Unlocking Proteomics With Dia Technology: The Future of High-Resolution Protein Analysis
In the age of precision medicine and big data analytics, the need for comprehensive and high-resolution analysis of clinical samples has become increasingly important. Traditional methods, such as Data Dependent Acquisition (DDA), have played a crucial role in proteomics research but are often limited by their inability to provide comprehensive and consistent data across complex samples. The next-generation technology, Data Independent Acquisition (DIA), is revolutionizing the field, offering deeper insights into proteomics and enabling a more robust and reproducible analysis process.
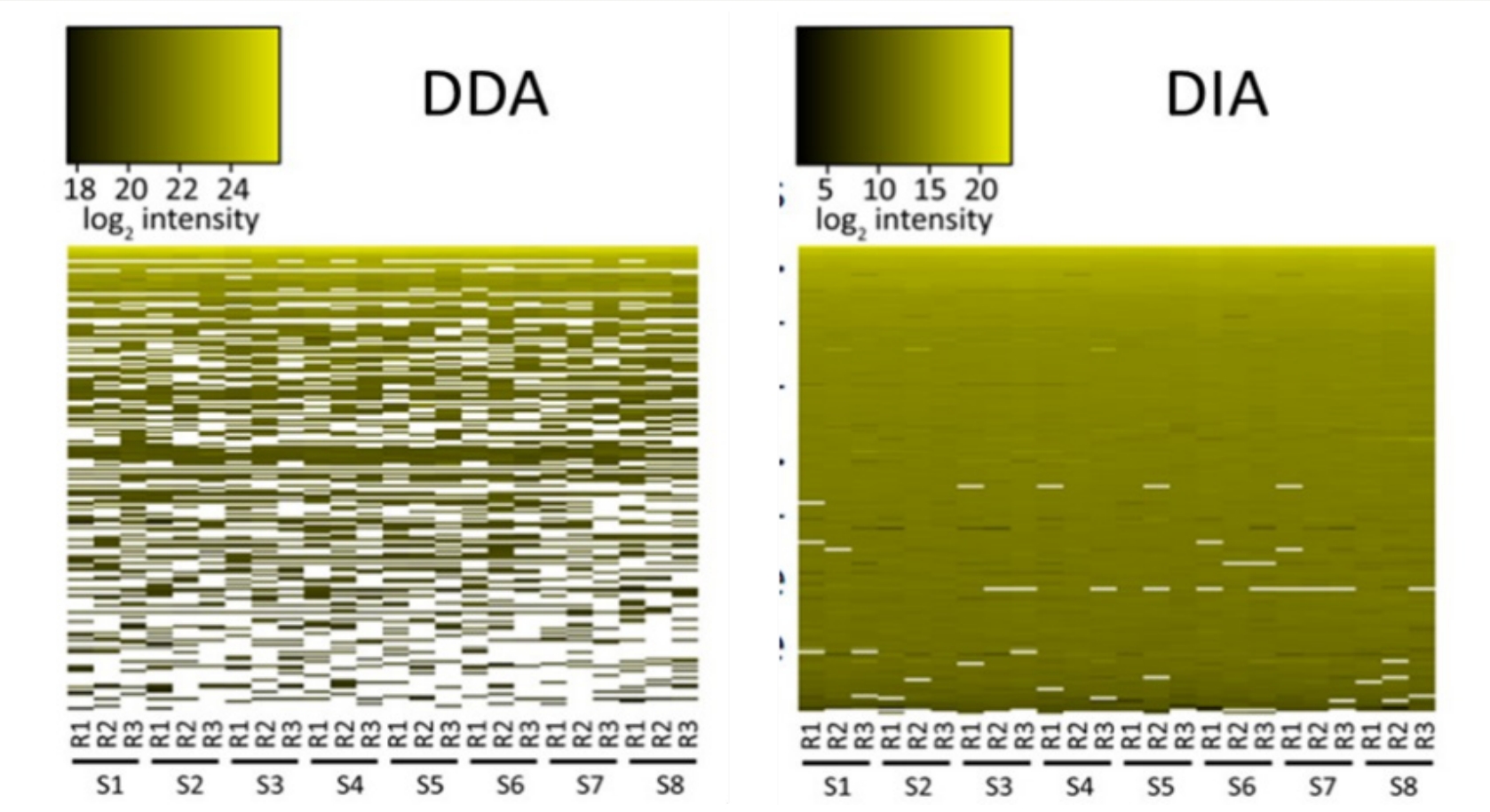
Figure1. DIA and DDA Scanning Modes (Roland Bruderer, Oliver M. Bernhardt, et al)
The Evolution of DIA Technology
DIA emerged as a solution to the limitations of DDA. While DDA relies on the top N precursor ions to acquire fragmentation data, often resulting in loss of important data from less abundant proteins, DIA scans all ions across a predefined mass-to-charge range, providing consistent and comprehensive coverage of the entire proteome. This development allows for more accurate and reproducible analysis of complex biological samples, making DIA a critical tool for modern proteomics research.
