Native Mass Spectrometry Analysis Service
Native mass spectrometry (Native MS) facilitates direct determination of a protein's molecular weight. It facilitates the study of intact proteins, non-covalent protein-protein interactions, and protein-ligand complexes within biological systems, addressing the limitations of traditional mass spectrometry technologies in the precise quantification of complex drug molecules.
Native mass spectrometry is extensively employed for various applications, including the determination of the drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) in antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs): ADCs are categorized into two types based on the site of antibody conjugation, lysine-conjugated ADCs and cysteine-conjugated ADCs, with the majority being conjugated to small molecule drugs via lysine. The analysis of these ADCs typically relies on the conventional RPLC/MS technology platform, requiring the protein to be analyzed under denaturing conditions. However, these denaturing conditions may result in the dissociation of the light and heavy chains in cysteine-conjugated ADCs, making native mass spectrometry a preferable method for their detection.
MtoZ Biolabs has established a non-denatured protein profiling platform utilizing high-resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. This platform is capable of analyzing the structure, topology, and assembly of proteins and protein complexes that preserve their tertiary and quaternary structures in states closely resembling their natural conditions. Additionally, the platform facilitates the detailed characterization of monoclonal antibody/ADCs, PEG-modified proteins, oligomeric proteins, glycans, and assembled proteins.
Since the protein-ligand non-covalent binding force is usually weak, it is imperative that the intermolecular forces remain intact during mass spectrometry analysis. Electrospray ionization of proteins using an MS-compatible, non-denaturing buffer system in non-denaturing mass spectrometry conditions can keep many proteins in folded states, exhibiting characteristic low-charge states and requiring excellent sensitivity across a broader and higher mass-to-charge (m/Z) range compared to the analysis of denatured proteins. Combining size exclusion chromatography (SEC) with non-denaturing electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (Native ESI-MS) effectively mitigates potential denaturation during ionization and separation in conventional Native MS detection.
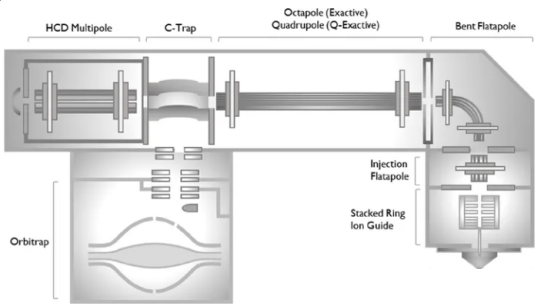
Figure 1. A High-Resolution, Extended-Mass Range Orbitrap Platform for Native Mass Spectrometry Analysis
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample pre-treatment, such as running non-denaturing non-reducing adhesives.
