Protein Amino Acid Sequence Analysis Service
The amino acid sequence of a protein determines its structure and function, serving as the foundation for studying biomolecular mechanisms and developing biotechnological applications. Proteins are macromolecules formed by amino acids linked through peptide bonds, with their sequence representing the specific order of amino acids. Even minor changes in the amino acid sequence can significantly impact a protein's molecular structure, stability, and functionality. The primary methods for analyzing protein amino acid sequences are Edman degradation and mass spectrometry (MS). Each method has unique strengths that complement the other. Mass spectrometry is ideal for full-length protein sequencing and the identification of modified amino acids, while Edman degradation excels in accurate and straightforward N-terminal sequence analysis. De novo sequencing, which does not rely on existing databases, enables direct derivation of amino acid sequences from experimental data, making it suitable for discovering new proteins and analyzing unknown ones.
Protein amino acid sequence analysis service has broad applications. For instance, in drug development, analyzing the amino acid sequence of target proteins can guide the design of specific drug molecules, improving efficacy and selectivity. In genetic engineering, synthesizing or modifying specific amino acid sequences allows for constructing proteins with tailored functions. Furthermore, protein sequence information provides foundational data for proteomics research, enhancing the understanding of intracellular protein interaction networks and regulatory dynamics.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs has established protein amino scid sequence analysis service platform that combines mass spectrometry and Edman degradation techniques. We offer comprehensive services, including amino acid composition analysis, N-terminal sequencing, C-terminal sequencing, full-sequence analysis, and Edman degradation-based N-terminal sequencing.
1. Mass Spectrometry-Based Protein Amino Acid Sequence Analysis Service
Using Thermo’s latest Orbitrap Fusion Lumos mass spectrometer, MtoZ Biolabs delivers unparalleled sequence analysis for protein samples. The Orbitrap Fusion Lumos, renowned for its high resolution and sensitivity, ensures precise identification of low-abundance peptide fragments. By integrating HCD and ETD fragmentation modes, the system maintains the integrity of peptide fragments during analysis. This advanced platform enables detailed sequence analysis of protein N-termini, C-termini, and full-length proteins.
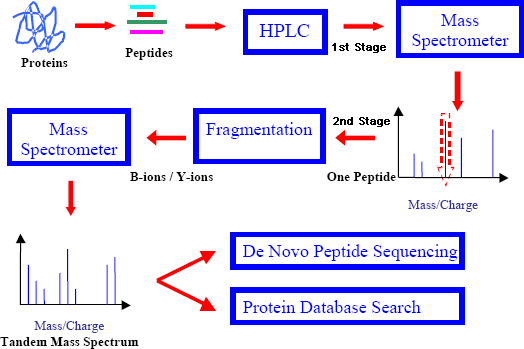
Chong, K. F. et al. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2012.
Figure 1. Pipeline involved in Peptide Sequencing using Tandem Mass Spectrometry
2. Edman Degradation-Based N-Terminal Sequencing Service
MtoZ Biolabs utilizes Shimadzu's Edman sequencing system to provide a state-of-the-art Edman sequencing service platform, ensuring reliable, rapid, and highly accurate analysis.
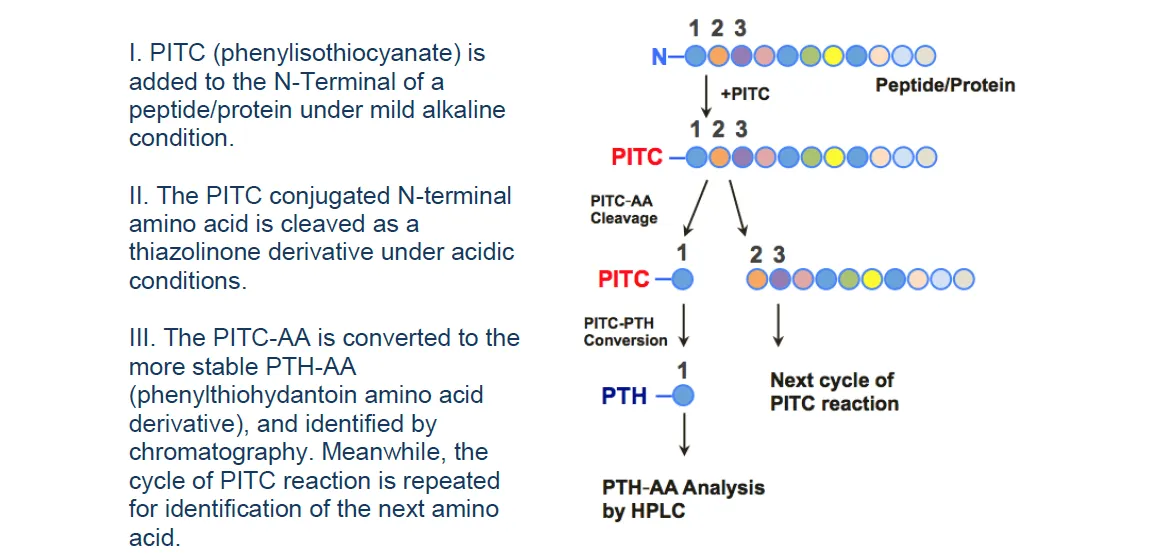
Figure 2. N-Terminal Sequencing Analysis Based on Edman Degradation.