Principles of DIA Technology
DIA is a high-throughput mass spectrometry technique that differs significantly from DDA in its data acquisition strategy. Instead of targeting individual ions based on their abundance, DIA captures all ions within a specified range. The mass spectrometer continuously cycles through this range, fragmenting all precursors in fixed windows. This approach ensures that no peptide is overlooked, providing highly reproducible and quantitative data across a wide range of samples.
One of the key advantages of DIA is its ability to perform label-free quantification, which eliminates the need for isotopic labeling and reduces sample preparation time. Additionally, DIA's consistent coverage allows for the detection of low-abundance proteins that might otherwise be missed using traditional DDA methods.
Technical Advantages of DIA
The DIA technology stands out for its superior performance in several key areas:
1. Unbiased Data Acquisition: Unlike DDA, DIA captures data without bias towards the most abundant peptides, ensuring a more comprehensive analysis of complex proteomes. Compared with label free proteomics, DIA data coverage is increased by nearly 40%.
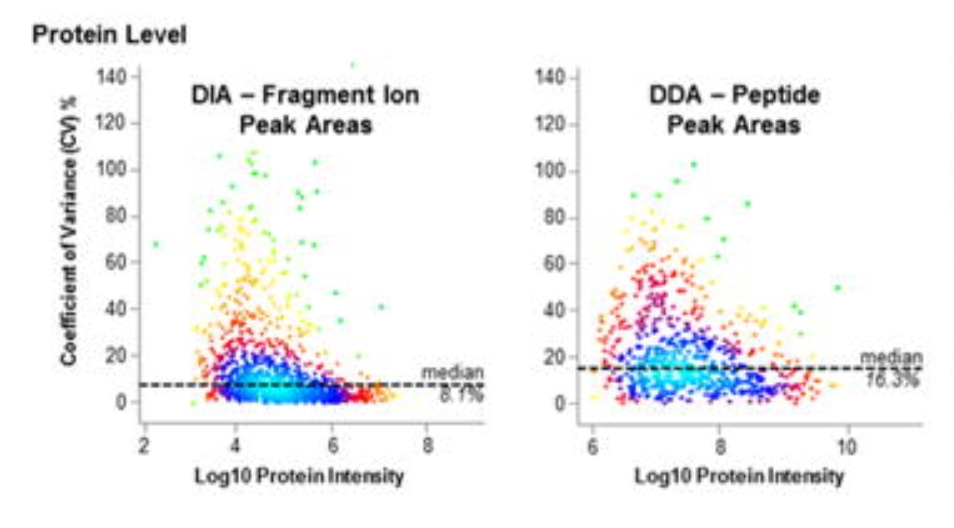
Figure2. DDA and DIA Technology Protein Low Abundance Coverage Map
(Reference source: Jan Muntel, Yue Xuan, et al)
2. High Quantification Accuracy: DIA has been shown to increase quantification accuracy by up to 40% compared to DDA. The quantitative capability is close to the gold standard SRM/MRM targeted technology, which is particularly useful for researchers who need reliable data for protein quantification studies.
