How to Determine the Extinction Coefficient
What is the Extinction Coefficient?
The extinction coefficient is a crucial physical parameter that describes the absorption ability of a solution to light. It is typically expressed in units of L·mol⁻¹·cm⁻¹. This coefficient quantifies the degree to which light is absorbed as it passes through a solution and is closely related to the concentration of the solution, the path length of the light, and the wavelength of the light. According to Beer-Lambert's law, the extinction coefficient is directly proportional to the absorbance of a solution, making it a key parameter in many optical experiments and analytical applications.
The extinction coefficient holds significant importance across various scientific fields and industrial applications. In chemistry, it is used to accurately measure the concentration of different substances in a solution, aiding scientists in studying chemical reactions and changes in substances. In biology, the extinction coefficient is widely used in the analysis of biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids, providing insights into their structural and functional properties. In pharmaceutical research, the extinction coefficient is a vital tool for evaluating the solubility, stability, and bioavailability of drugs.
Glorius, M. et al. Catalysts. 2020.
Determination of Extinction Coefficient
Moreover, the measurement of the extinction coefficient extends beyond laboratory research, playing a critical role in environmental monitoring, food safety, and other areas. For instance, scientists measure the extinction coefficient of pollutants in water to assess the level of environmental contamination. In the food industry, the extinction coefficient is employed to quickly analyze the composition and quality of ingredients, ensuring food safety and standards.
Select Service
Extinction Coefficients Analysis Service
Principle of Extinction Coefficient Determination: The Beer-Lambert Law
The determination of the extinction coefficient is based on the Beer-Lambert Law, one of the most fundamental principles in spectroscopy. This law describes the relationship between the absorbance of a solution, its concentration, path length, and extinction coefficient. The mathematical expression is:
A = ε ⋅ c ⋅ l
Where:
A: Absorbance (dimensionless), representing the extent to which the solution absorbs light.
ε: Molar extinction coefficient (L·mol⁻¹·cm⁻¹), the ability of the solution to absorb light at a specific wavelength.
c: Concentration of the solution (mol/L), which is the concentration of the target substance in the solution.
l: Path length of light (cm), which is the distance the light travels through the solution.
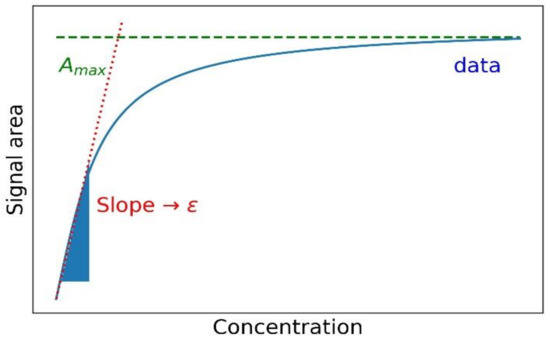
The Beer-Lambert Law reveals a linear relationship between the absorbance of a solution and three factors: the concentration of the solution, the path length, and the molar extinction coefficient. During the absorption process of monochromatic light passing through the solution, absorbance increases with the concentration of the solution, and it also increases linearly with the path length. Therefore, theoretically, we can calculate the extinction coefficient of a solution by measuring the absorbance, provided the concentration and path length are known.
Extinction Coefficient Determination Method: Spectrophotometry
Spectrophotometry is the most commonly used and straightforward method for determining the extinction coefficient. By using a spectrophotometer, researchers can measure the absorbance of a solution at different wavelengths and subsequently calculate the extinction coefficient. This method is not only simple to perform but also provides high-precision measurements, making it widely applicable in fields such as chemistry, pharmaceutical analysis, and environmental monitoring.
