Cellular Proteomics Service
Cellular proteomics is a scientific discipline that explores the expression, modification, interaction, and function of all proteins within cells. As a significant branch of proteomics, the development of cellular proteomics is closely linked to the progress of proteomics itself. In 1995, the term "proteomics" was introduced, marking the official start of proteomics research. With advancements in mass spectrometry technology, studies on intracellular proteins became increasingly sophisticated. In the early 21st century, cellular proteomics emerged as a subfield of proteomics, gaining widespread attention. Since then, new technologies and methods have continuously driven progress in this field, providing critical insights into cell biology, disease mechanisms, and drug development.
Currently, the primary technical methods in cellular proteomics include: 2D gel electrophoresis and liquid chromatography to separate proteomes into different subgroups for easy identification and quantification; mass spectrometry analysis to identifies protein sequences and modification states using high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry; immunoprecipitation and affinity purification to capture the target proteins and highly purify the proteins using specific antibodies or ligands; and bioinformatics analysis to reveal the biological significance of the proteins by integrating, mining, and visualizing the histological data.
Analysis Workflow
1. Protein Extraction
Disrupt cells and remove non-protein components such as lipids, nucleic acids, and small metabolites.
2. Protein Separation and Purification
Use 2D gel electrophoresis and liquid chromatography to separate and purify protein samples
3. Protein Identification
Apply high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS, ESI-MS/MS, etc.) to analyze the purified proteins, identifying their sequence and structural information.
4. Protein Quantification
Conduct quantitative analysis using isotope labeling methods (e.g., iTRAQ, TMT, SILAC) and label-free methods (e.g., Label Free, SWATH-MS) to compare protein expression differences under different conditions.
5. Data Processing and Analysis
Process, analyze, and interpret mass spectrometry data using bioinformatics methods, including protein identification, quantitative analysis, protein function annotation, interaction network analysis, and pathway analysis.
Service Advantages
1. High Throughput
Leveraging HPLC and mass spectrometry, a large number of proteins can be identified and quantified in a short period of time.
2. High Efficiency
Bioinformatics tools can mine, integrate, and visualize large datasets.
3. Diversity
Suitable for various organisms and cell types, cellular proteomics analysis can be used to study protein changes under different environments, disease states, or genetic mutations.
4. Systematic
By comprehensively revealing the expression, modification, and interaction of all proteins within cells, it provides systematic and holistic information for biological research.
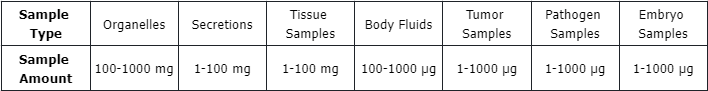
Sample Submission Requirements
Deliverables
In the technical report, MtoZ Biolabs will provide you a detailed technical information, including:
1. Experimental Procedures
2. Relevant Mass Spectrometry Parameters
3. Cellular Proteomics Analysis Details
4. Mass Spectrometry Images
5. Raw Data
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Subcellular Proteomics Service
How to order?







