Sequencing Analysis
In life science research and biopharmaceutical development, sequencing analysis is a core method for deciphering the structure and function of protein molecules. This field encompasses amino acid sequencing of proteins, peptides, and antibodies, as well as post-translational modification site identification, antibody CDR region determination, full-length protein reconstruction, single-molecule sequencing, and de novo protein sequencing. From basic research to drug development, from mechanistic studies to quality control, sequencing technologies are continuously expanding the boundaries of molecular-level exploration.
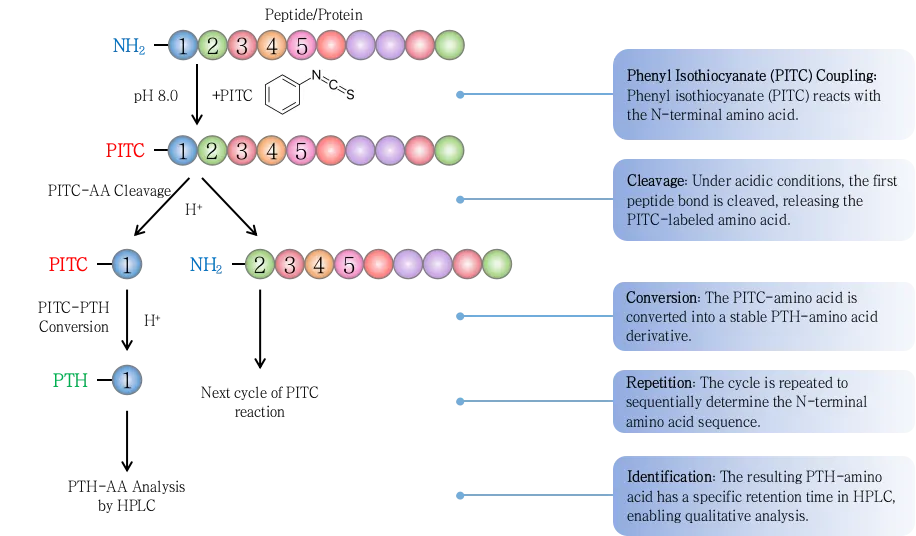
Figure 1. Protein Sequencing by Edman Degradation
With the advancement of multi-omics technologies, sequencing analysis now includes single-cell protein sequencing, TCR/BCR sequencing, antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) sequencing, and epitope decoding, empowering researchers to achieve higher-resolution insights into biomolecules.
As a specialized service provider in proteomics and molecular bioanalysis, MtoZ Biolabs has established an end-to-end sequencing analysis platform based on high-resolution mass spectrometry and robust bioinformatics support. Our comprehensive service portfolio covers protein sequencing, antibody sequencing, single-molecule sequencing, terminal sequencing, and more. Additionally, we offer Single-cell Sequencing Service designed for low-input samples and high-resolution expression profiling.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs’ Sequencing Analysis platform integrates mass spectrometry-based sequencing technologies with other high-throughput systems to offer a professional, comprehensive, and customizable solution across the following core areas:
Table 1. Comprehensive Sequencing Analysis Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Service Advantages
1. Comprehensive Sequencing Platforms
We operate multiple high-resolution mass spectrometry systems (such as Orbitrap and Q Exactive HF), Edman degradation instruments, and nanopore sequencing platforms. This diverse infrastructure supports both conventional and cutting-edge sequencing strategies, adaptable to various sample types and resolution needs.
2. De Novo Sequencing Capabilities
For proteins lacking database references, our de novo algorithms enable full-sequence reconstruction. This is essential for novel protein discovery, functional annotation, and antigen research.
3. Customized Services
Recognizing the variability in sample types, research goals, and downstream applications, MtoZ Biolabs offers highly customizable sequencing services. Whether your project involves full-length protein sequencing, antibody CDR region identification, or low-abundance de novo analysis, we tailor enzymatic digestion strategies, MS acquisition methods, and bioinformatics workflows to meet your specific needs.
4. High-Quality Data Delivery
All sequencing projects undergo cross-validation and standardized quality control processes to ensure reproducibility, sequence coverage, and high confidence—making the results reliable for further bioinformatics and functional analyses.
5. One-Time Charge
Our pricing is transparent and straightforward, with no hidden fees or unexpected costs.
Applications
1. Validation of recombinant protein expression and processing sites
2. Functional assessment and CDR affinity evaluation for monoclonal/polyclonal antibodies
3. Epitope mapping and antigen confirmation in vaccine development
4. Novel protein identification and function prediction
5. Humanization and structural optimization of therapeutic antibodies
6. Site-specific payload mapping and structural analysis of ADCs
Sample Submission Suggestions
We accept a wide range of sample types, including purified proteins, antibody solutions, protein mixtures, conjugated antibodies, cell lysates, and gel bands. Sample quantity, concentration, and storage conditions vary depending on the project. Please consult our technical team in advance to receive a detailed submission guideline tailored to your study.
Deliverables
1. Amino acid sequence results of proteins or peptides (FASTA format)
2. Raw mass spectrometry data (.raw/.mzML) and annotated spectra
3. Epitope, modification, or cleavage site annotations (if applicable)
4. De novo sequence assembly reports and confidence scoring (if applicable)
5. Comprehensive project report including methods, visual results, and references
From structural and functional protein research to antibody drug development, sequence data is the foundation for understanding molecular mechanisms. Powered by state-of-the-art instrumentation and a professional scientific team, MtoZ Biolabs provides standardized, customizable sequencing analysis services to accelerate your research goals.
If you have sequencing needs, feel free to contact our technical support team for a tailored consultation.
How to order?







