Proximity Extension Assay Service
- Biomarker Discovery and Validation
- Drug Development and Target Validation
- Multiplex Protein Quantification
- Clinical and Translational Research
- Protein Interaction Studies
Proximity Extension Assay (PEA) is an advanced method that combines antibody-based recognition with DNA amplification techniques for highly sensitive and specific protein detection and quantification. The core principle of Proximity Extension Assay involves the use of pairs of antibodies, each labeled with unique oligonucleotide probes. When the antibodies bind to their target protein in close proximity, their attached probes hybridize, forming a DNA template. This template is then amplified using quantitative PCR (qPCR), allowing for precise detection even at extremely low protein concentrations. By combining the specificity of antibody-antigen recognition with the sensitivity of nucleic acid amplification, PEA enables unparalleled performance in protein analysis, especially in complex biological matrices such as plasma, serum, or tissue lysates.
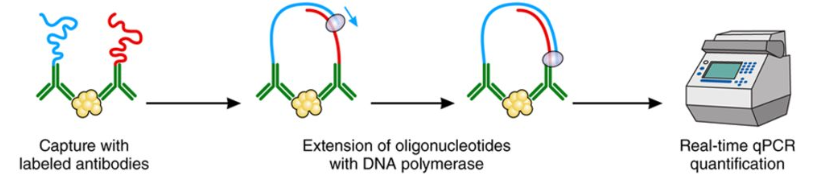
Figure 1. Principle of Proximity Extension Assay
Proximity extension assay addresses key challenges in biomarker discovery, diagnostics, and disease monitoring by enabling the detection of low-abundance proteins with high specificity and supporting multiplex protein analysis within a single sample. Proximity extension assay provides comprehensive insights into protein networks, immune responses, and cell signaling pathways, driving advancements in both basic and translational research.
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs offers a cutting-edge Proximity Extension Assay Service to meet the diverse needs of researchers. Leveraging advanced PEA platforms and a highly skilled team, we provide comprehensive services from assay design to data analysis. Our service enables high-throughput, multiplex protein quantification with exceptional accuracy and reproducibility, even from minimal sample volumes.
Whether you aim to identify novel biomarkers, analyze complex protein networks, or validate therapeutic targets, MtoZ Biolabs’ Proximity Extension Assay Service delivers reliable results tailored to your research needs. We empower researchers to achieve breakthroughs in disease diagnostics, drug development, and personalized medicine. For more information about our Proximity Extension Assay Service, please contact us.
Service Advantages
1. Advanced Analysis Platform: MtoZ Biolabs established an advanced Proximity Extension Assay Service platform, guaranteeing reliable, fast, and highly accurate analysis service.
2. Multiplexing Capability: Proximity Extension Assay Service allows the simultaneous analysis of multiple proteins within a single sample, saving time and resources while providing comprehensive data on complex biological systems.
3. Minimal Sample Requirement: With its efficient design, PEA requires only a small amount of sample, making it ideal for precious or limited clinical samples such as serum, plasma, or tissue lysates.
4. One-Time-Charge: Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
5. High-Data-Quality: Deep data coverage with strict data quality control. AI-powered bioinformatics platform integrates all proximity extension assay data, providing clients with a comprehensive data report.
6. Rapid Turnaround Time: Our streamlined workflow ensures fast and efficient processing, enabling timely delivery of high-quality data to support your research progress.
Applications
Case Study
1. Identifying Biomarkers for Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB) Using Proximity Extension Assay
Diagnosing dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is particularly challenging due to overlapping symptoms with other dementias, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The identification of specific biofluid biomarkers is crucial for improving diagnostic accuracy and understanding disease mechanisms. Using proximity extension assay technology, researchers analyzed cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples from 534 individuals, including cognitively unimpaired controls (CON), DLB patients, and AD patients. Over 900 proteins were profiled, revealing 49 uniquely dysregulated proteins in DLB, such as FCER2, ENTPD5, and MMP1. Custom multiplex PEA panels were developed and validated in three independent cohorts, ensuring robust and reproducible results. A volcano plot analysis identified significant changes, with proteins like DDC and GH showing upregulation in DLB, while MMP1 was downregulated. Functional enrichment analysis highlighted biological pathways associated with DLB, including the regulation of myelination and Notch signaling pathways. This case demonstrates the power of Proximity Extension Assay in identifying disease-specific biomarkers and advancing the understanding of DLB pathogenesis, paving the way for improved diagnostics and targeted therapies.
