Ubiquitination Proteomics Service
Ubiquitination proteomics is a specialized field of proteomics dedicated to studying ubiquitination, a crucial post-translational modification (PTM) that involves the covalent attachment of ubiquitin, a 76-amino-acid regulatory protein, to target proteins. This modification occurs through a cascade of enzymatic reactions involving E1 activating enzymes, E2 conjugating enzymes, and E3 ligases. Depending on the type of ubiquitin chain formed (monoubiquitination or polyubiquitination), ubiquitination can influence various cellular processes, such as protein degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome system, DNA repair, cell cycle progression, and immune responses. Ubiquitination proteomics leverages cutting-edge mass spectrometry (MS) and enrichment techniques to identify ubiquitination sites, quantify modified proteins, and uncover complex ubiquitin-mediated signaling pathways.
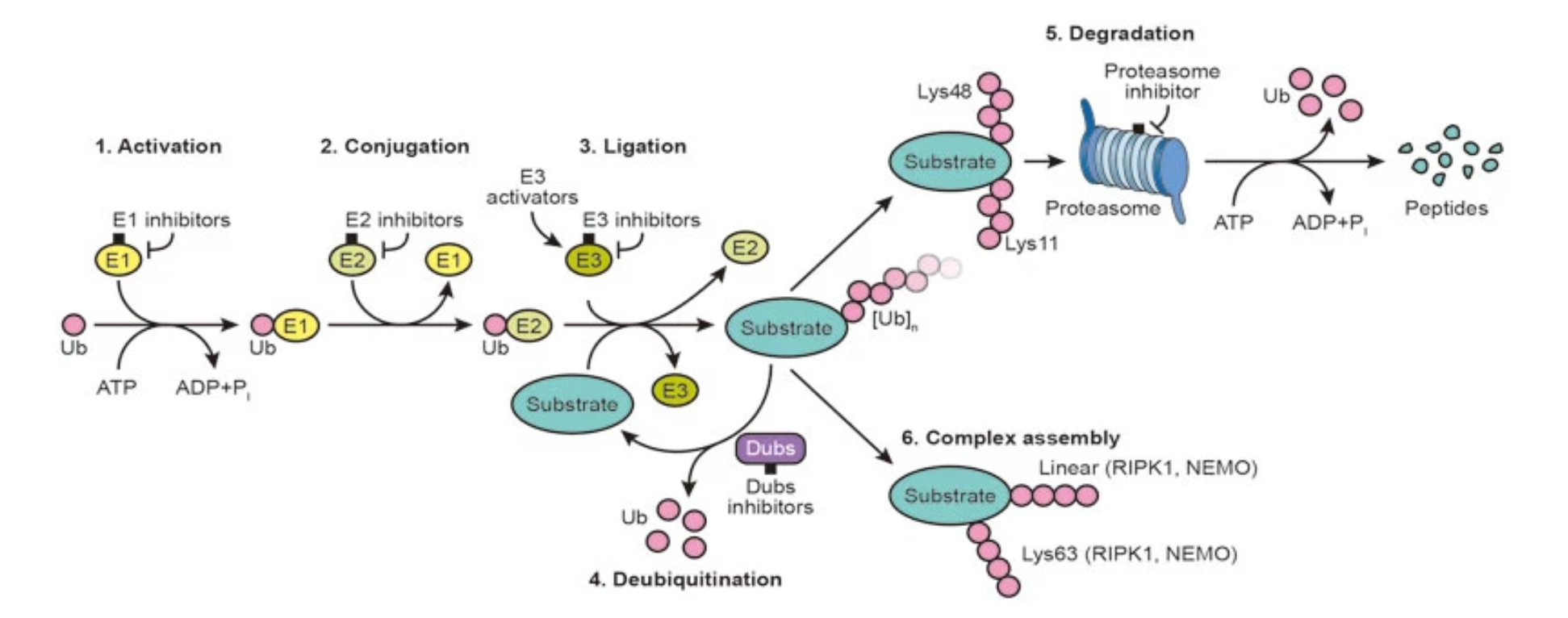
Figure 1. Summary of the Ubiquitin System and Possible Intervention Nodes
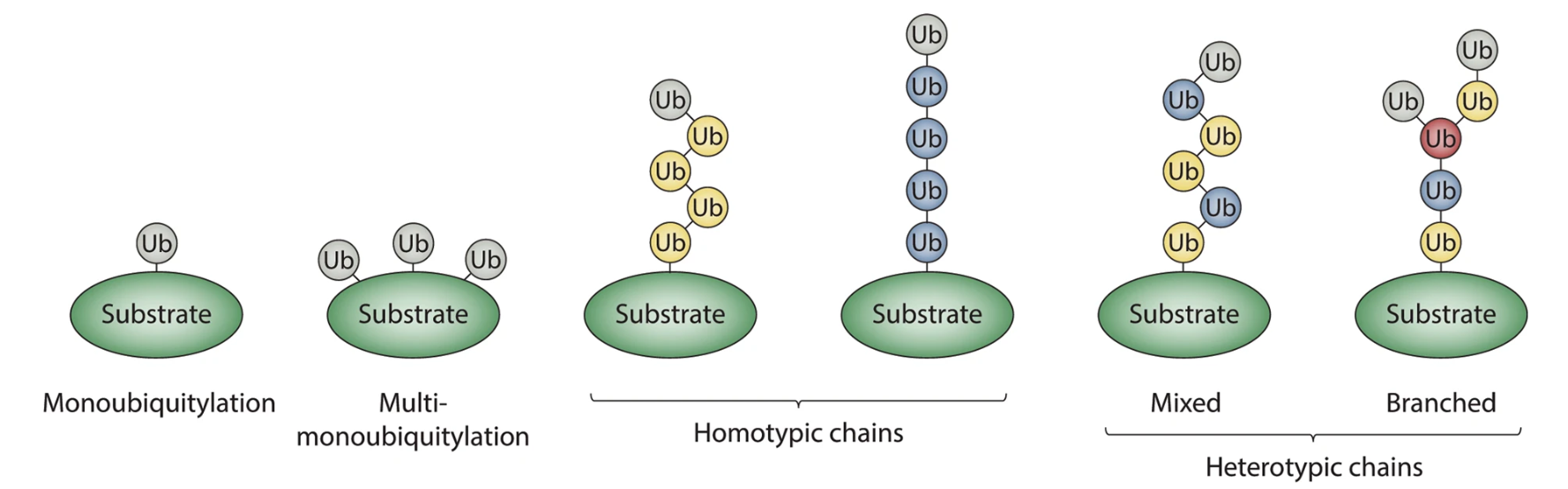
Figure 2. Classification of Ubiquitin Modifications
Ubiquitination proteomics plays a pivotal role in understanding cellular homeostasis and disease mechanisms. By analyzing ubiquitin-modified proteomes, researchers can gain insights into the dynamic regulation of protein stability, interaction networks, and intracellular trafficking. Ubiquitination proteomics has become indispensable in identifying dysregulated ubiquitination pathways associated with cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and immune diseases. Furthermore, ubiquitination proteomics is instrumental in drug discovery, enabling the identification of therapeutic targets and biomarkers. Advanced mass spectrometry-based workflows have significantly improved the sensitivity and specificity of ubiquitination detection, making it a transformative tool for both basic and applied research.
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
To meet the growing demand for precise and comprehensive ubiquitination analysis, MtoZ Biolabs offers a state-of-the-art Ubiquitination Proteomics Service. With our cutting-edge mass spectrometry platforms, including the Thermo Orbitrap Fusion Lumos, and expertise in protein post-translational modification analysis, we provide unparalleled Ubiquitination Proteomics Services for identifying ubiquitination sites, profiling ubiquitin linkages, and quantifying ubiquitinated proteins. Our service is tailored to support diverse research needs, from elucidating signaling pathways to uncovering disease biomarkers.
