Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) Analysis
Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis is a comprehensive analytical approach designed to characterize the complex structure and functionality of ADC. An ADC consists of an antibody targeting cancer cell antigens, a linker controlling drug release, and a cytotoxic drug acting as a warhead to destroy cancer cells. Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis focuses on determining critical quality attributes such as drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR), conjugation sites, stability, and structural integrity. By leveraging advanced techniques like LC-MS/MS and HR-MS, antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis provides detailed insights into the molecular architecture and behavior of ADCs, ensuring their consistency, efficacy, and safety during drug development and production.
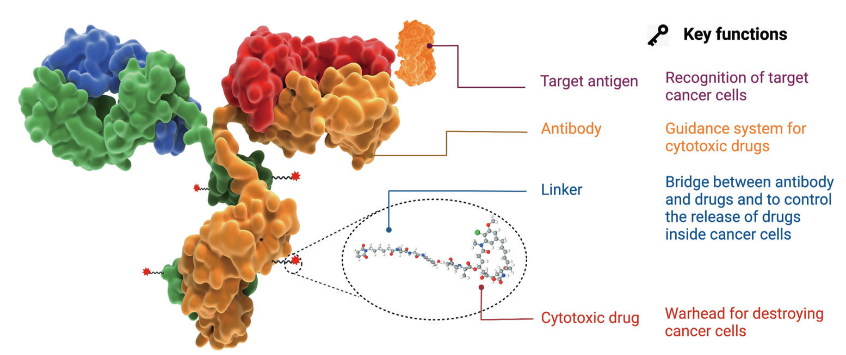
Fu, Z. et al. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022.
Figure 1. The Structure of Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC)
Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis involves a systematic workflow to characterize ADCs in matrix samples using mass spectrometry techniques. The process begins with sample preparation, including protein or drug isolation using immunocapture or extraction techniques such as PP, SPE, or LLE. Free payload analysis is performed using LC-MS/MS, while conjugated antibody analysis involves enzymatic digestion with trypsin or papain, producing peptide fragments analyzed by LC-MS/MS. Conjugated payload analysis utilizes Cathepsin B to release the payload, followed by LC-MS/MS for drug quantification. Total antibody analysis can be conducted through enzymatic digestion (trypsin or papain), reduction (IdeS), or PNGase F treatment, generating peptide fragments, subunits, or intact ADCs, respectively. Each fraction is analyzed using LC-MS/MS (bottom-up) or LC-HRMS (middle-up and top-down) to provide insights into ADC structure, drug distribution, and stability, ensuring comprehensive characterization and quality control.
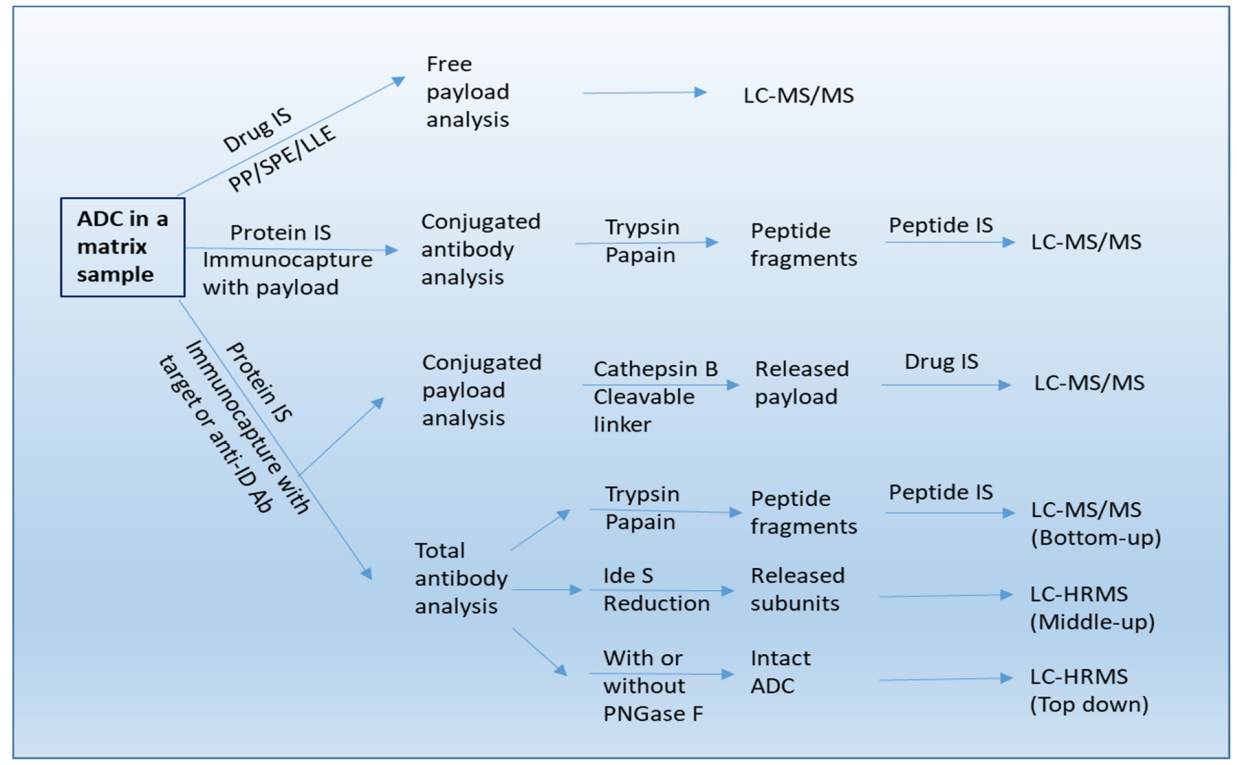
Qin, Q. et al. Molecules. 2022.
Figure 2. The Workflow of Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) Analysis
Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis addresses key challenges in ADC research and development, including identifying heterogeneous drug distribution, assessing structural modifications during manufacturing or in vivo circulation, and evaluating pharmacokinetics and biotransformation pathways. It helps detect potential impurities, quantify payload release, and monitor structural stability, enabling researchers and manufacturers to optimize ADC design, ensure batch-to-batch consistency, and meet regulatory standards for therapeutic applications.