Top-Down Proteomics Service
Top-Down Proteomics is a technique for directly analyzing intact proteins without digestion, preserving their complete structural information, including post-translational modifications (PTMs), splice variants, and genetic polymorphisms. This approach enables the detailed characterization of proteoforms while maintaining their native state. Top-down proteomics begins with the extraction of proteins from biological samples through lysis, producing a complex mixture. The proteins are then separated using liquid chromatography (LC) and analyzed by mass spectrometry (MS). Intact proteins undergo ionization and are first analyzed for their molecular weight using MS1, followed by tandem mass spectrometry (MS2) to produce product ions for in-depth structural analysis. The raw data is further processed to identify proteoforms, evaluate sequence information, and determine post-translational modification sites.
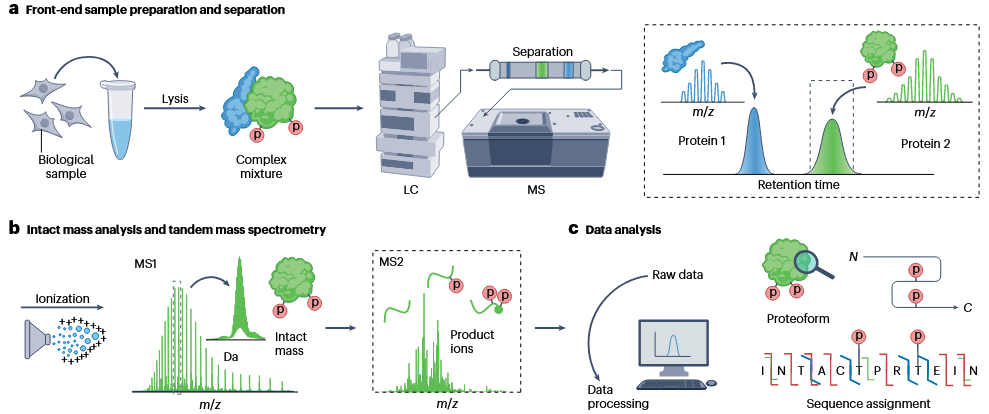
Roberts, DS. et al. Nat Rev Methods Primers. 2024.
Figure 1. The Workflow of Top-down Proteomics
Top-Down Proteomics specializes in intact protein analysis, enabling the comprehensive characterization of proteoforms, including their sequences, post-translational modifications, and structural variants. This approach is particularly effective in addressing protein heterogeneity and understanding biological systems at the proteoform level. In contrast, Bottom-Up Proteomics focuses on peptide-level analysis generated by protein digestion, making it particularly suitable for large-scale protein identification and achieving extensive proteome coverage.
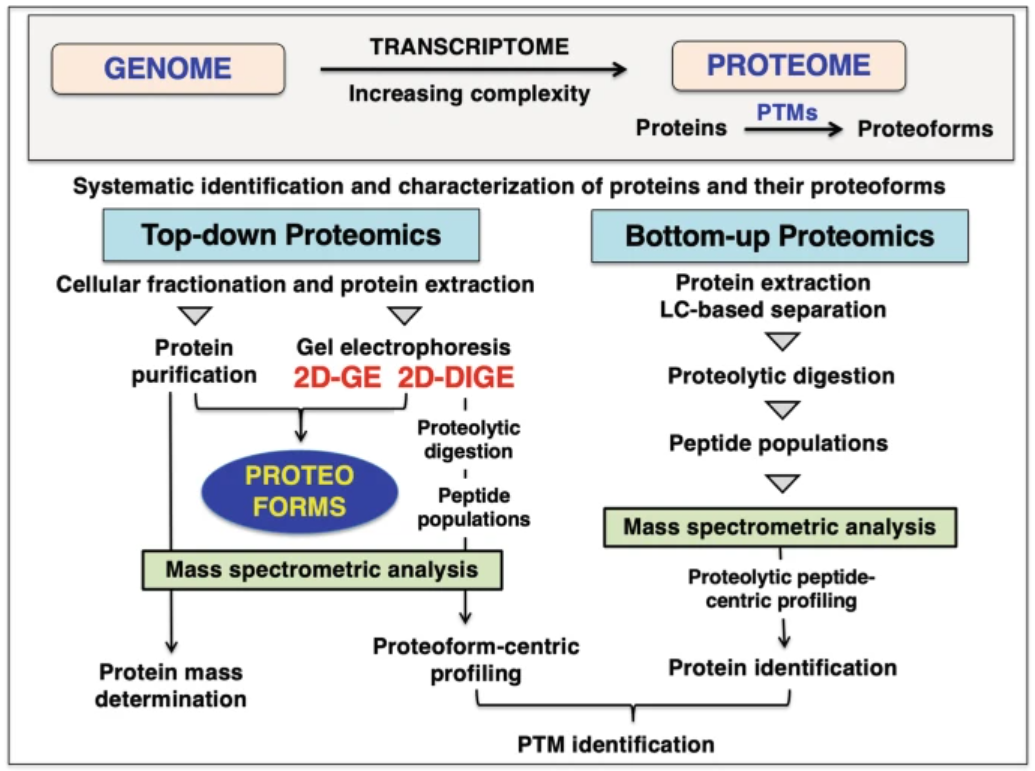
Ohlendieck, K. Methods Mol Biol. 2023.
Figure 2. The Comparision of Bottom-up and Top-down Proteomics
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Service Advantages
1. Cutting-edge Instruments and Optimized Experimental Workflows
MtoZ Biolabs' top-down proteomics service utilizes state-of-the-art mass spectrometry instruments and optimized sample preparation workflows, including intact protein separation and tandem mass spectrometry techniques. This ensures high sensitivity and high-resolution protein spectrum analysis, offering reliable technical support for scientific research.
2. Advancing Precision Medicine and Disease Mechanism Research