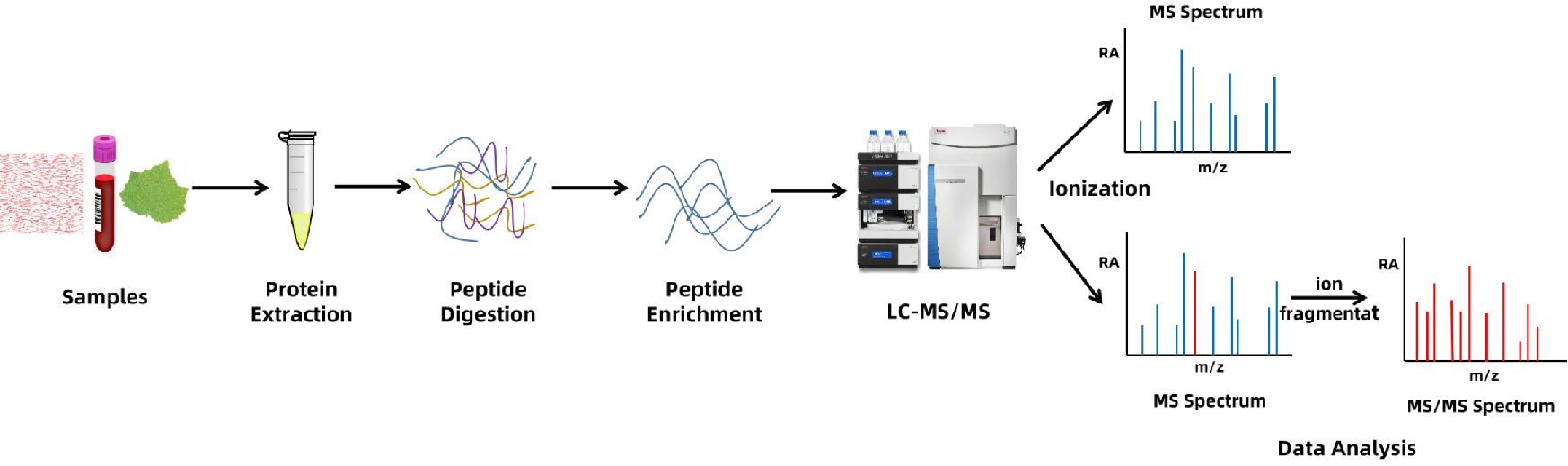
Figure 3. Workflow for Ubiquitination Proteomics Service
Service Advantages
1. Advanced Analysis Platform: MtoZ Biolabs established an advanced Ubiquitination Proteomics Service platform, guaranteeing reliable, fast, and highly accurate analysis service.
2. High Coverage: To ensure comprehensive identification of ubiquitinated proteins and their modification sites, we employ multi-enzyme digestion strategies that enhance peptide coverage and improve the detection of low-abundance and challenging ubiquitination sites.
3. One-Time-Charge: Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
4. High-Data-Quality: Deep data coverage with strict data quality control. AI-powered bioinformatics platform integrates all ubiquitination proteomics data, providing clients with a comprehensive data report.
Applications
1. Disease Research: Use Ubiquitination Proteomics to uncover dysregulated ubiquitination pathways in tumors, neurodegenerative and other disorders, providing insights into therapy development and understanding protein aggregation mechanisms.
2. Immune Regulation: Explore ubiquitination in immune signaling pathways to understand autoimmune diseases and develop immunotherapies.
3. Drug Discovery: Discover ubiquitination-related drug targets and validate therapeutic candidates in preclinical studies.
4. Signal Transduction: Investigate ubiquitination’s role in regulating pathways for insights into cellular communication and disease progression.
Case Study
Uncovering the Role of USP11 in Tauopathy Using Ubiquitination Proteomics
A recent study investigated the role of USP11, an X-linked deubiquitinating enzyme, in tauopathy vulnerability. By reducing tau ubiquitination, USP11 inhibits proteasomal and autophagy-mediated tau degradation, leading to tau accumulation and promoting neurotoxic tau tangles. Using ubiquitination proteomics, researchers employed tryptic digestion to generate diGly-modified tau peptides, which were analyzed through LC-MS/MS. This approach identified specific tau ubiquitination sites and confirmed USP11's regulatory effect on tau clearance via Western blotting. The findings revealed sex-specific vulnerability, with higher USP11 expression in females, advancing understanding of tauopathy mechanisms and highlighting the utility of ubiquitination proteomics in uncovering therapeutic targets.
