Host Cell Protein (HCP) Detection Service
Biopharmaceuticals, drugs produced by living cells, have revolutionized the treatment of various diseases since Eli Lilly and Company's introduction of the first human recombinant protein, Humulin (human insulin), in 1982. To date, over 200 biopharmaceuticals have been approved, encompassing hormones, growth factors, blood factors, vaccines, and monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), with mAbs being the predominant category.
In producing recombinant biopharmaceuticals for human diseases, in vitro cultured cell expression systems are predominantly used. This is followed by purifying the product from impurities, a process accounting for a significant portion of the total production costs in protein product downstream processing. The impurities comprise digested and undigested culture medium components, cellular elements (HCP, DNA), chemical additives (antibiotics, methotrexate, protease inhibitors, etc.), and leachables (like Protein A, heavy metals, plastics, etc.). Applying well-controlled manufacturing processes can significantly reduce these impurities in both raw and finished pharmaceutical products. Host cell protein (HCP) are a major category of cell-derived impurities with potential immunogenicity that can compromise the product's quality, activity, integrity, and stability during processing and storage. Thus, HCP is identified as a Critical Quality Attribute (CQA) in mAb formulations.
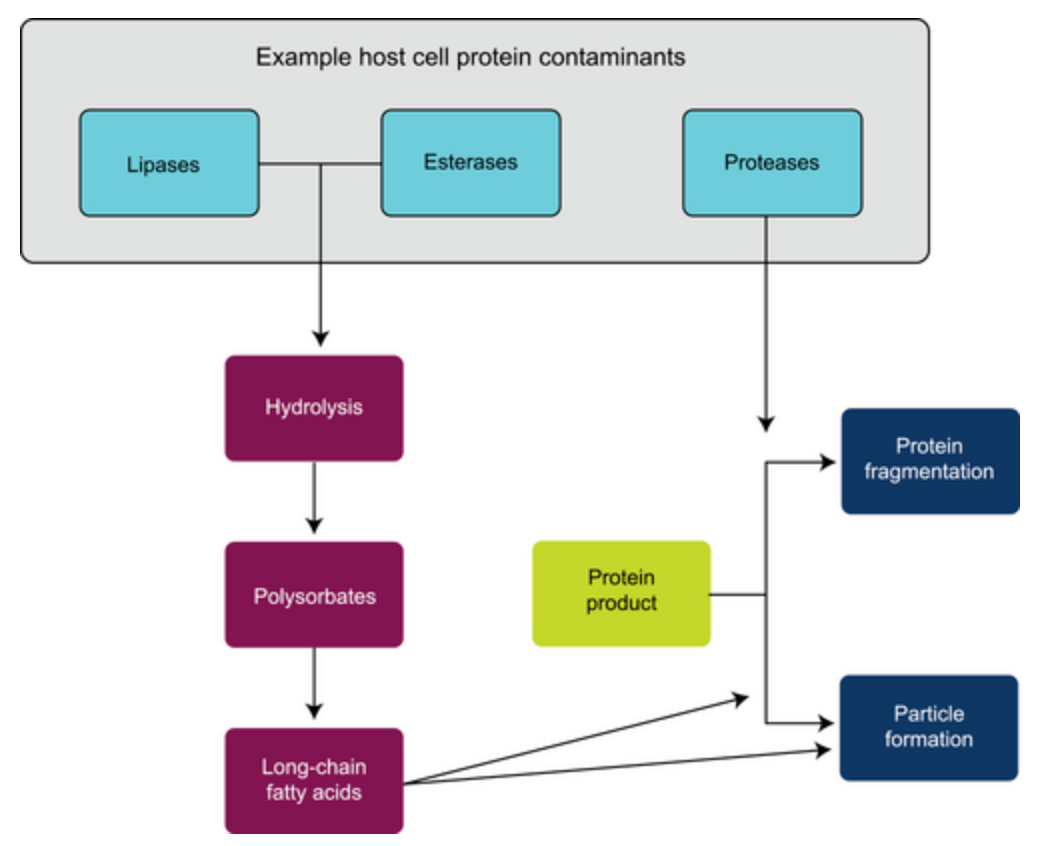
Figure 1. Effect of HCP on Protein Preparations [1]
To mitigate potential HCP concerns in biopharmaceuticals, various methods are employed in their development to identify and quantify HCP. ELISA kits, available for commercial or internal use, are employed to detect HCP. These methods offer high throughput and sensitivity; however, due to antibody-host similarity, some HCP may be missed. Additionally, anti-HCP antibodies can also use to separate HCP in two-dimensional gels based on isoelectric point and molecular weight, followed by mass spectrometry identification of the separated proteins. Although this technique provide an estimate of the number and diversity of HCP in biopharmaceuticals, they might not completely identify all