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider, provides advanced proteomics, metabolomics, and biopharmaceutical analysis services to researchers in biochemistry, biotechnology, and biopharmaceutical fields. Our ultimate aim is to provide more rapid, high-throughput, and cost-effective analysis, with exceptional data quality and minimal sample consumption. Utilizing advanced instruments such as Thermo Fisher Orbitrap Fusion Lumos and Agilent LC-MS/MS systems, MtoZ Biolabs offers antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis service that delivers precise and comprehensive molecular characterization of ADCs. Our scientific team comprises seasoned experts from fields including mass spectrometry, medicinal chemistry, and biopharmaceuticals, bringing extensive research and industry experience to ensure highly accurate and reproducible antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis results. With years of expertise in biopharmaceutical analysis, MtoZ Biolabs provides reliable and actionable insights to support ADC drug development and regulatory compliance. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us.
1. Comprehensive Structure Analysis
Leveraging advanced mass spectrometry techniques including LC-MS/MS and HR-MS, antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis at MtoZ Biolabs enables precise characterization of the antibody, linker, and payload structures along with their binding sites, ensuring clients gain a comprehensive understanding of ADC molecular properties.
2. Accurate Drug-to-Antibody Ratio (DAR) Measurement
Focusing on the critical quality attribute of ADC, antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis provides highly sensitive and accurate DAR measurements, supporting clients in optimizing product quality and assessing therapeutic efficacy effectively.
3. Pharmacokinetics and Stability Evaluation
Using mass spectrometry-based approaches, antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis evaluates the pharmacokinetics, in vivo stability, metabolic pathways, and drug release behavior of ADCs, delivering detailed insights that support both preclinical and clinical research.
4. Post-Translational Modifications and Impurity Characterization
Addressing structural variations caused by chemical modifications or degradation, antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis conducts comprehensive post-translational modification (PTM) analysis and impurity characterization, identifying factors such as deamidation, oxidation, and glycosylation to mitigate potential quality risks and ensure ADC product integrity.
