Metabolomics Analysis
- Blood & Plasma & Serum Metabolomics Service
- Urine Metabolomics Service
- Feces Metabolomics Service
- Exosomes Metabolomics Service
- Plant Metabolomics Service
- Animal Metabolomics Service
- Microbial Metabolomics
- Advanced technical platform: Our LC-MS, GC-MS, and UPLC-MS platforms can perform high-sensitivity, high-resolution, and high-throughput metabolite analysis.
- Rich experience: Our team has rich experience in metabolomics analysis.
- Comprehensive solutions: We provide comprehensive metabolomics solutions from sample processing, metabolite analysis, to data processing and interpretation.
- One-time charge: Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
Metabolomics is the study of all metabolites in a biological organism, including small molecule metabolites and related metabolic pathways. With the continuous development of mass spectrometry technology, metabolomics has become an important tool for disease research, drug development and biomarker discovery. Our metabolomics analysis service uses a variety of chromatographic and mass spectrometric methods to identify and quantify metabolites in biological samples. By using our analytical platform, we can screen thousands of metabolites from a single biological sample, providing a comprehensive solution for disease mechanism research and biomarker discovery.
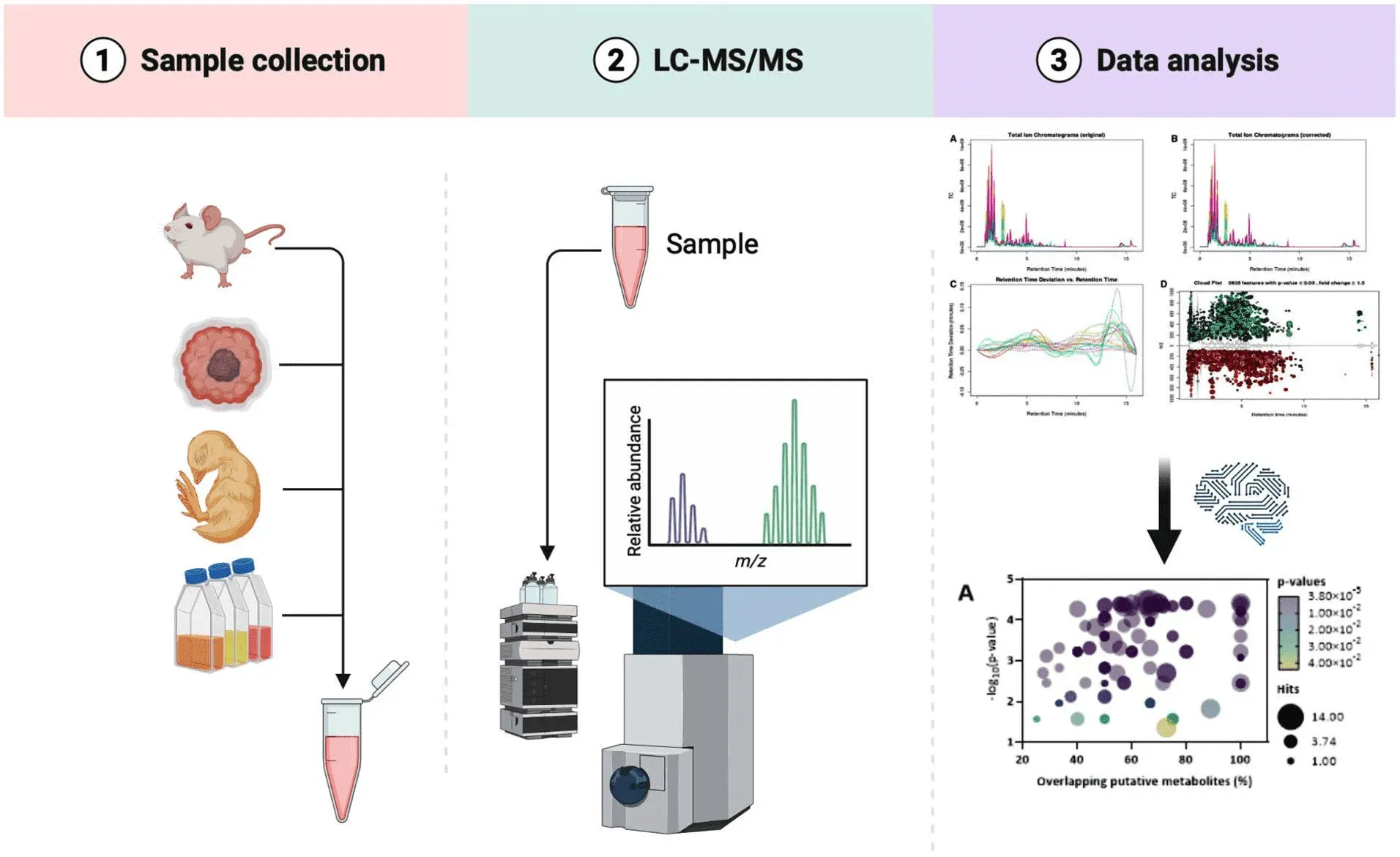
Marques, C.F. et al. Separations. 2023.
