Multi-Omics Analysis Service
With the widespread application of high-throughput technologies, researchers can obtain omics data on a large scale from various molecular levels, including the genome, transcriptome, proteome, interactome, epigenome, metabolome, lipidome, and microbiome. Multi-omics integrated data analysis has revolutionized biology, enhancing our understanding of biological processes and molecular mechanisms. The use of high-throughput omics methods in biological sample analysis generates data files ranging from terabytes to gigabytes in size daily. Research at the molecular level is gradually improving, and a shift from partial to holistic approaches is an inevitable trend. Multi-omics integrated data analysis involves more than merely integrating data; it represents an in-depth investigation into biological interpretation, providing new insights for fundamental biology and disease research.
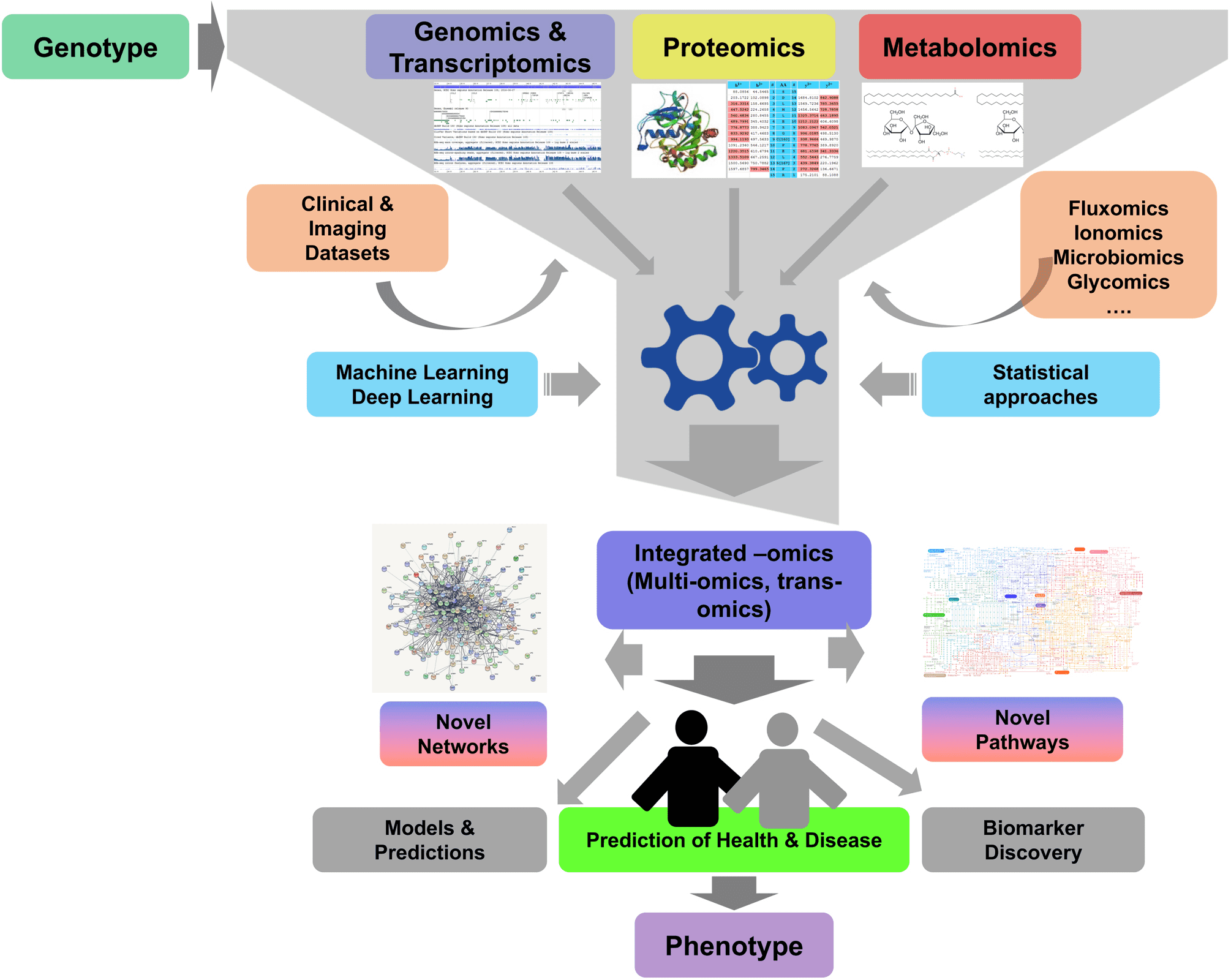
Misra, B. B. et. al. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018.
Diagram of Multi-Omics Integrated Analysis
Service Advantages
Single-omics analysis methods can provide information on biological processes that differ between various life processes or disease groups compared to normal groups. However, these analyses often have limitations. Multi-omics methods integrate information from several omics levels, offering more evidence for biological mechanisms and identifying candidate key factors more thoroughly. By integrating data from different levels, such as genes, mRNA, regulatory factors, proteins, and metabolites, a gene regulatory network can be constructed to understand the regulatory and causal relationships between various molecules more deeply. This leads to a more profound understanding of the molecular mechanisms and genetic bases of complex traits in biological processes and diseases.
Applications
1. Agriculture and Forestry
Research on growth and development, stress and non-stress mechanisms, crop breeding, conservation of rare species, medicinal plant research, etc.
2. Animal Husbandry
Research on growth and development, identification of functional genes for important economic traits of livestock and poultry, research on pathogenic mechanisms, discovery of biological stress and stress transcription factors in forage grass, etc.
3. Marine Fisheries
Research on growth and development, biological evolution studies, toxicology and seafood safety, etc.
4. Biomedicine
Biomarkers, disease mechanisms, drug targets, disease classification, personalized treatment, etc.
5. Microbiology
Research on pathogenic mechanisms, resistance mechanisms, pathogen-host interactions, etc.
6. Environmental Science
Optimization of fermentation processes, biofuel production, environmental hazard risk assessment, etc.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
1. Integrated Transcriptomics and Proteomics analysis
2. Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics analysis
3. Integrated Proteomics and Metabolomics Analysis
4. Integrated Metabonomics and Microbiomics Analysis
5. Integrated Transcriptomic and Lipidomics Analysis
6. Integrated Proteomics and Lipidomics Analysis
7. Integrated Transcriptomic, Proteomic, and Metabolomic Analysis
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Integrative Lipidomics-Proteomics Analysis Service
How to order?