Service Advantages
1. Advanced Analytical Platform
MtoZ Biolabs has established a cutting-edge protein amino acid sequence analysis service platform, ensuring reliable, fast, and high-precision analytical services.
2. Transparent Pricing
Our pricing is transparent, with no hidden or additional fees.
3. High-Quality Data
With comprehensive data coverage and strict quality control, our AI-driven bioinformatics platform integrates all spatial proteomics data to deliver complete data reports to clients.
4. Customized Research Solutions
MtoZ Biolabs provides tailored services to address your unique research questions and experimental needs.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types
Capable of analyzing a wide range of samples, including peptides, proteins, antibodies, and more.
2. Salt Concentration
Please avoid excessive salt concentrations in samples.
Note: If you have any specific requirements or need assistance with sample preparation, please contact us.
Applications
1. Protein Function Research
By understanding the amino acid sequence of proteins, researchers can infer tertiary structures and potential functions, which are crucial for drug development and molecular biology studies.
2. Disease Mechanism Studies
Alterations such as mutations, insertions, or deletions in amino acid sequences can be linked to various diseases.Understanding these changes through protein amino acid sequence analysis service can help reveal the molecular basis of disease.
3. Biomarker Identification and Drug Development
Protein amino acid sequence analysis can identify proteins specifically expressed in certain disease states, serving as biomarkers or drug targets.
4. Quality Control and Drug Development
Peptide mapping and mass spectrometry techniques are employed to confirm protein amino acid sequences, identify modifications, and perform quantitative analysis, ensuring the quality and consistency of drugs.
Additionally, applications extend to evolutionary biology, protein structure prediction, and novel protein discovery.
Case Study
1. Determining Protein Amino Acid Sequence to Uncover a Novel Immune Response Mechanism Against Group A Streptococcus (GAS)
Group A Streptococcus (GAS), a common pathogen, induces various acute inflammatory diseases. Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin B (SpeB), a critical virulence factor of GAS, aids in its colonization of the epidermis and systemic dissemination, though the mechanism of SpeB action remains unclear. Researchers aimed to elucidate the mechanism through which SpeB induces pyroptosis in cells. Using a CRISPR/Cas9 genome-wide knockout screening platform, the research team identified GSDMA—a key executor of pyroptosis in the Gasdermin family—as the critical protein mediating SpeB-induced keratinocyte pyroptosis.
The research team further detailed the molecular mechanism of SpeB activation of GSDMA: (1) SpeB specifically cleaves GSDMA (but not other Gasdermin family members), generating an ~27 kDa N-terminal fragment that induces pyroptosis. (2) Edman sequencing and mass spectrometry identified the cleavage site of GSDMA at amino acid 246. Intracellular introduction of purified GSDMA 1-246aa fragments directly induced pyroptosis. (3) Lipid membrane strip and liposome binding assays revealed that GSDMA 1-246aa could bind to cell membrane phospholipids as well as liposomes containing the corresponding phospholipids. Liposome leakage assays demonstrated that GSDMA 1-246aa could form pores on specific liposomes. (4) Sequence alignment results showed that the cleavage site is conserved in mouse Gsdma1; SpeB-induced Gsdma1 cleavage could trigger pyroptosis in mouse epithelial cells. (5) Gsdma1 cleavage was detected at GAS infection sites in mice; compared to wild-type mice, Gsdma1 knockout mice were more susceptible to GAS infection. This case illustrates how Edman sequencing facilitated researchers in uncovering a novel immune response mechanism against GAS, clarifying disease pathways, and guiding therapeutic development.