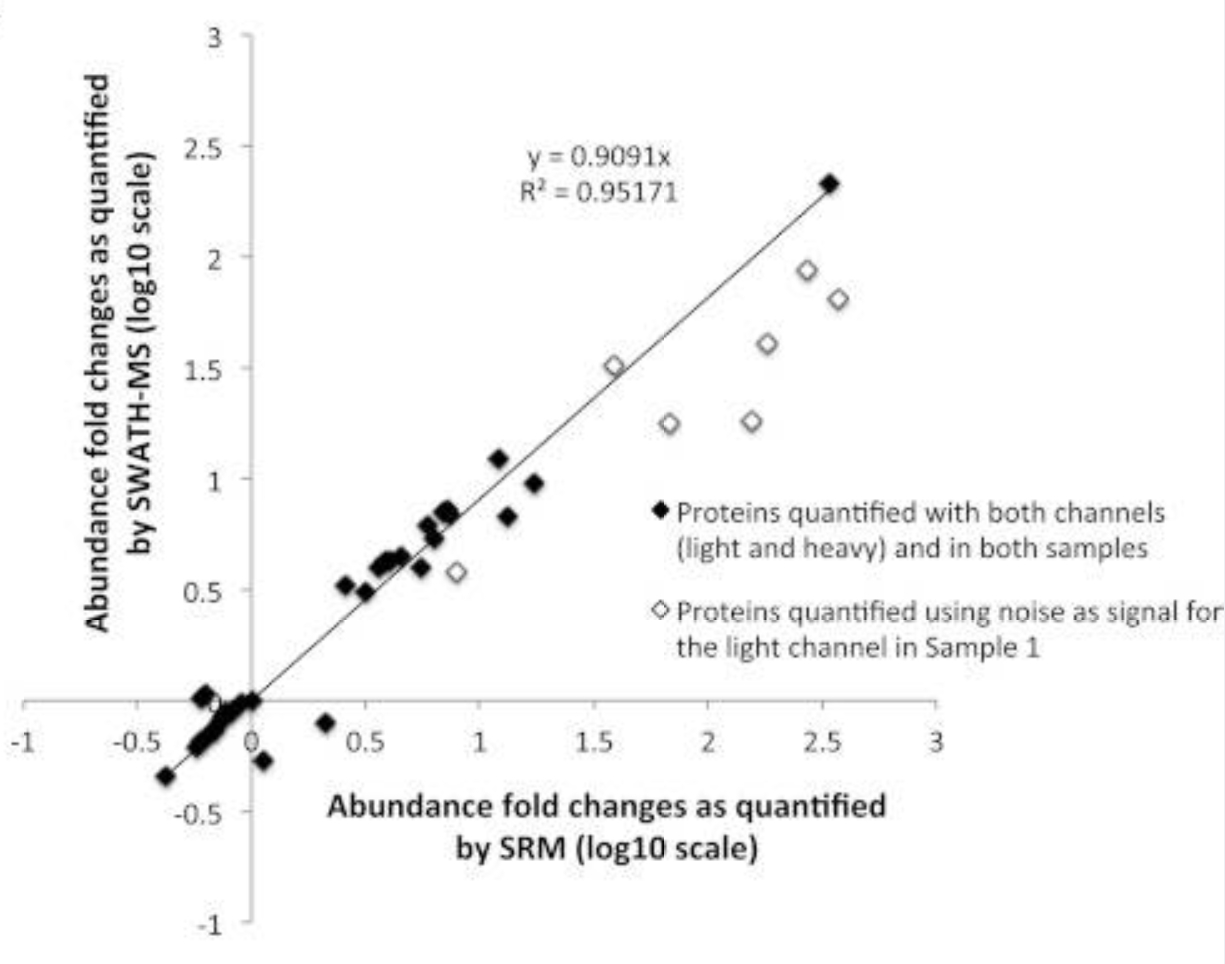
Figure3. Correlation Diagram Between DIA Quantitative Technology and
Targeted SRM Quantitative Technology
(Reference source: Ludovic C. Gillet, Pedro Navarro, et al)
3. Improved Reproducibility: DIA's automated scanning protocol reduces variability, ensuring that data can be consistently reproduced across different experiments and laboratories.
