Edman Degradation Service
Edman Degradation Service utilizes Edman degradation to determine the N-terminal amino acid sequence of peptides and proteins. By using phenyl isothiocyanate (PITC) under mild acidic conditions, N-terminal residues are sequentially removed while preserving the integrity of the protein or peptide. Edman degradation is highly precise and reliable, making it suitable for sequencing short peptides, analyzing protein modifications, and verifying the N-terminal sequences of purified proteins. The Edman degradation service is particularly ideal for researchers who need precise identification of N-terminal residues in their samples, especially in cases where mass spectrometry methods may not be applicable or sufficient. It addresses challenges such as determining the exact sequence of short peptides, verifying the structure of recombinant proteins, and analyzing N-terminal modifications (e.g., acetylation). This service provides highly accurate solutions for fields such as structural biology, biopharmaceuticals, and protein engineering.
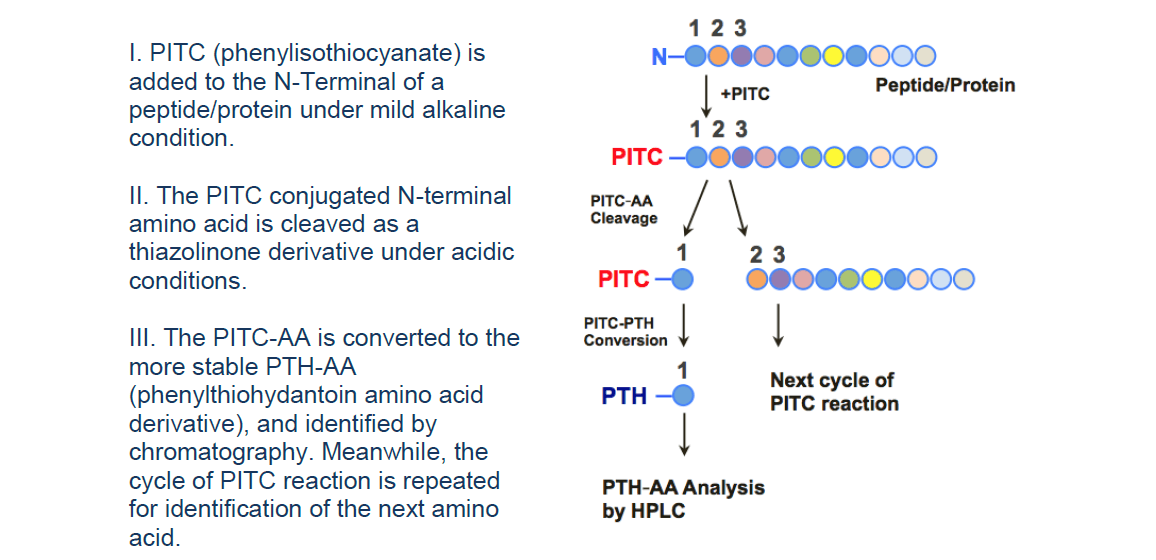
Figure 1. The Workflow of Edman Degradation Sequencing
MtoZ Biolabs offers Edman degradation service using advanced high-sensitivity amino acid analyzers and precision chromatography equipment, ensuring high accuracy and reliability in N-terminal amino acid sequencing. Our team, composed of experienced proteomics experts, is skilled in Edman degradation techniques and employs optimized sample processing workflows to provide customized solutions for our clients. We stay at the forefront of the field by improving Edman degradation methods to meet diverse research needs, such as optimizing reaction conditions for low-abundance samples or complex peptides. Additionally, we integrate Edman degradation with other technologies, such as mass spectrometry, to enhance the analysis of protein modifications and complex sequences, offering comprehensive support for both fundamental research and applied development.
Service Advantages
1. Efficient N-terminal Amino Acid Sequencing
MtoZ Biolabs' Edman degradation service utilizes mild acidic conditions combined with phenyl isothiocyanate (PITC) labeling to precisely cleave and identify N-terminal amino acid residues. This approach ensures the integrity of peptides or proteins while providing high-resolution sequence analysis, making it ideal for sequencing peptides and short-chain proteins.