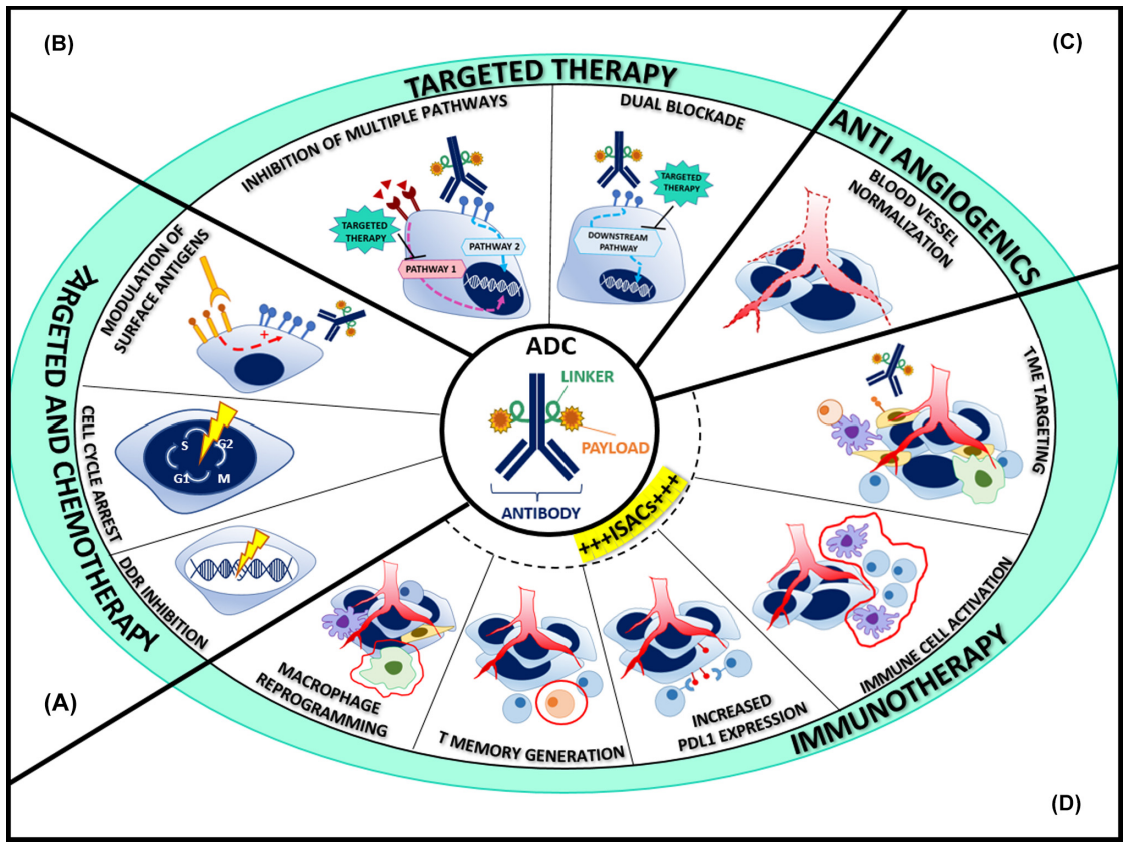
Fuentes-Antrás J, et al. Trends Cancer. 2023.
Figure 3. The Content of Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) Analysis
Case Study
1. Antibody-Drug Conjugate Pharmacokinetics Analysis
The study presents a comprehensive study on the pharmacokinetics and biotransformation of ADCs. The researchers developed an intact quantification method utilizing liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS) with a linear dynamic range of 1-10 μg/mL, requiring only 25 μL of plasma sample. This method was qualified for measuring naked monoclonal antibodies and ADCs with varying DARs in rat plasma. Comparative analyses with traditional ligand binding assays (LBA) and LC-multiple reaction monitoring (LC-MRM) approaches revealed that the LC-HRMS method could detect new ADC species, unveiling potential biotransformation products not observed with conventional techniques. The study demonstrates that antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis via LC-HRMS offers novel insights into ADC in vivo characterization, which can enhance drug candidate optimization, immunogenicity evaluation, and safety assessment.
