Protein Circular Dichroism Analysis Service
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Protein Secondary Structure Analysis Service
Submit Inquiry
How to order?


Email:
info@MtoZ-Biolabs.comEmail:
info@MtoZ-Biolabs.comProteins exhibit asymmetric secondary structures such as α-helices, β-sheets, β-turns, and others, leading to differential absorption of left and right circularly polarized light. Upon transmission through these proteins, the circularly polarized light becomes elliptically polarized, a phenomenon known as protein circular dichroism (CD). CD Spectroscopy is an essential technique for analyzing the secondary and tertiary structures of optically active molecules (e.g., proteins, DNA) in solution. It is widely utilized in studying the structure-function relationship and interactions of macromolecules.
MtoZ Biolabs offers professional CD services for analyzing and determining the spatial configurations of proteins.
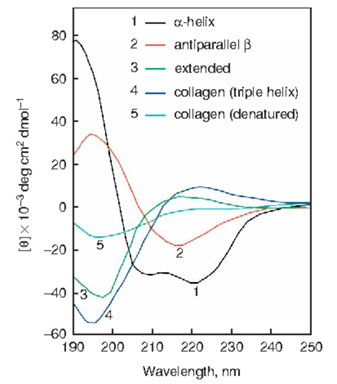
Norma, J. G. et al. Nat. Protoc. 2006.
Figure 1. CD Spectroscopy Illustrates the Representative Secondary Structures of Peptides and Proteins
Protein sample concentration should exceed 0.5 mg/mL, with purity exceeding 90%. The minimum quantity of solid protein should not be less than 200 μg.
In the technical report, MtoZ Biolabs will provide you with a detailed technical information, including:
Protein Secondary Structure Analysis Service
How to order?


Submit Inquiry