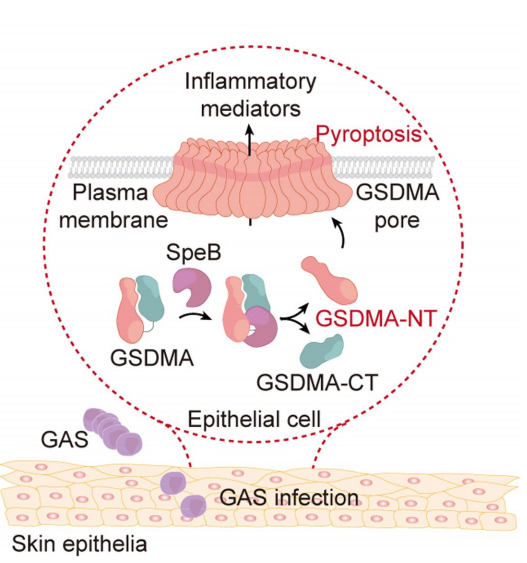
Deng, W. et al. Nature, 2022.
Figure 3. Model of Streptococcus Pyogenes (GAS) Virulence Factor SpeB Triggering Pyroptosis in Skin Epithelial Cells through GSDMA Cleavage and Activation.
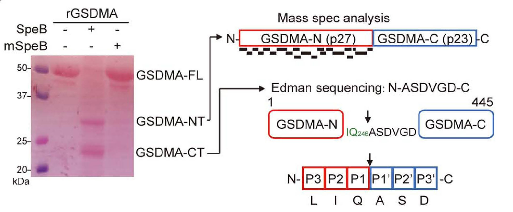
Deng, W. et al. Nature, 2022.
Figure 4. Mass Spectrometry (MS) and Edman Sequencing Analysis of GSDMA N-Terminal and C-Terminal Cleavage Products.
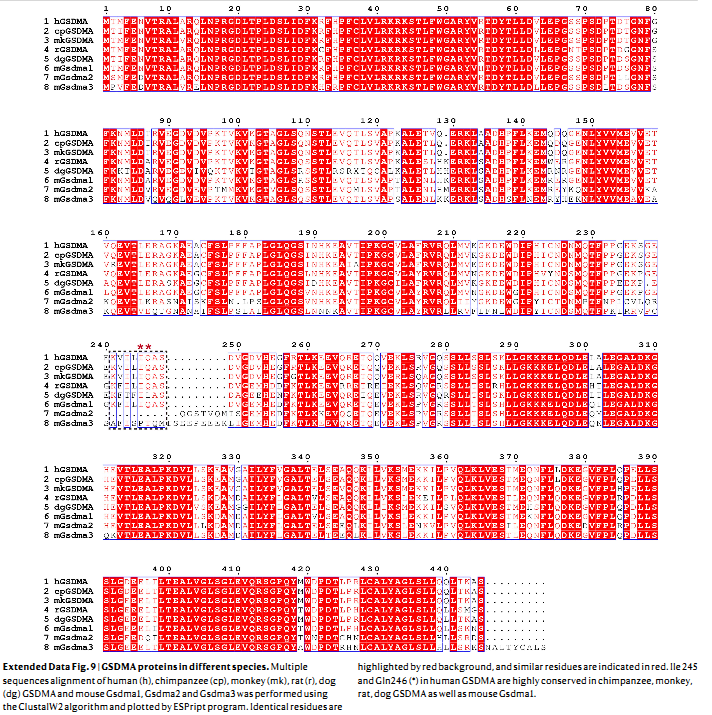
Deng, W. et al. Nature, 2022.
Figure 5. GSDMA Protein Amino Acid Sequences Across Different Species.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Total Ion Chromatogram & Quality Control Assessment
4. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation
5. Raw Data Files
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (MS) Services Provider, provides advanced proteomics, metabolomics, and biopharmaceutical analysis services to researchers in biochemistry, biotechnology, and biopharmaceutical fields. Our ultimate aim is to provide more rapid, high-throughput, and cost-effective analysis, with exceptional data quality and minimal sample consumption. Free project evaluation, welcome to learn more details!
How to order?







