Peptide Biomarker Discovery & Validation Service
Biomarkers are measurable traits that serve as indicators of normal biological activities, disease processes, or pharmacological responses to therapeutic interventions. Peptides are particularly suitable as biomarkers due to their ability to circulate among various body compartments. Many disease processes can be inferred from the characteristic peptide profiles and pathological changes observed in different body fluids. Moreover, variations in peptide abundance associated with various diseases are detectable.
Two prevalent approaches to developing peptide biomarkers are pattern recognition and single/oligo biomarker assay. Pattern recognition does not require identifying the candidate biomarkers and relies solely on mass spectrometry's exceptional specificity and sensitivity to derive patient information. In contrast, the single/oligo biomarker assay is more effective as their expression levels can be verified across various biological samples. Mass spectrometry-based methods can accurately determine analyte concentrations and feature precise mass measurement and sequencing capabilities.
Lee, J. E. Genomics & Informatics. 2016.
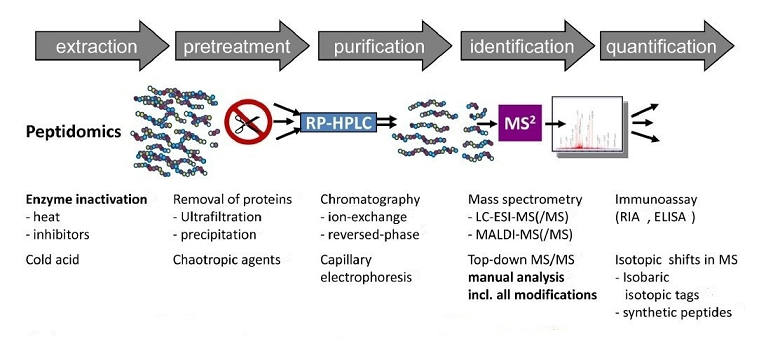
Figure 1. Peptide Biomarkers Analysis
To screen and validate peptide biomarkers, it is necessary to identify the peptides in a sample (qualitative analysis) and quantify their concentrations (quantitative analysis). Effective screening requires integrating both steps. Numerous analytical techniques are employed in biomarker detection, among which the combination of mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography (e.g., UPLC and nanoLC) stands out for its high resolution, sensitivity, throughput, and quantification capabilities.
MtoZ Biolabs employs the Thermo Fisher's Orbitrap Fusion Lumos mass spectrometry system along with nanoLC chromatography for advanced peptide biomarkers analysis services.
How to order?







