Protein Sumoylation Identification Service
Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) is a post-translational modification of proteins that refers to the covalent attachment of a small ubiquitin-associated modifier to a protein. Unlike ubiquitination, which targets proteins for degradation, sumoylation modulates protein function across several cellular processes including nucleocytoplasmic transport, transcription regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, stress response, and cell cycle progression. Despite low amino acid sequence similarity between SUMO and ubiquitin, they share very similar structural folds. SUMOs are about 100 amino acids in length, with variations in sequence length and mass among different family members and organisms.
Sumoylation is pivotal in controlling the subcellular localization of various proteins. Depending on the specific protein, sumoylation can occur in either the cytoplasm or nucleus. For instance, sumoylation can regulate the transport of the ribonucleoprotein RanGAP1 within the nuclear pore complex (NPC). Additionally, sumoylation affects the transcription process, as the activity of several transcription factors depends on their interaction with promyelocytic leukemia (PML) bodies and nuclear bodies (NBs), which require the sumoylation of PML protein for their assembly. Moreover, sumoylation plays a crucial role in chromosome congression and kinetochore assembly. If the function of SUMO-1 is abnormal, it can disrupt the correct distribution of chromatin during replication.
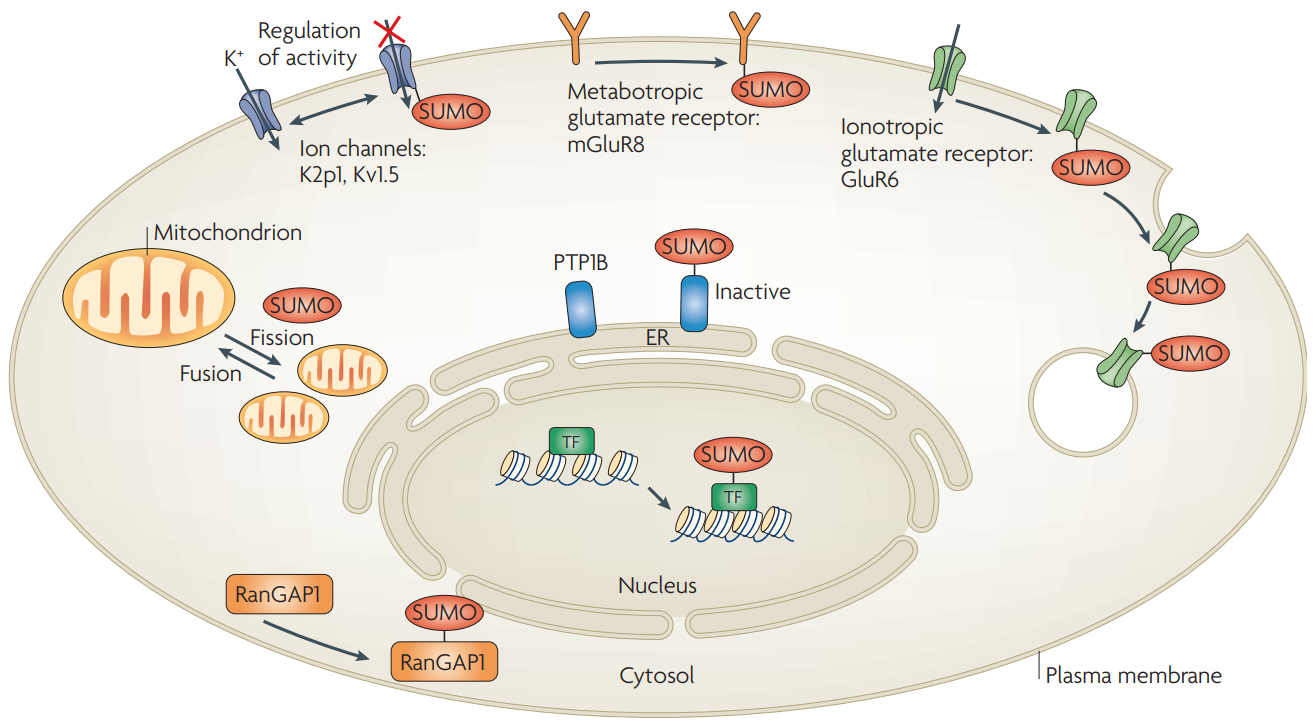
Geiss-Friedlander, R. et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007.