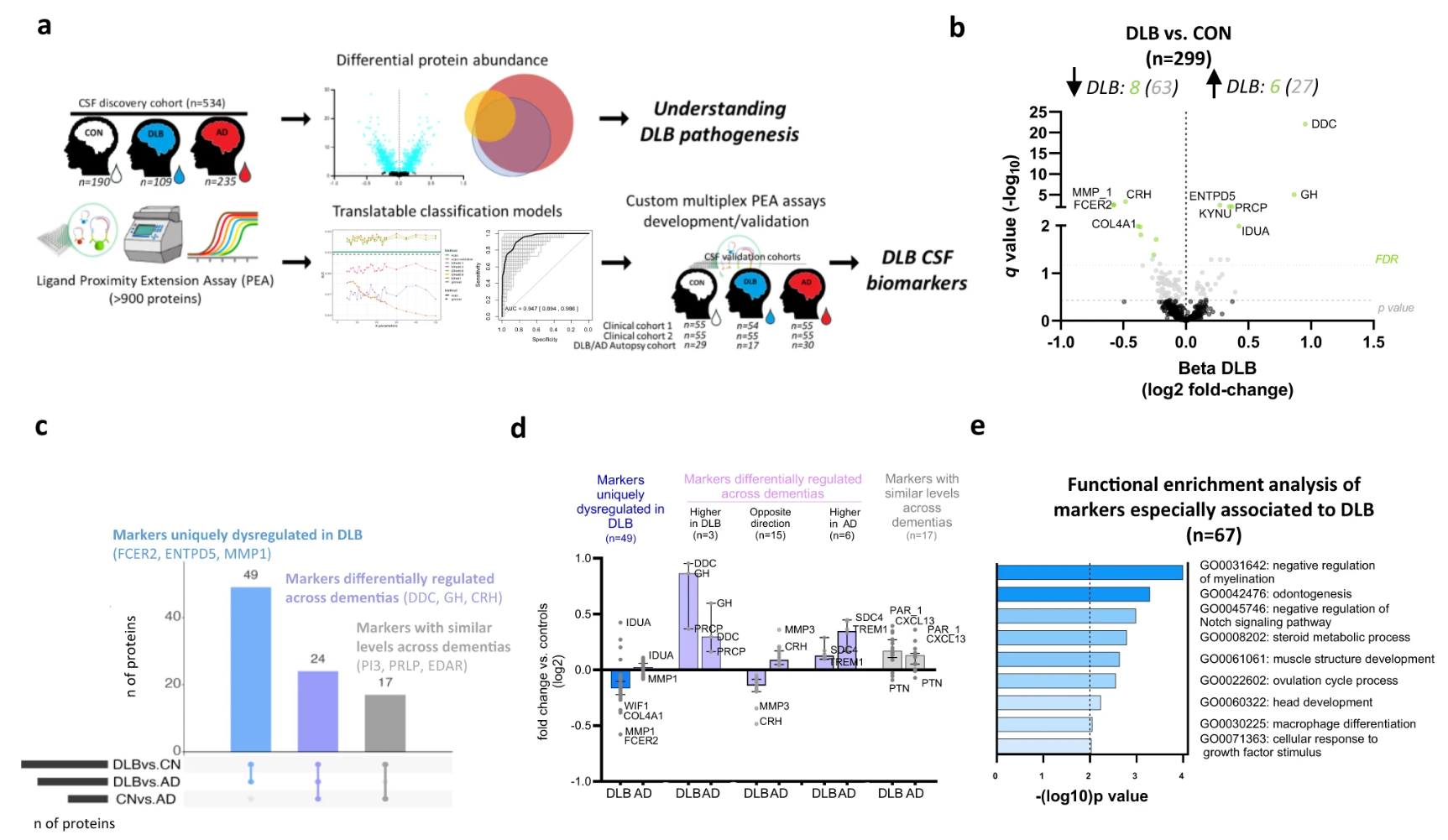
Del Campo, M. et al. Nat Commun. 2023.
Figure 2. Study Overview and Differential Abundance of CSF Proteins in DLB
2. Predicting Immunotherapy Outcomes in Esophageal Cancer Using Proximity Extension Assays
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have transformed cancer therapy, yet their effectiveness in esophageal cancer is limited to certain patient subgroups, with clinically useful predictive biomarkers still lacking. To address this, researchers collected plasma samples from 91 patients with esophageal cancer before and after ICI treatment. Using the Olink Immuno-Oncology panel and proximity extension assay technology, dynamic changes in 92 plasma proteins were analyzed to identify potential biomarkers linked to treatment outcomes. The study revealed significant changes in 47 plasma proteins during ICI treatment, many of which were involved in immune-related processes like T-cell activation and intercellular adhesion. Among these, baseline levels of three angiogenesis-associated proteins—IL-8, TIE2, and HGF—were strongly correlated with survival outcomes (p<0.050). Based on these findings, an angiogenesis-related risk score was developed, providing superior predictive value for ICI response and prognosis. Furthermore, combining antiangiogenic therapy with ICIs significantly improved overall survival compared to ICI monotherapy (p=0.044). This case highlights the power of plasma protein profiling with proximity extension assay technology in identifying biomarkers and optimizing immunotherapy strategies, offering new avenues for personalized cancer treatment.
