Peptide Purity Analysis Service
Peptide purity is defined as the ratio of the target peptide to all analytes, essentially reflecting the proportion of the target peptide to impurities. It is typically determined using HPLC analysis at 220nm, the peak absorption wavelength for peptide bonds. The purity of peptides critically influences research outcomes, with potential contaminants arising during chemical synthesis, culturing, or the extraction and purification phases. Impurities may include peptides with incomplete sequences, truncated sequences, incompletely deprotected peptides, and by-products from synthesis or final cleavage processes.
Figure 1. 3D Structure of Peptides
Applications
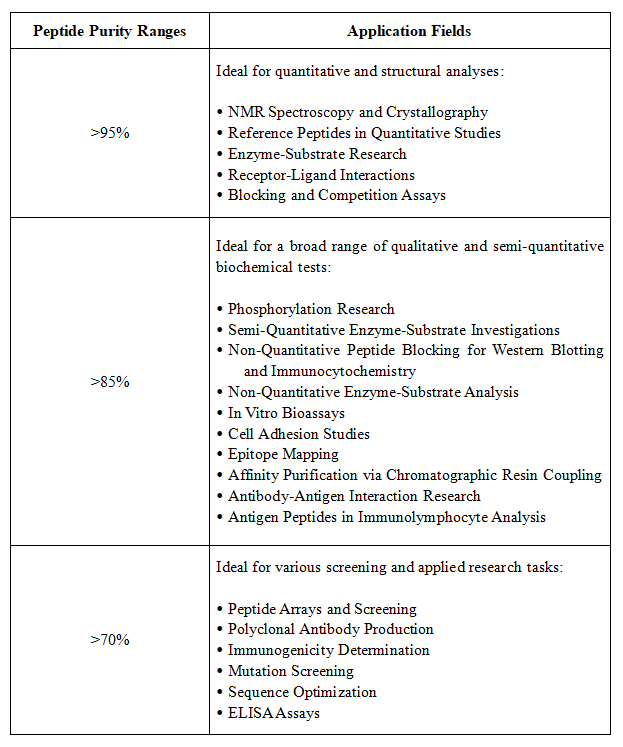
Figure 2. Application Areas for Peptides of Different Purities
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
1. RP-HPLC
Chromatograms from reverse phase HPLC are utilized to assess peptide purity by quantifying the peak area of the fully purified peptide relative to the total detected peak areas, facilitating the determination of by-product quantities and proportions.
2. Mass Spectrometry
Chromatograms from RP-HPLC are utilized to assess peptide purity by quantifying the peak area of the fully purified peptide relative to the total detected peak areas, facilitating the determination of by-product quantities and proportions.
3. Amino Acid Analysis (AAA)
Determines the amino acid composition in peptide or protein products, ensuring experimental accuracy and consistency.
MtoZ Biolabs delivers peptide purity analysis services leveraging RP-HPLC and mass spectrometry, dedicated to high-quality results. Each project requires a unique approach, so please engage our technical team to discuss specific needs.
How to order?