2. Segmented Strategy for Improved Large Protein Sequencing Efficiency
MtoZ Biolabs' Edman degradation service employs enzymatic or chemical reagents to cleave large proteins into smaller peptide fragments. Coupled with efficient chromatographic separation techniques, this segmented strategy enables precise sequencing of complex protein samples, improving accuracy and streamlining the analysis of large proteins.
3. One-Time-Charge
Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
Case Study
1. Edman Degradation Reveals Unequivocal Analysis of the Disulfide Connectivity in Peptides and Proteins
This study explores the use of Edman degradation (ED) for analyzing disulfide connectivity in peptides and proteins, focusing on phenyl thiohydantoin (PTH) derivatives of cysteine, such as PTH-S-methyl cysteine and PTH-S-carbamidomethyl cysteine. These derivatives were validated as bioanalytical standards for cysteine detection and quantification. The method was tested using model peptides and applied to native disulfide-bonded peptides, including human insulin, to determine disulfide bond connectivity without relying on mass spectrometry. Edman degradation service can provide precise analysis of N-terminal sequences and disulfide connectivity in peptides, offering reliable solutions for studying peptide structures.
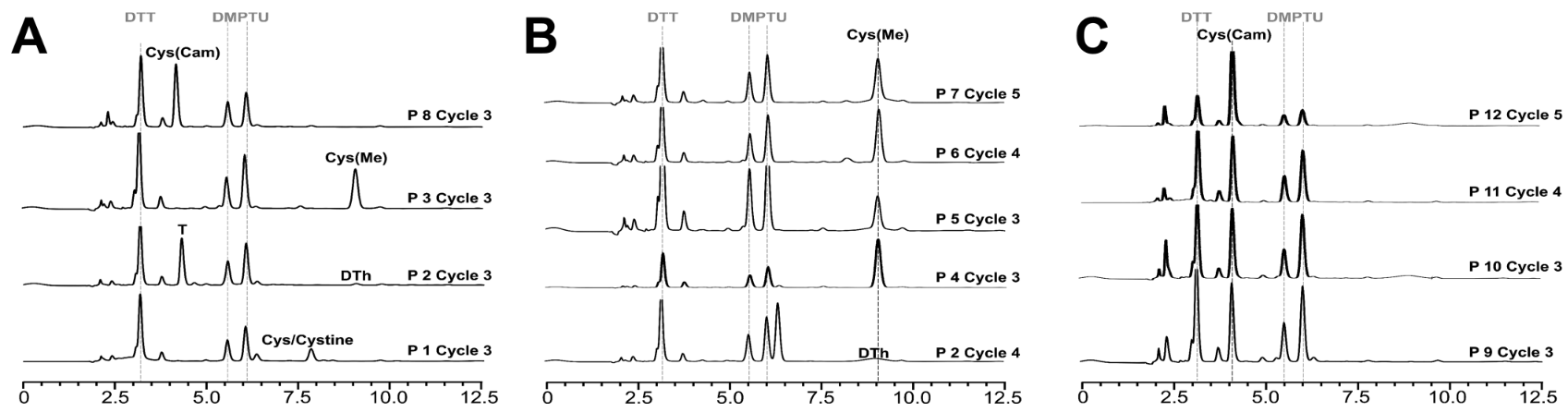
Elsayed, YY. et al. Anal Chem. 2024.
Figure 2. N-Terminal Sequencing Based on Edman Degradation
2. Edman Degradation Combined with LC-MS/MS Offers a Reliable Approach for Protein Analysis and Quantification
This study investigates the use of Edman degradation for amino acid quantification by developing an isotope-dilution liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS/MS) method for phenylthiohydantoin (PTH)-amino acid derivatives. The method utilizes stable isotope-labeled internal standards and demonstrated high accuracy and reproducibility. Various model proteins, including human serum albumin, pepsin, and insulin, were tested for N-terminal amino acid analysis, showing high yield and reliability. This approach highlights the potential of Edman degradation for absolute protein quantification without requiring external protein standards. Edman degradation service integrates advanced techniques for N-terminal analysis and amino acid quantification to support complex protein studies.