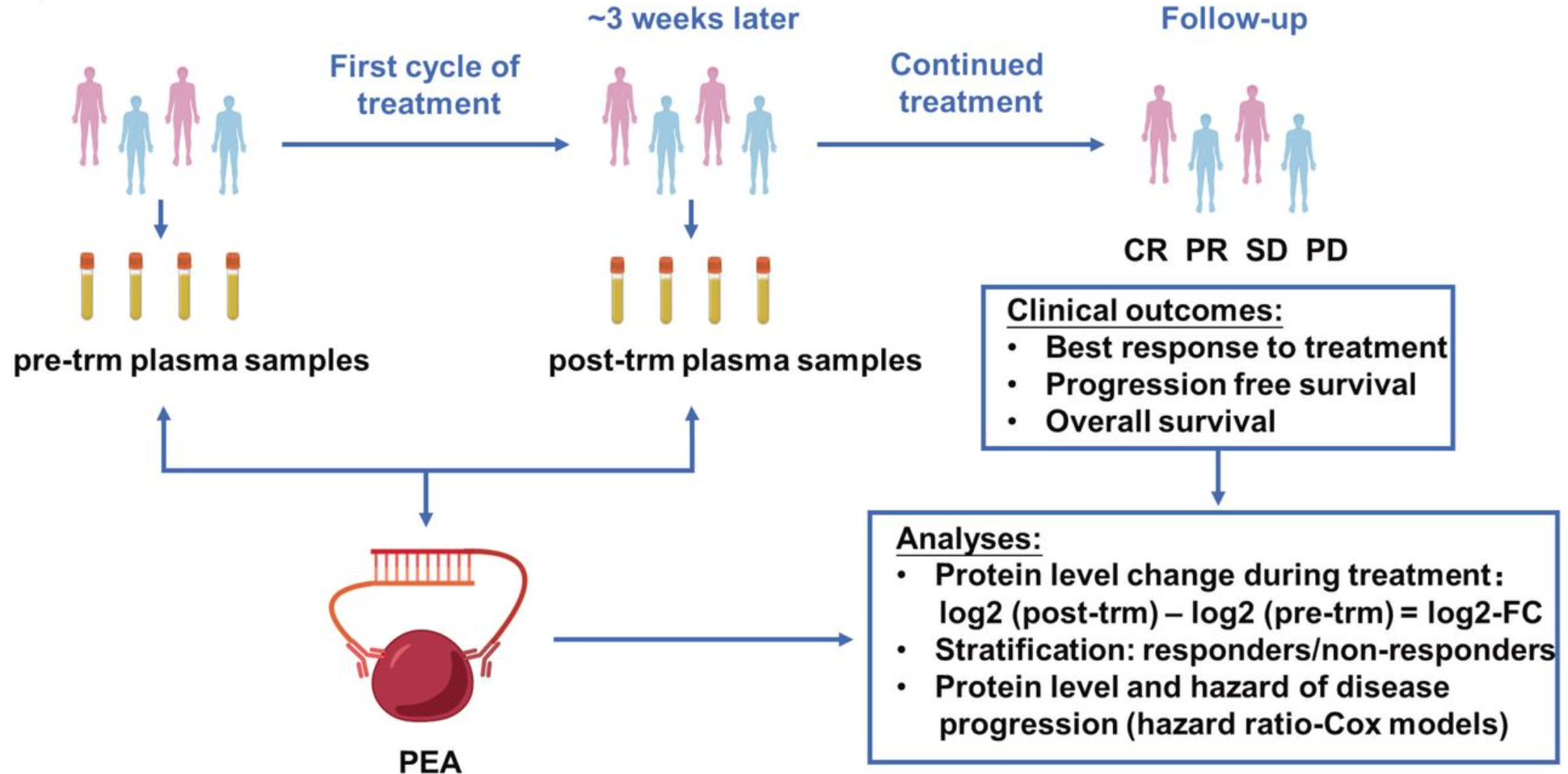
Gao, M. et al. J Immunother Cancer. 2024.
MtoZ Biolabs' Proximity Extension Assay Service provides robust technical support for drug development, disease mechanism research, and biomarker discovery, accelerating research progress and driving breakthroughs in life sciences. If you are interested in our service, please feel free to contact us.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