Top-down proteomics service enables the identification and characterization of critical proteoforms, providing robust support for disease mechanism research and the discovery of potential biomarkers. MtoZ Biolabs leverages this technology to drive the development of precision medicine, helping clients decode the complex relationships between genotypes and phenotypes.
3. Broad Applications Across Multiple Fields
Top-down proteomics service is widely applicable in biomedical, pharmaceutical, and clinical research, encompassing the human proteoform project, drug development, and the identification of therapeutic targets. MtoZ Biolabs is committed to extending this technology to more areas, providing innovative solutions and helping clients achieve their research goals.
Applications
1. Neurodegenerative Disease Research
Top-down proteomics service enables comprehensive analysis of complex proteoforms in brain tissue samples through MS1 and MS2 mass spectrometry, aiding in the identification of protein modifications and functional changes associated with neurodegenerative diseases.
2. Cancer Research
In colorectal cancer research, top-down proteomics service can analyze KRAS4b protein variants in tumor patients, distinguishing between the wild-type (WT) and mutant (G13D) forms, providing critical insights for precise cancer subtyping and target discovery.
3. Cardiovascular Disease Research
Top-down proteomics service uses high-resolution mass spectrometry to analyze the phosphorylation states of cardiac troponin I (cTnI), revealing its regulatory changes in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) and offering key data for understanding disease mechanisms.
4. Hemoglobinopathy Diagnosis
Top-down proteomics service allows direct analysis of hemoglobin variants in clinical blood samples, accurately differentiating between subtypes such as Hb A α and Hb A β, supporting the diagnosis and study of hemoglobin-related diseases.
5. Characterization of Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
Top-down proteomics service characterizes drug-to-antibody ratios (DAR) in ADCs through HIC-MS and identify conjugation sites using enzymatic digestion combined with RPLC-MS, providing precise characterization for ADC development and quality control.
6. Drug Binding Site Analysis
Top-down proteomics service leverages CID, ETD, and ECD mass spectrometry techniques to localize drug binding sites and analyze sequence information, facilitating the development and optimization of complex protein-based therapeutics in biopharmaceutical research.
