Free Sulfhydryl Quantification Service
Sulfhydryl and disulfide bonds often participate in enzymatic catalysis, cofactor binding, and maintenance of protein active conformations in the form of active functional groups. Analyzing the quantity and characteristics of sulfhydryl groups constitutes a critical method for acquiring specific structural insights in contemporary biochemistry and molecular biology.
Currently, the Ellman method is widely utilized for the detection of the concentration levels of free sulfhydryl groups, based on the principle that DTNB reagent undergoes a reaction with free sulfhydryl groups to produce 2-nitro-5-thiobenzoic acid (TNB-), which ionizes in water under neutral or alkaline pH conditions, producing TNB2- divalent anions. The resulting TNB2- ion, being yellow in color, is quantifiable through measurement of its visible absorbance at 412 nm, allowing for free sulfhydryl quantification using a cysteine standard or through molarity-based sulfhydryl quantification methods.
MtoZ Biolabs offers free sulfhydryl quantitation services to quantify free cysteine in a sample.
Sulfhydryl-containing compounds are capable of reacting with DTNB, cleaving DTNB's disulfide bonds to yield 2-nitro-5-thiobenzoic acid (NTB-), which, at neutral or alkaline pH, ionizes in water to form NTB2- divalent anions. The NTB2- ion is characterized by its distinctive yellow hue. Cysteine standards at varying concentrations, along with the test samples, were subjected to reaction with the DTNB reagent. Subsequently, the absorbance at 412 nm was measured. A standard curve was then constructed based on the absorbance values of the standards. By interpolating the sample's absorbance value onto this standard curve, the concentration of free sulfhydryl groups was deduced.
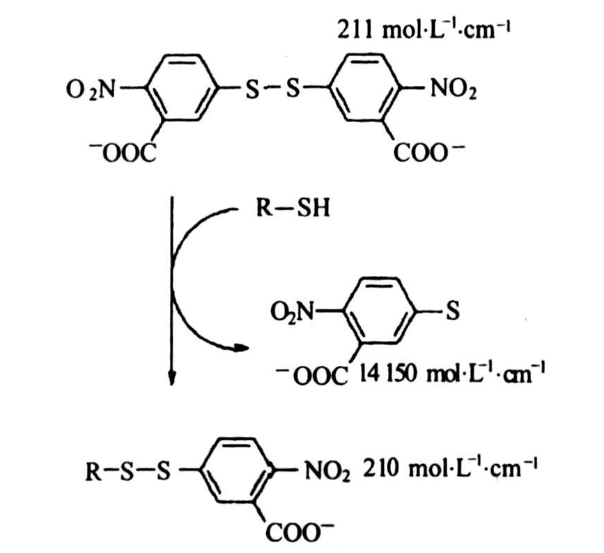
Figure 1. The Reaction Process of DTNB with Sulfhydryl Groups
Analysis Workflow
1. Prepare standard products.
2. Dilute the sample to the appropriate concentration.
3. The standards and samples react with DTNB reagent and the absorbance values are detected with a UV spectrophotometer.
4. Establish a standard curve based on the standard and calculate the sulfhydryl concentration in the sample.
Figure 2. Experimental Procedure
Quantitative measurement of free sulfhydryl groups at MtoZ Biolabs:
1. Free sulfhydryl groups can be quantified.
2. Both free and reduced total sulfhydryl groups can be quantified.
Sample Results
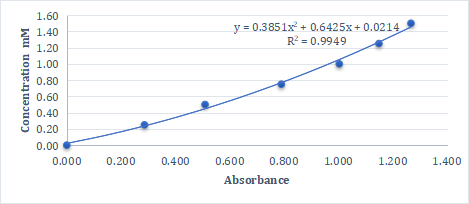
Figure 3. Standard Curve, Abscissa is Absorbance, Ordinate is Cysteine Standard Concentration
Sample Submission Requirements
1. The sample buffer is as close to neutral as possible.
2. The sample concentration should be as high as possible.
3. Sample types we have tested: proteins, reduced proteins.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Absorbance, standard curve, sulfhydryl concentration of the sample after reaction of the standard and sample with DTNB.
Applications
The concentration of free thiol groups is intricately linked to the characteristics and presence of certain proteins, exerting a profound influence on the biological functionality of antibodies. Quantifying the content of free thiol groups facilitates the screening of cell lines in the initial phases of the process, and has certain significance for studying the structure of proteins.
FAQ
Q1: What are the influencing factors of the Ellman method for measuring free sulfhydryl groups?
(1) The appropriate amount of EDTA is helpful for the stability and gradient linearity of TNB color development.
(2) The maximum absorption wavelength of TNB is slightly different in different buffers, so their absorption at 412 nm is also different, which should be determined according to the selected buffer.
(3) The degradation rate of DTNB is accelerated with the increase of pH.
(4) The molar absorption coefficient varies at different temperatures and decreases with increasing temperature.
Q2: What are the advantages of the Ellman method for measuring free sulfhydryl groups?
High sensitivity, easy operation, short time consumption, etc.
How to order?







