.
4. Multiple Modification Analyses
In addition to conventional protein sequence analysis, MtoZ Biolabs’ Mass Spectrometry Protein Sequencing Service supports both qualitative and quantitative analyses of post-translational modifications (such as phosphorylation, glycosylation, and ubiquitination), helping customers gain deeper insights into the regulatory mechanisms of protein function.
How to order?