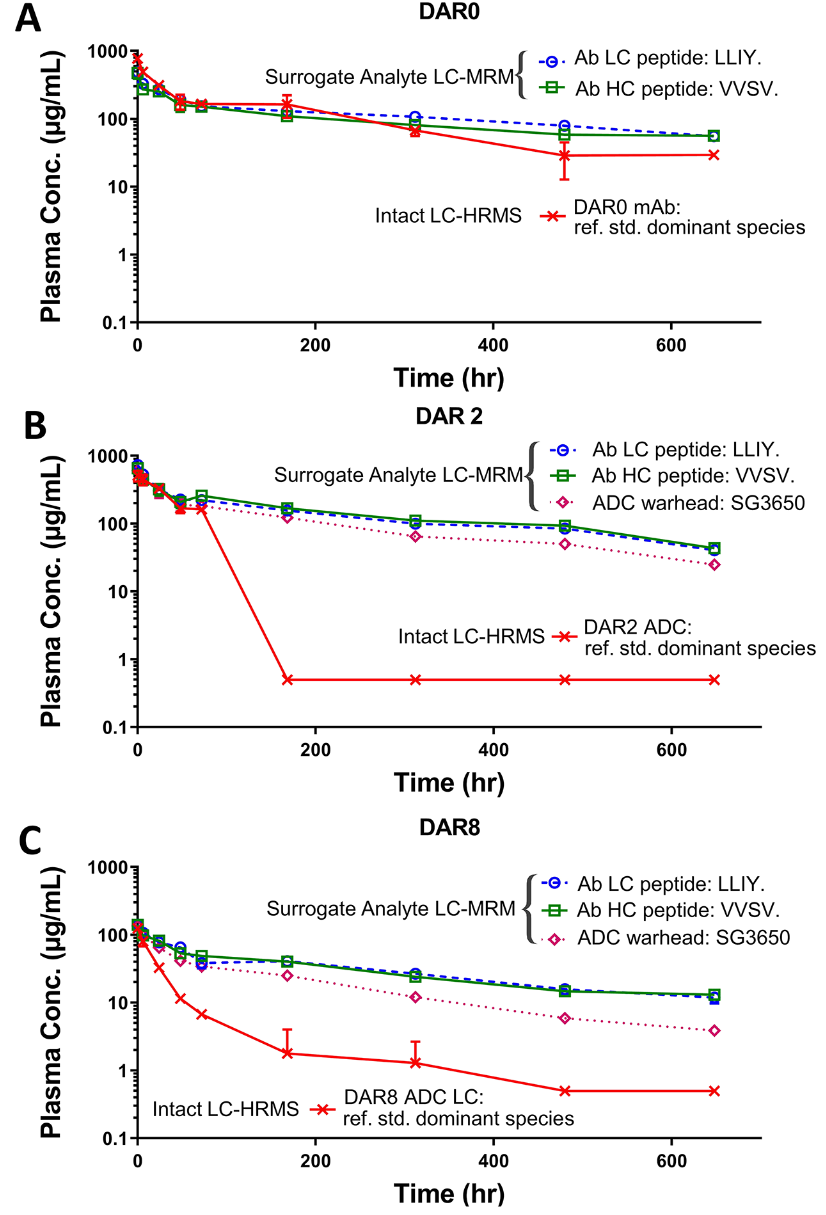
Huang, Y. et al. Anal Chem. 2021.
Figure 4. Average Concentration-Time Profile Plot for Antibody-Drug Conjugate Using LBA-LC-MRM and LBA-LC-HRMS
2. Antibody-Drug Conjugate Structure Analysis
The study presents a method for swiftly analyzing reduced ADCs without the need for enzymatic digestion. By employing online liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) coupled with high-resolution fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FTICR) mass spectrometry, the researchers achieved rapid determination of the DAR, primary sequence characterization, and precise localization of drug conjugation sites. This streamlined approach enhances the efficiency of ADC structural analysis, which is crucial for ensuring their safety and efficacy in therapeutic applications.