potential HCP in specific products and cannot directly aid in identifying and selectively removing HCP with potential immunogenicity. Recently, the use of Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) has been initiated for the identification and assessment of individual HCP, enabling the detection of even low-concentration HCP in biopharmaceuticals. This advancement from 3D Western-blot to LC-MS/MS has enhanced the ability to identify HCP with high immunogenicity and mitigate their associated risks.
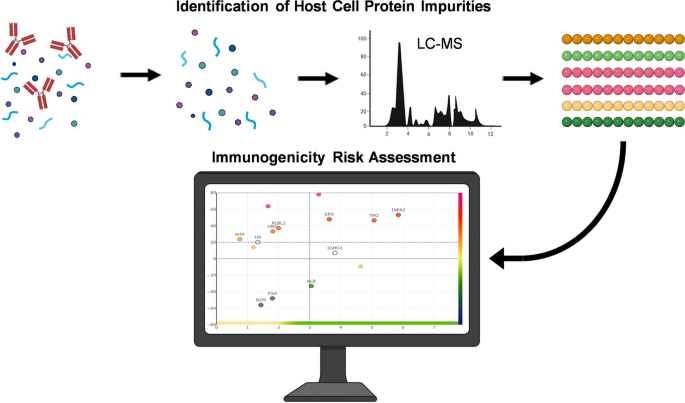
Figure 2. Immunoinformatics Risk Assessment of HCP in the Process Development of Biotherapeutic Drugs [2]
MtoZ Biolabs boasts a comprehensive HCP analysis platform and an associated antibody product development platform. The services we offered include identifying various HCP, preparing HCP antigens, conducting animal immunization, purifying anti-HCP antibodies (including rabbit and mouse monoclonals), screening antibodies, and developing related HCP antibody kits. This facilitates research in animal immunization, antibody production, and screening. The team of MtoZ Biolabs employs multi-gradient experiments to identify optimal conditions, gathers data through various experimental methods like mass spectrometry, and utilizes bioinformatics for HCP identification and quantification. MtoZ Biolabs provides a full range of services, from HCP antigen preparation, animal immunization, and antibody screening to antibody production and ELISA kit development, offering a comprehensive solution for HCP analysis.
References
[1] Tuameh A, Harding SE, Darton NJ. Methods for addressing host cell protein impurities in biopharmaceutical product development. Biotechnol J. 2023 Mar;18(3):e2200115. doi: 10.1002/biot.202200115. Epub 2022 Dec 13. PMID: 36427352.
[2] Haltaufderhyde K, Roberts BJ, Khan S, Terry F, Boyle CM, McAllister M, Martin W, Rosenberg A, De Groot AS. Immunoinformatic Risk Assessment of Host Cell Proteins During Process Development for Biologic Therapeutics. AAPS J. 2023 Sep 11;25(5):87. doi: 10.1208/s12248-023-00852-z. Erratum in: AAPS J. 2023 Dec 19;26(1):6. PMID: 37697150.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
HCP Antibody Development Service
How to order?