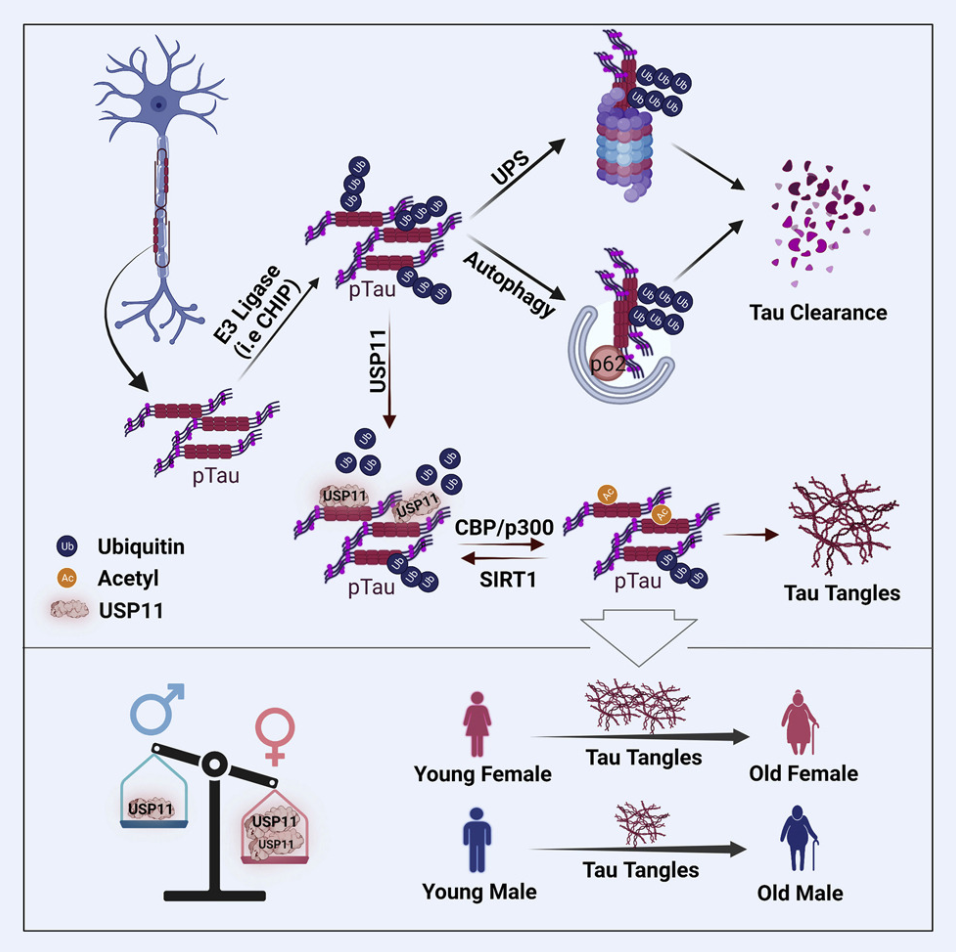
Figure 4. Mechanism of X-Linked Ubiquitin-Specific Peptidase 11 Increases Tauopathy Vulnerability in Women
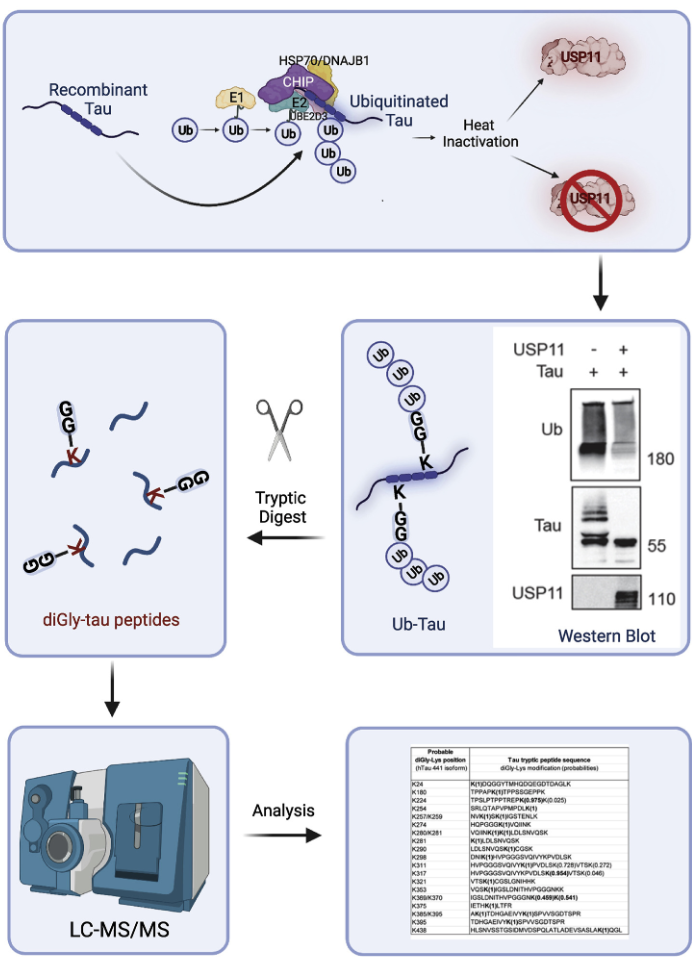
Figure 5. Schematic of Recombinant Tau Ubiquitination by CHIP, Deubiquitination by USP11, and Detection of diGly-ub Peptide Signatures by LC-MS/MS
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Total Ion Chromatogram & Quality Control Assessment
4. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation
5. Bioinformatics Analysis
6. Raw Data Files
How to order?