2. Samples are tested using the Exactive Plus EMR high-resolution mass spectrometry platform.
3. In data analysis, use deconvolution software to analyze the results.
4. Molecular weight information of the sample is obtained, and if the ADCs are detected, the DAR measurement results will be obtained at the same time.
Sample Results
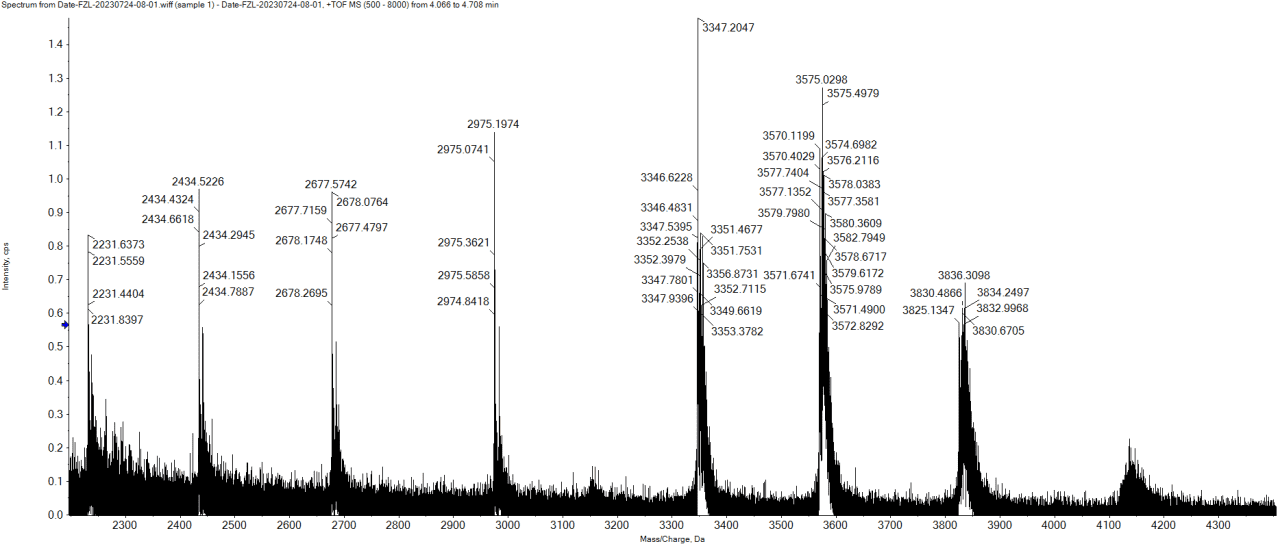
Figure 2. Sample Mass Spectrum
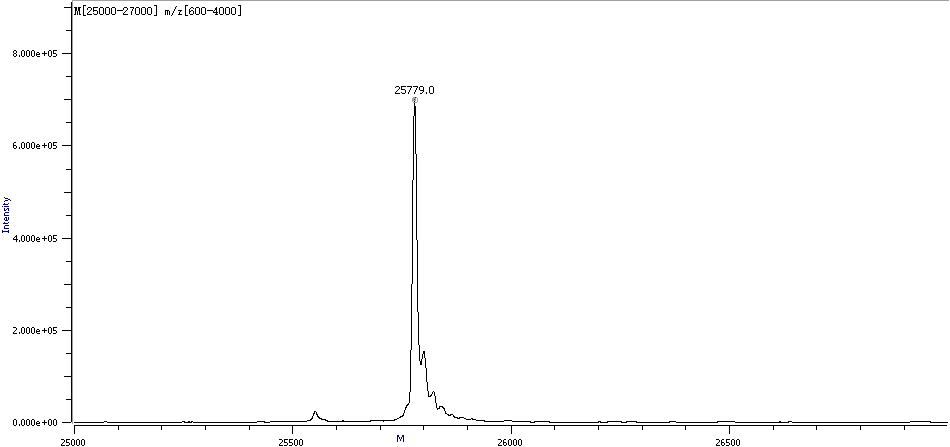
Figure 3. Sample Deconvolution Molecular Weight Spectra
The main deconvolution molecular weight details of the sample are as follows:
Sample Submission Requirements
1. Protein samples and small molecule samples can be provided at the same time.
2. Provide high purity samples as far as possible.
3. Both solid and liquid samples can be tested.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Native ESI-MS technology enables the precise characterization of protein structures following SEC separation and assess the impact of non-specific interactions between proteins and stationary phases on protein structures, to fulfill the demand for precise identification of complex therapeutics. Analyzing the drug-to-antibody ratio in antibody-drug conjugate assessments is important to assessing inter-batch stability.
Applications
1. ADCs drug assays, such as DAR assays.
2. Peg-modified protein or polysaccharide-modified protein analysis.
3. Study of assembled proteins or protein complexes.
4. Determine the molecular weight of protein and protein complex in natural structure.
5. Studies on the structure and topology of non-denatured proteins and protein complexes.
FAQ
Q1: How to minimize the effect of denaturation on the results during the experiment and detection?
The condition of SEC Elution has great influence on the structural integrity of protein. To preserve the protein's natural structure during SEC separation, employing an ammonium acetate eluent with high ionic strength and a pH close to physiological conditions is most effective, whereas the use of ammonium formate and ammonium bicarbonate eluents tends to result in greater protein denaturation. To maintain the protein in its native state, it is advisable to utilize a high ionic strength ammonium acetate eluent in SEC-ESI-MS analyses.
Q2: What are the advantages of high resolution mass spectrometer in native mass spectrometry analysis?
The scope of data acquisition has been broadened, with the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) ranging from 350 to 20,000. Optimization of experimental conditions has been facilitated by the improved HCD pressure and mass spectrometry parameters like voltage and temperature. It can capture shorter time-domain signals to improve signal-to-noise ratio.
How to order?