Figure 1. Protein Sumoylation Identification
MtoZ Biolabs leverages the Thermo Fisher's Orbitrap Fusion Lumos mass spectrometry platform, coupled with nanoLC-MS/MS chromatography, to deliver a comprehensive protein sumoylation analysis service. Clients are invited to submit their experimental objectives and samples, and our team will manage all aspects of the project thereafter.
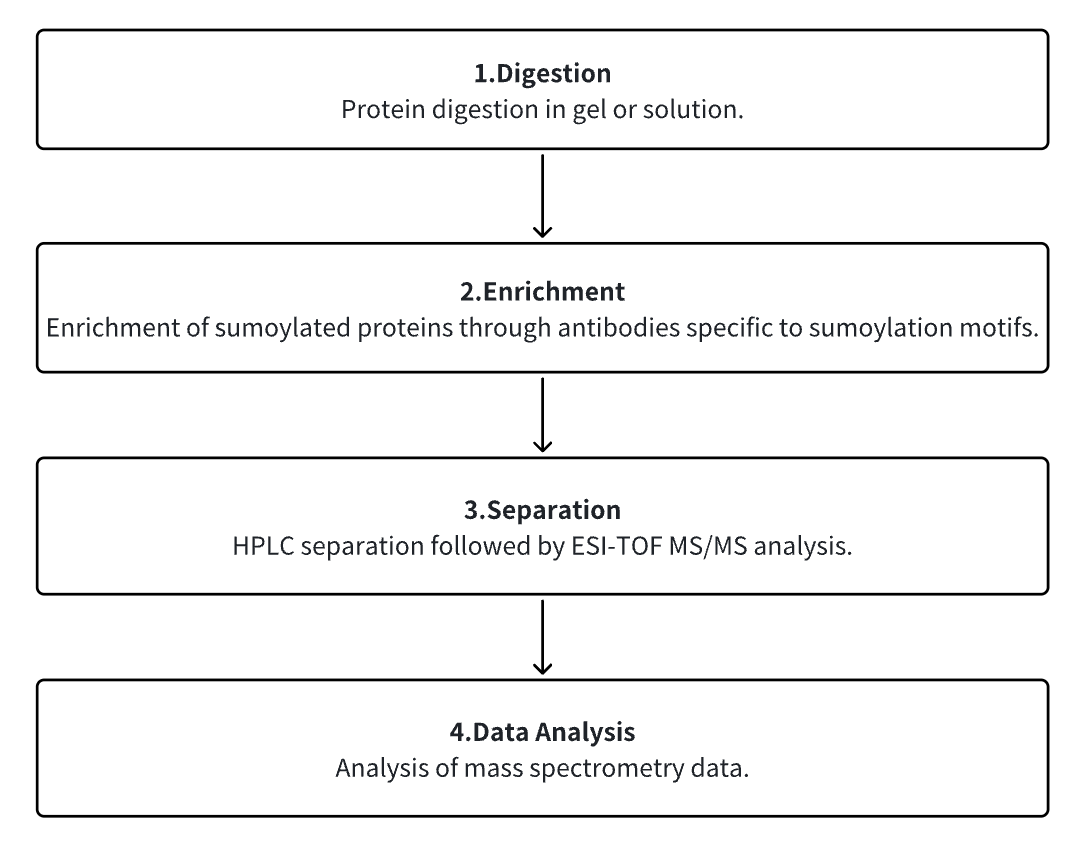
Analysis Workflow
1. Protein Digestion in Gel or Solution
2. Enrichment of Sumoylated Proteins Through Antibodies Specific to Sumoylation Motifs
3. HPLC Separation Followed by ESI-TOF MS/MS Analysis
4. Analysis of Mass Spectrometry Data
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
1. Functional Annotation and Enrichment Analysis
2. Cluster Analysis
3. Network Analysis
4. Statistical Analysis
5. Analysis of Post-Translational Modification in Proteomics
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Post-Translational Modifications Proteomics Service
How to order?