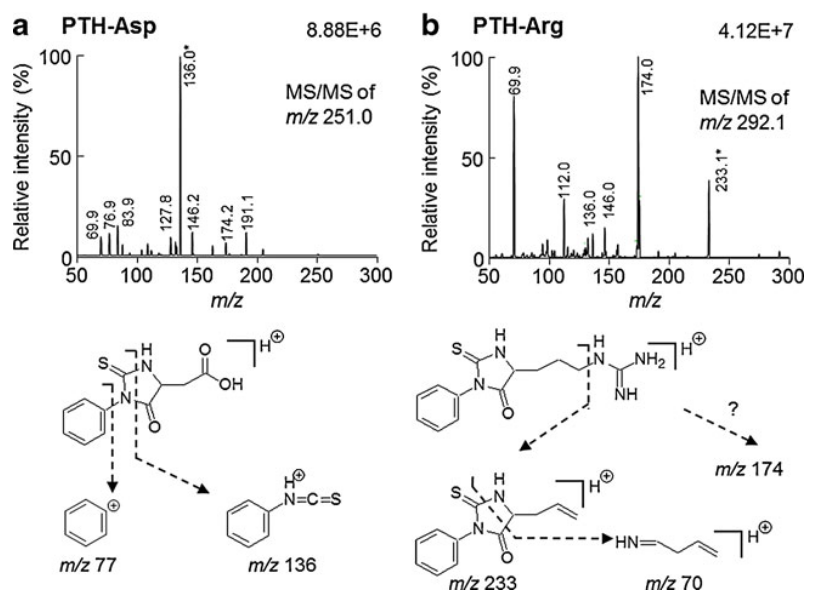
Satoh, R. et al. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013.
Figure 3. Typical MS–MS Spectra Obtained from PTH-AAs
3. Single-Molecule Fluorosequencing Based on Edman Degradation
This study presents a method for highly parallel single-molecule identification of proteins in zeptomole-scale mixtures. By selectively fluorescently labeling cysteine, lysine, and phosphoserine residues, peptides are immobilized on a glass surface and analyzed using total internal reflection microscopy to monitor fluorescence reductions during consecutive rounds of Edman degradation. Sparse fluorescent sequence information obtained for each molecule is matched to its parent protein in a reference database. The approach was successfully demonstrated on synthetic and naturally-derived peptides, achieving high efficiency in dye labeling, survival, and cleavage, paving the way for sensitive, high-throughput proteomic studies. Edman degradation service enables the analysis of small-scale or complex peptide samples.
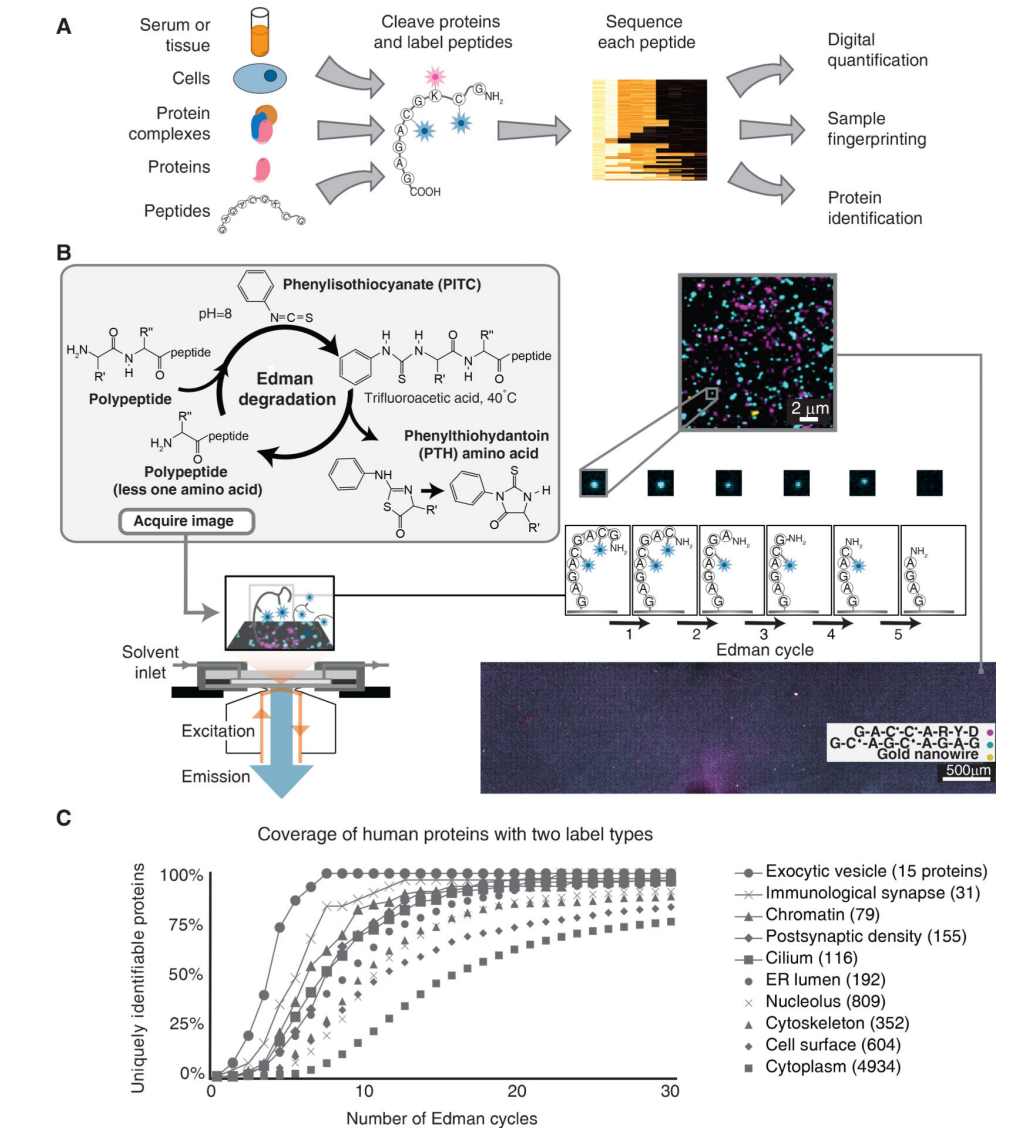
Swaminathan, J. et al. Nat Biotechnol. 2018.
Figure 4. Single-Molecule Fluorosequencing Based on Edman Degradation
FAQ
Q1: What types of proteins are not suitable for Edman degradation sequencing?
Answer: Proteins that are not suitable for Edman degradation sequencing include those with N-terminal modifications (such as acetylation or formylation), missing N-terminals, or cyclic structures, as these characteristics interfere with PITC labeling of the N-terminal amino acid. Additionally, long-chain proteins or those with complex disulfide bond structures may also reduce degradation efficiency. Edman degradation service can provide optimized sequencing strategies tailored to sample characteristics, making them ideal for high-precision N-terminal sequence analysis of unmodified or short-chain peptides.
Q2: What is the terminator for the Edman degradation?
Answer: Edman degradation is an automated, continuous reaction process and does not have a specific "terminator." The process is concluded by controlling reaction conditions rather than using a chemical terminator. If the Edman degradation process needs to be stopped, the following methods can be employed:
Stoping reagents addition: Cease the addition of phenyl isothiocyanate (PITC) to the reaction system to prevent the initiation of new cycles.
Sample washing: Repeated washing can remove residual reagents and partially eliminate reaction by-products.
Changing the reaction environment: Altering the solution's pH or introducing unfavorable conditions (e.g., significant temperature changes) can stabilize the formed thiourea derivative, preventing it from further reacting into PTH-amino acid.
Using blocking agents: Although Edman degradation typically does not utilize "terminators," certain chemical agents, such as excess water or specific chemical inhibitors, can be introduced to competitively suppress or interfere with the reaction between PITC and amino acids.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Relevant Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Parameters
4. The Detailed Information of Results
5. Mass Spectrometry Image
6. Raw Data
How to order?







