2D-DIGE Based Protein Quantitative Service
Two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis (2D-DIGE) is a novel quantitative proteomics technique that evolved from traditional two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE). The principle of 2D-DIGE for separating mixed proteins is the same as traditional 2-DE. It uses differences in protein isoelectric points and molecular weights to separate protein mixtures. At the same time, the sensitive fluorescent dyes and the internal standard make it significantly better than traditional 2-DE in quantitative proteomics. The fluorescent dyes used in DIGE are Cy2, Cy3, and Cy5, which react with the lysine side chain amino groups of proteins to label the proteins without affecting their isoelectric points and molecular weights. After mixing equal amounts of the labeled proteins, two-dimensional electrophoresis is conducted. The internal standard Cy2 is used to match different gels and eliminate gel viriation, while changes in protein expression levels are reflected by fluorescence intensity of Cy3 and Cy5. As a classic method of quantitative proteomics, 2D-DIGE is widely applied and suitable for various samples.
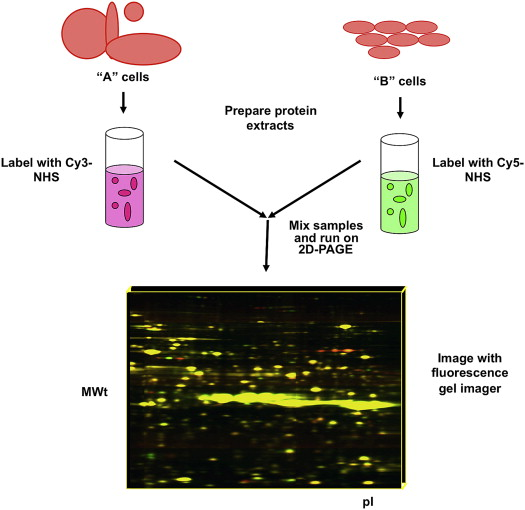
Blundon, M. Methods Mol Biol. 2019.
Figure 1. 2D-DIGE Quantitative Proteomics
MtoZ Biolabs provides SDS-PAGE and 2D-DIGE services. Combining Thermo Fisher's Orbitrap Fusion Lumos mass spectrometer platform and nanoLC-MS/MS nano-liquid chromatography, We provide comprehensive proteomics identification and quantification services for researchers.
Sample Submission Requirements
Both Liquid and Solid Samples are Acceptable
Applications
Suitable for Various Samples
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
1. Experimental Procedures
2. Relevant Experimental Parameters
3. Gel and Mass Spectrometry Images
4. Raw Data
5. Results of the 2D-DIGE Quantitative Proteomics Analysis
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Label-Free Quantitative Proteomics Service, MS Based
How to order?