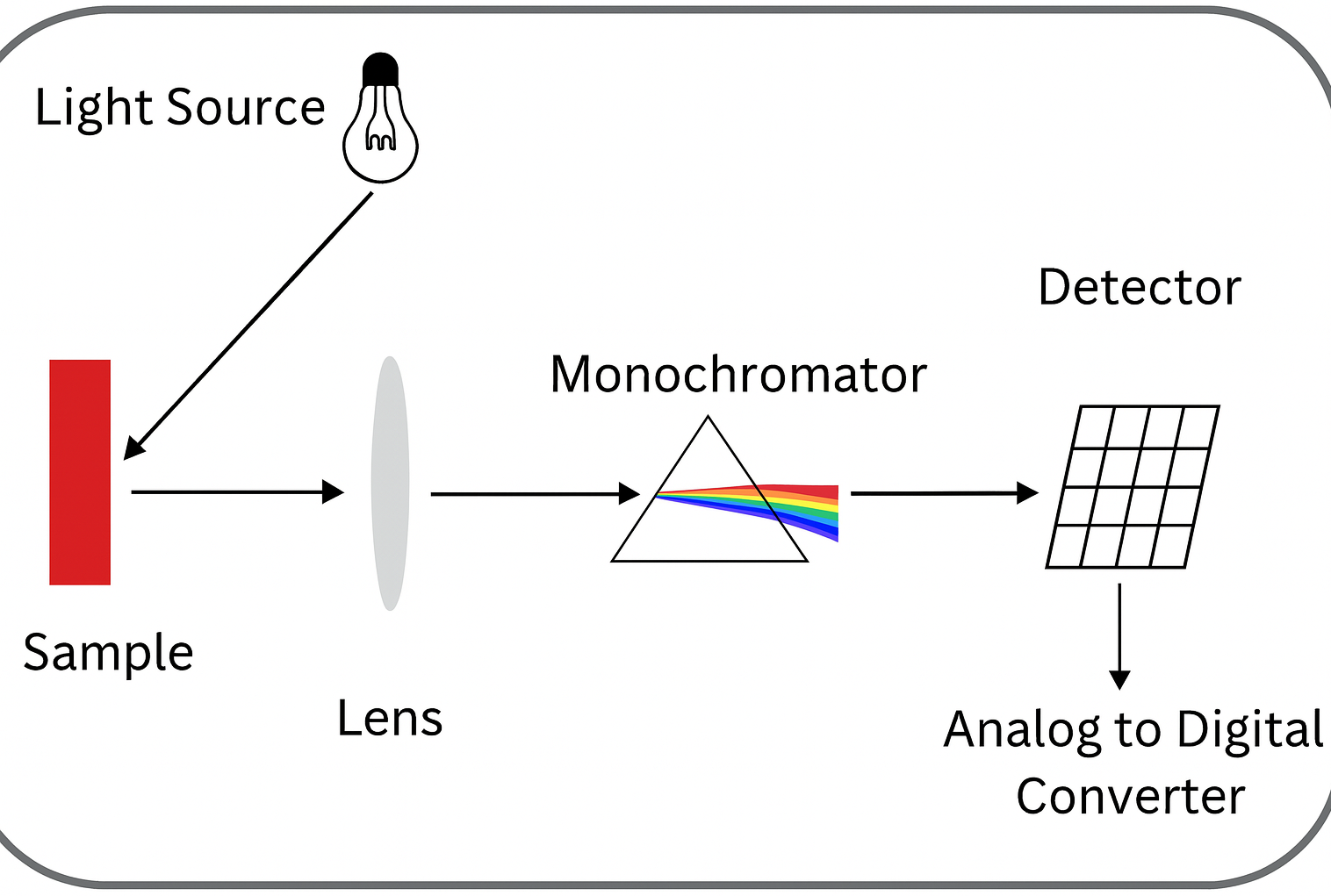
Spectrophotometer Working Principle
1.Reagent Preparation
Prepare the solution to be tested and a series of standard solutions with known concentrations. Ensure the solutions are homogeneous and free of air bubbles to avoid affecting the accuracy of absorbance measurements. Standard solutions are used to create a calibration curve, which allows concentration calculations based on absorbance.
2. Instrument Setup
Turn on the spectrophotometer and allow it to stabilize. Select the appropriate wavelength for measurement, usually based on the absorption characteristics of the substance being tested. Use a blank solution (such as the solvent) to calibrate the instrument to zero, ensuring accurate readings.
3. Standard Solution Measurement
Measure the absorbance of the series of standard solutions with known concentrations. Ensure that the sample container is clean and free of bubbles during each measurement. Record the absorbance of each standard solution at the selected wavelength.
4. Plotting the Calibration Curve
Plot a concentration-absorbance calibration curve based on the absorbance and concentration relationship of the standard solutions. Perform linear regression analysis to determine the slope and intercept of the curve. This calibration curve will be used to calculate the concentration of the test samples.
