How to Calculate the Isoelectric Point of Amino Acids?
The Isoelectric Point (pI) of an amino acid refers to the state where the net charge of the amino acid molecule is zero at a specific pH value. The basic method for calculating the isoelectric point of an amino acid involves considering the pKa values (negative logarithm values of acid dissociation constants) of various functional groups (such as, amino and carboxyl groups) in the amino acid molecule, and using these values to find the pH value at which the net charge of the amino acid molecule is zero within the pH range where these functional groups are all or partially protonated.
For Standard Amino Acids with No Special Functional Groups
First, find the pKa values of the carboxyl (-COOH) and amino (-NH2) groups of the amino acid. Use the following formula to calculate the isoelectric point:
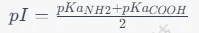
Figure 1
For Amino Acids with One Additional Functional Group (Such as Amino Acids with an Additional Carboxyl or Amino Group)
Find the pKa values of all functional groups of the amino acid. Sort the pKa values from low to high. Use the middle two pKa values to calculate the isoelectric point:
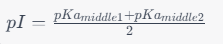
Figure 2
For Amino Acids with Two or More Additional Functional Groups
Similar to above, first determine the pKa values of all functional groups. Sort the pKa values from low to high. Select the appropriate middle pKa values to calculate the isoelectric point based on the total net charge of the amino acid at neutral pH.
Particularly note that the pKa values of amino acids may vary depending on the literature or source, so it is important to use accurate pKa values. In fact, the best method is to directly look up the pI value of the specific amino acid given in the literature. If precise calculations or specific applications are needed, the effects of solution conditions (such as ionic strength, temperature, etc.) on pKa values may also need to be considered.
How to order?







