Subcellular Proteomics Service
The distribution and compartmentalization of proteins encoded by intracellular nucleic acids enable specific cellular functions. Therefore, analyzing the protein expression of their subcellular compartments is a practical and necessary functional assay for cellular proteomics.
The powerful combination of subcellular fractionation and mass spectrometry protein identification technologies has helped us develop methods that can characterize subcellular-level proteomics. Subcellular proteomics, built on decades of biochemical research, has already enabled subcellular fractionation. Advances in techniques such as density, size, and charge separation also allow subcellular structure separation to limit the level of contaminants. Coupled with mass spectrometry, high-level analysis at the subcellular level containing 500-4000 proteins can be achieved. Compared to the whole-cell proteome, which contains 12,000-40,000 proteins, subcellular proteomics reduces the complexity of exploring the proteome.
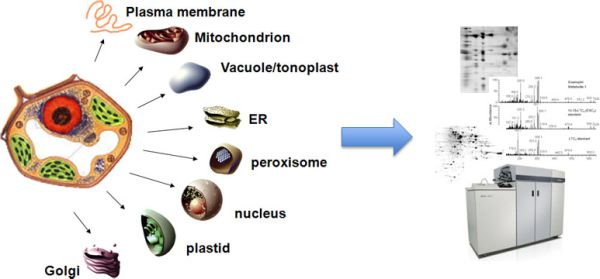
Figure 1. Subcellular Proteomics
Combining subcellular fractionation with proteomic analysis seems to be an effective approach to simplify the complex proteins extracted from cells or tissues and facilitate the detection of low-abundance proteins. However, realizing subcellular proteomic analysis involves each complex step in sample preparation, analysis, and verification, and only by ensuring the quality of each step can the potential of subcellular proteomic analysis be fully utilized.
MtoZ Biolabs uses Thermo Fisher's Orbitrap Fusion Lumos mass spectrometry platform combined with nanoLC chromatography to provide subcellular proteomic analysis services, including qualitative and quantitative analysis of membrane proteomes, mitochondrial proteomes, histones, chloroplast proteomes, and more.
Deliverables
In the technical report, MtoZ Biolabs will provide you with detailed technical information, including:
1. Experimental Procedures
2. Relevant Mass Spectrometry Parameters
3. Mass Spectrometry Images
4. Raw Data
5. Bioinformatics Analysis
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?