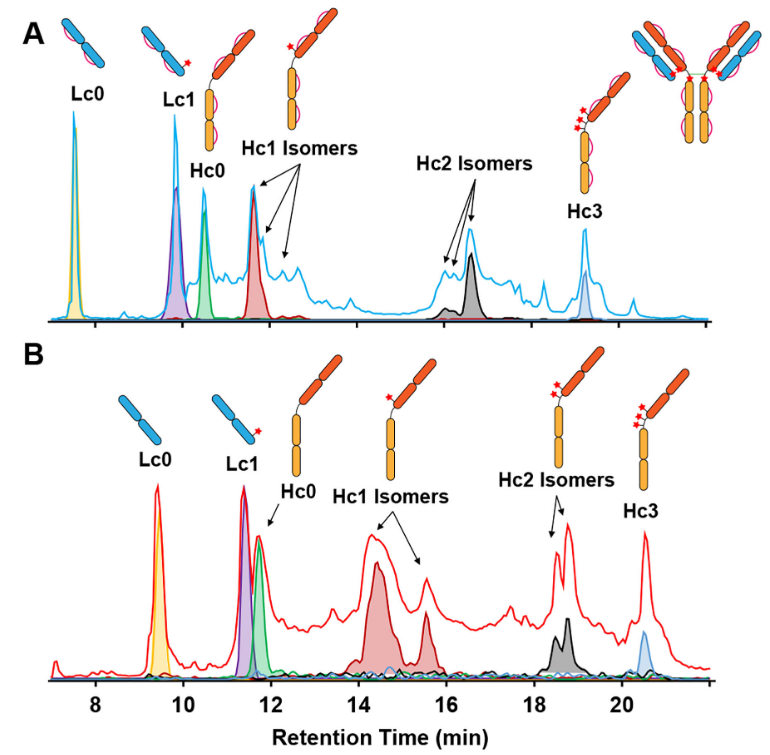
Larson, EJ. et al. Anal Chem. 2020.
Figure 5. Online RPLC-MS of Partially Reduced ADC Subunits and Fully Reduced ADC Subunits
FAQ
Q1: Which part serves as the targeting component in ADCs and peptide-drug conjugates (PDCs)?
Answer: ADCs and PDCs are innovative drug modalities designed to deliver therapeutic agents specifically to disease-associated targets. In both types of conjugates, the targeting function is primarily mediated by the following components: the antibody serves as the targeting component in antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis by recognizing and binding to specific markers (antigens) on the surface of cancer cells while ensuring high specificity and strong affinity that allow ADCs to release their payload selectively at disease sites (e.g., cancer cells) and significantly minimize off-target effects on healthy cells. In PDCs, peptides act as the targeting moiety. Comprising several to dozens of amino acids, peptides specifically recognize and bind to disease-associated targets. This specificity enables precise drug release within disease cells, such as cancer cells, reducing adverse effects on normal tissues.
In both ADCs and PDCs, the targeting function relies on the inherent specificity of antibodies or peptides. These macromolecular components enable the precise delivery of therapeutic agents to disease-associated organs or tissues, thereby enhancing drug efficacy while minimizing side effects.
Q2: Can the average DAR value of an ADC be measured using MALDI-TOF?
Answer: The average DAR of an ADC is typically measured using LC-MS/MS. MS applied in antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis determines the mass or mass-to-charge ratio of molecules or molecular ions while liquid chromatography separates and identifies various compounds in complex ADC samples, providing critical insights into the molecular structure and composition.
1. Why choose LC-MS/MS in antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis?
1. Accuracy and Sensitivity
LC-MS/MS used in antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis offers high accuracy and sensitivity, enabling precise determination of the drug load on ADCs while distinguishing different drug load states to ensure reliable data interpretation.
2. Separation Capability
Liquid chromatography applied in antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis effectively separates different components in an ADC sample before they enter the mass spectrometer, allowing each component to be individually analyzed to achieve detailed molecular characterization.
3. Structural Information
MS/MS integrated into antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis provides valuable structural insights by identifying the location and type of conjugated drugs, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of ADC structure and functionality.
2. Suitability of MALDI-TOF for antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis
While MALDI-TOF is a powerful mass spectrometry technique often used for peptides and small proteins, its application in antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis faces challenges when dealing with large biomolecules. The resolution and sensitivity limitations of MALDI-TOF reduce its effectiveness in accurately determining drug loading in ADCs.
In comparison, LC-MS/MS technology used in antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) analysis demonstrates superior accuracy, resolution, and sensitivity, providing essential structural and quantitative information required for precise characterization of complex ADC molecules.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Relevant Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Parameters
4. The Detailed Information of Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) Analysis
5. Mass Spectrometry Image
6. Raw Data
How to order?