Figure 1. Metabolomics Solutions
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs's metabolomics analysis service provides comprehensive metabolomics solutions using technical platforms such as liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS). Our services include, but are not limited to:
1. Non-Targeted Metabolomics Service
Non-targeted metabolomics offers a panoramic metabolic profile by analyzing small molecule metabolites in biological samples comprehensively. This method focuses on exploring unknown metabolites, identifying metabolic pathways, and understanding metabolic changes under different conditions. It is a hypothesis-generating, exploratory technique. Utilizing advanced techniques such as LC-MS and GC-MS, we can simultaneously quantify hundreds to thousands of metabolites.
2. Targeted Metabolomics Analysis Service
Targeted metabolomics concentrates on the precise measurement of specific, key metabolites. Researchers select and analyze a set of compounds of biological significance. This method is hypothesis-driven, often used for validation studies or quantitative analyses of predefined metabolites, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data.
3. Metabolic Pathways Analysis
MtoZ Biolabs uses advanced bioinformatics tools and extensive database resources to map identified metabolites to corresponding biochemical pathways, creating intuitive visual representations to reveal key metabolic pathways and regulatory mechanisms.
4. Metabolomics Data Analysis
Bioinformaticians and statisticians at MtoZ Biolabs employ cutting-edge analytical algorithms and statistical techniques to process raw data, identify key metabolites, and perform multivariate statistical analysis. This comprehensive approach ensures precise interpretation of complex metabolomics datasets, aiding researchers in understanding the functions and changes within biological systems.
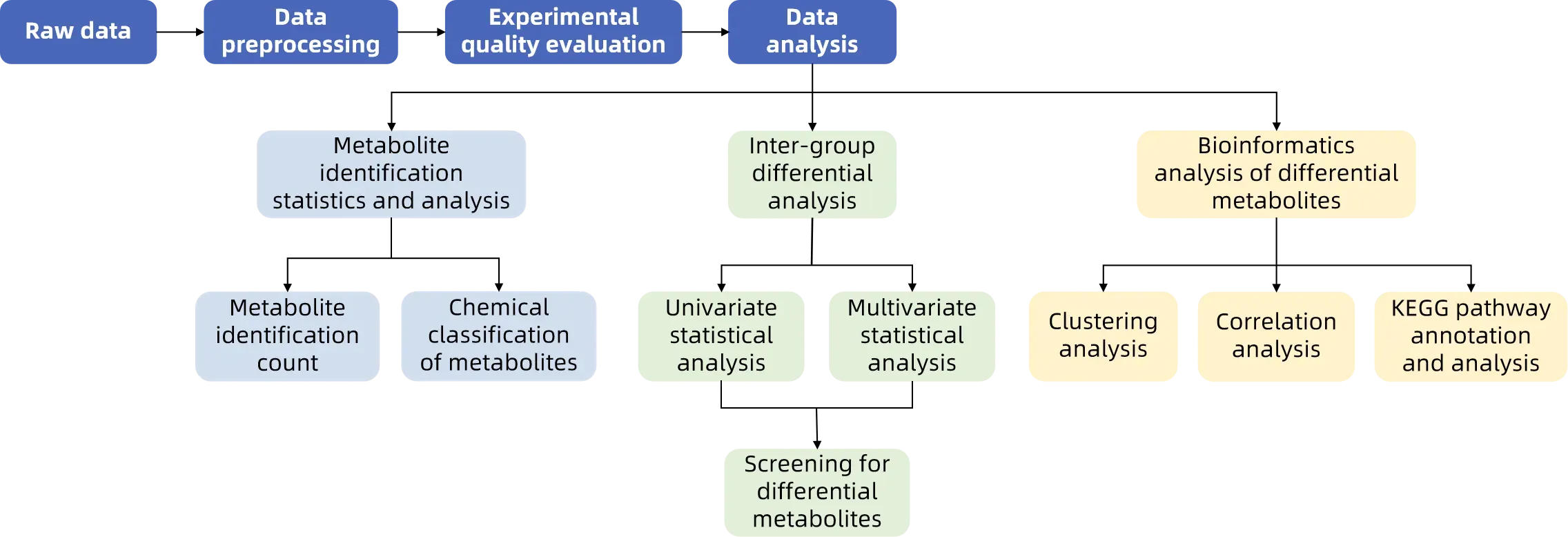
Figure 2. The Workflow of Metabolomics Data Analysis at MtoZ Biolabs
5. Spatial Metabolomics Service
At MtoZ Biolabs, we are dedicated to delivering high-quality spatial metabolomics analysis service to support comprehensive biological investigations. This service can be applied in both physiological and pathological contexts, particularly in cancer research, drug development, and environmental monitoring.