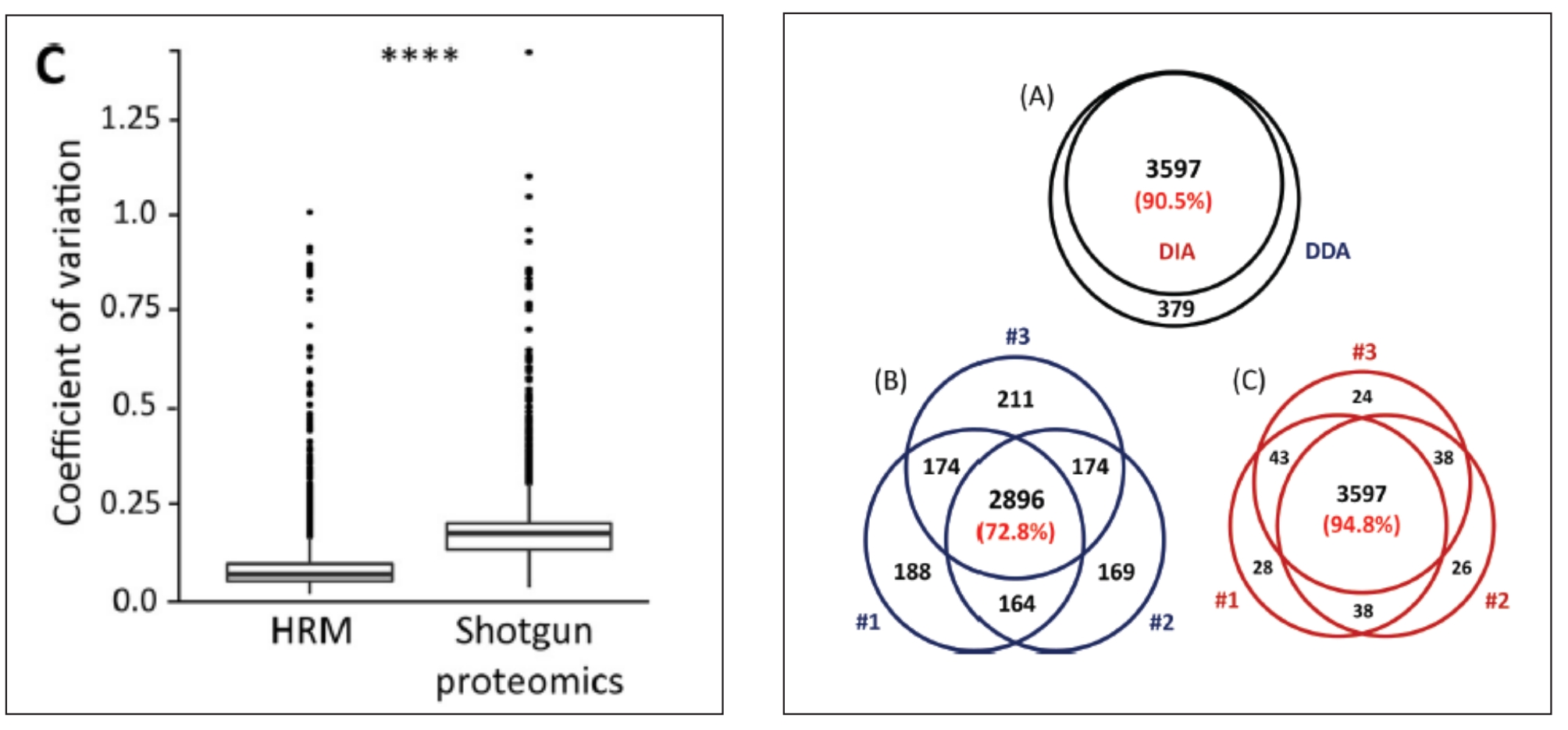
Figure4. Quantitative CV Values and Identification Repeatability Graphs of DDA and DIA Techniques
(Reference Source: Roland Bruderer, Oliver M.Berhardt, et al)
4. Increased Protein Identification: With DIA, the number of identifiable proteins increases significantly, offering a deeper insight into the proteomic landscape. This is especially beneficial for biomarker discovery and disease research.