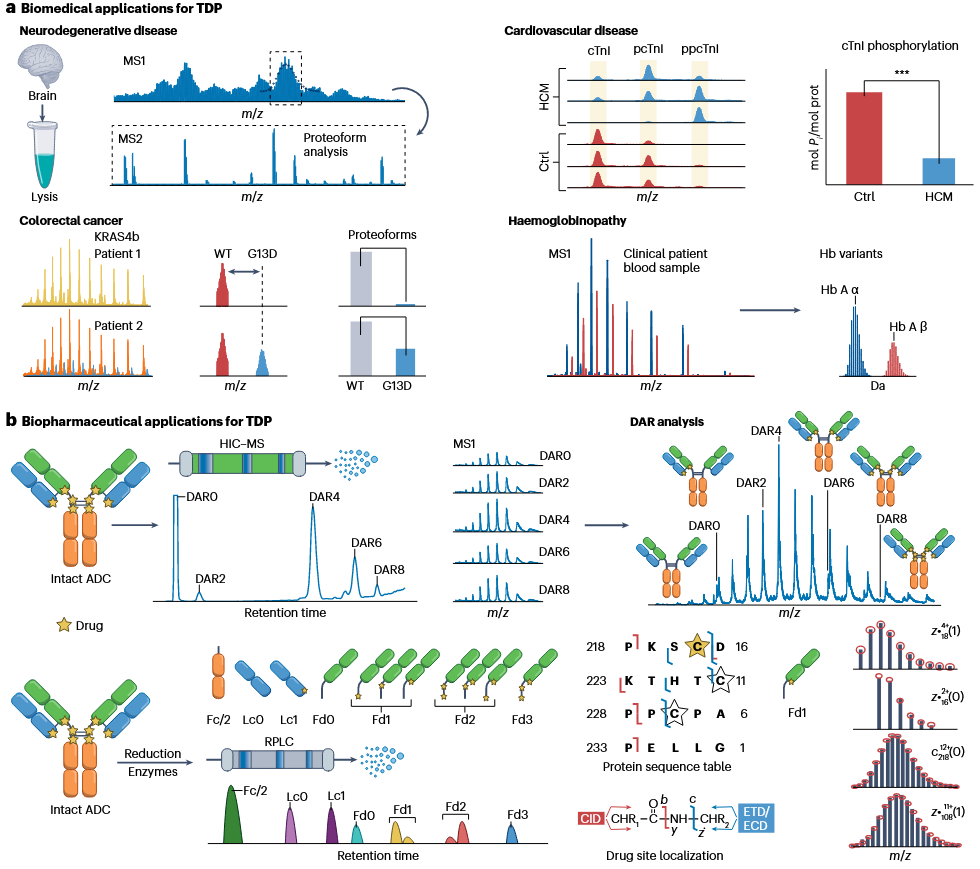
Roberts, DS. et al. Nat Rev Methods Primers. 2024.
Figure 3. The Applications of Top-down Proteomics Service
FAQ
Q1: What volatile buffers can be used to obtain intact protein analytes in top-down proteomics?
Answer: In top-down proteomics, volatile buffers such as ammonium acetate and ammonium bicarbonate are commonly used to obtain intact protein analytes. These buffers are highly suitable for mass spectrometry applications due to their volatility, which allows for easy removal during sample preparation without leaving interfering residues. Ammonium acetate is effective in maintaining protein stability in a neutral pH environment, while ammonium bicarbonate provides a slightly basic pH that helps preserve protein structures. Additionally, small amounts of volatile acids such as formic acid or acetic acid can be added to adjust pH as needed. These buffers stabilize proteins and ensure compatibility with downstream separation techniques, such as liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. Top-down proteomics service offers tailored extraction approach for intact proteins while preserving their structural and functional integrity for high-resolution studies.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Relevant Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Parameters
4. The Detailed Information of Proteomics
5. Mass Spectrometry Image
6. Raw Data
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Top-Down Protein Sequencing Service
How to order?