6. Sample Metabolomics Analysis
Metabolomics services at MtoZ Biolabs provide comprehensive analysis of metabolic profiles from various sample types, including but not limited to the following:
Service Advantages
MtoZ Biolabs's metabolomics services have the following advantages:
Sample Submission Suggestions
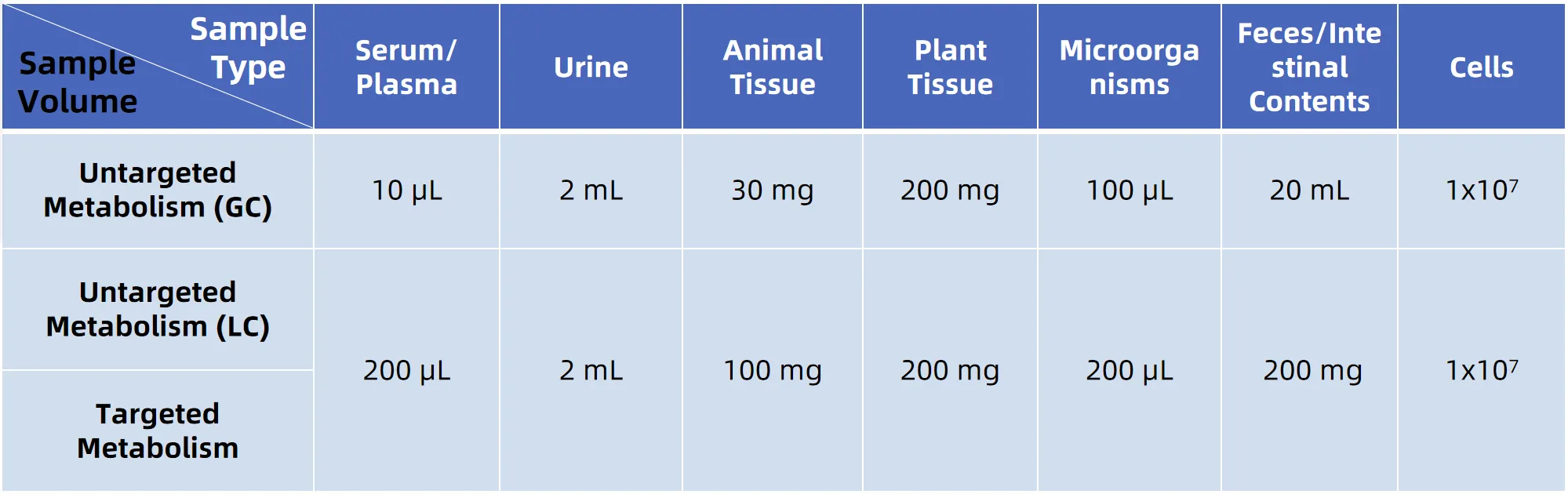
For more sample details, please consult our technical team.
MtoZ Biolabs is looking forward to cooperating with you. If you have any questions about our services, please feel free to contact us.
Related Services
Targeted Metabolomics Analysis Service
How to order?