5. Sample Measurement
Using the same wavelength, measure the absorbance of the sample to be tested, and record the data. Ensure that the conditions under which the sample and standard solutions are measured are consistent to guarantee accurate results.
6.Data Processing and Calculation
Using the calibration curve, calculate the concentration of the sample and then use the Beer-Lambert Law to calculate the extinction coefficient of the sample.
Advantages of Spectrophotometry
✅ Ease of Operation
Spectrophotometry is relatively simple to perform, and the equipment is easy to use. You only need to place the sample in the sample holder, select the appropriate wavelength, and measure absorbance. The process typically requires minimal sample preparation or specialized experimental skills.
✅ High Precision
Modern spectrophotometers are equipped with precise sensors and automated control systems, providing highly accurate measurement results. This makes spectrophotometry particularly suitable for experiments that require precise analysis, such as drug development and environmental monitoring.
✅ Minimal Sample Preparation
Compared to other analytical methods, spectrophotometry has relatively low sample preparation requirements. Most liquid samples can be measured directly without the need for extensive pre-treatment, which greatly simplifies the experimental procedure.
Considerations
❗❗High Concentration Effects
When the concentration of a solution is too high, the solution may experience light scattering, or the absorbance may exceed the instrument’s linear range, leading to measurement errors. Therefore, spectrophotometry is not suitable for extremely high-concentration samples, and samples typically need to be diluted.
❗❗Sample Transparency Requirement
The method requires that the sample be a transparent or clarified solution. It is ineffective for turbid, colloidal, or particulate-containing solutions. Any light scattering or reflection phenomena could lead to inaccurate data.
❗❗Environmental Sensitivity
Factors such as temperature, pH of the solution, and the type of solvent can influence the determination of the extinction coefficient. For some sensitive solutions, experimental conditions must be strictly controlled, as deviations could affect the accuracy of the results.
Applications of the Extinction Coefficient
1. Protein Concentration Determination
In biochemical experiments, accurate determination of protein concentration is essential for many downstream applications. Proteins typically exhibit a characteristic absorption peak around 280 nm. By measuring absorbance and using known extinction coefficients, protein concentration can be quickly and non-destructively determined. This method is simple, reproducible, and widely used in protein expression, purification, and quantification analyses.
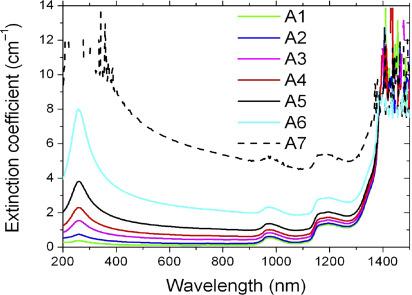
Sani, E. et al. 2010.
Spectral Extinction Coefficient for the Various Samples
2. Kinetic Studies
The extinction coefficient is also a crucial tool for studying protein dynamics. By continuously measuring changes in absorbance over time, researchers can monitor real-time processes such as enzyme reaction rates, protein-ligand interactions, and conformational changes. For example, tracking the characteristic absorption peaks of substrates or products helps in plotting reaction rate curves, which in turn can be used to analyze enzyme activity and inhibitor effects.
3. Protein Purity Assessment
In addition to quantification, the extinction coefficient can be used to evaluate the purity of protein samples. If the measured absorbance deviates from the expected extinction coefficient, it may indicate the presence of impurities or degradation products. Especially during protein preparation and quality control stages, comparing the actual measurement with the expected value helps identify abnormal components and optimize purification processes.
4. Analytical Method Development
In the development of protein analysis methods, the extinction coefficient is widely used as a standardized parameter. Whether validating new colorimetric reagents or evaluating the sensitivity and linear range of spectrophotometric methods, the extinction coefficient of the target protein is essential. It not only helps optimize measurement conditions but also provides foundational support for the reproducibility and accuracy of the methods.
5. Drug Development and Biopharmaceutical Quantification
Quantitative analysis is critical in the development of therapeutic proteins and biopharmaceuticals. By knowing the extinction coefficient, the concentration of target molecules can be accurately monitored at various stages (e.g., formulation development, pharmacokinetic studies, and quality control). This is crucial for ensuring the consistency, safety, and efficacy of drugs, especially in the development of biologics such as monoclonal antibodies and recombinant proteins.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
How to order?