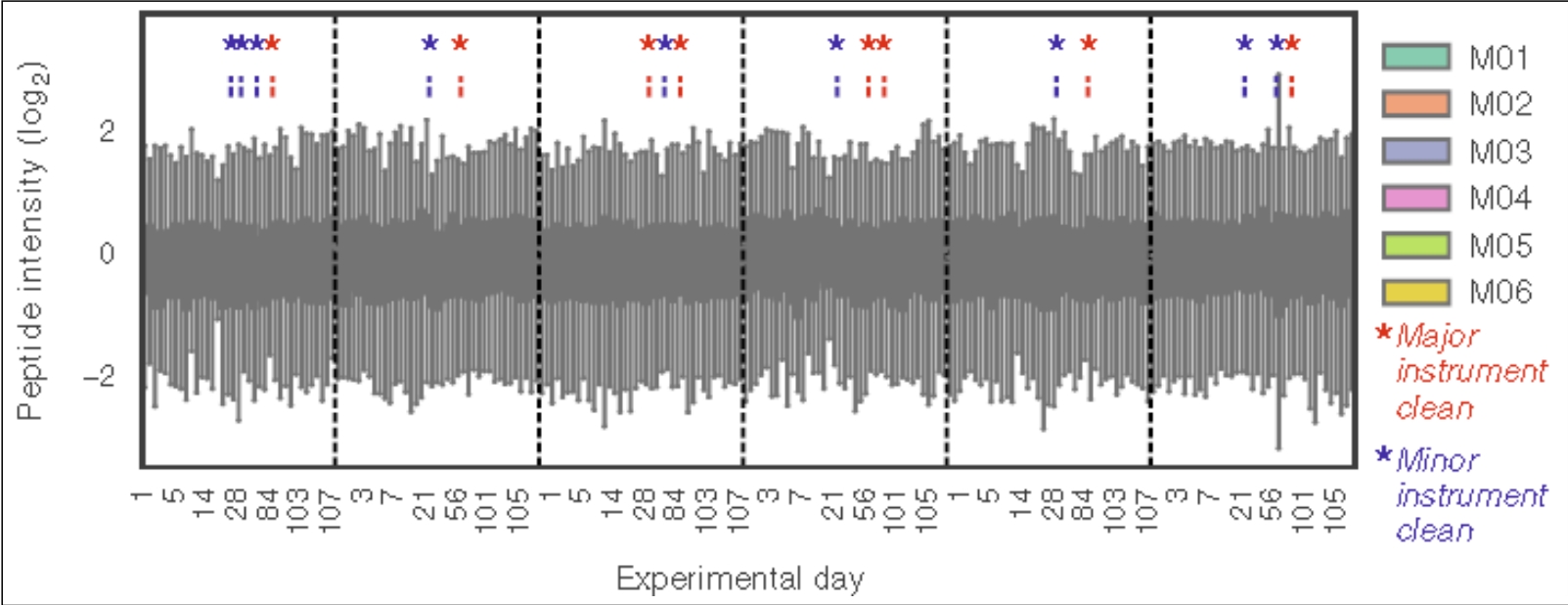
Figure5. Normalized Intensity Distribution Diagram of Peptide Detected by DIA
(Reference source: Ludovic C. Gillet, Pedro Navarro,et al)
DIA Proteomics Workflow
The DIA proteomics workflow begins with the preparation of the sample, followed by peptide digestion and separation using liquid chromatography (LC). The peptides are then introduced into the mass spectrometer, where DIA acquisition takes place. A crucial step in the DIA workflow is the use of a spectral library, which serves as a reference to match the fragmented ions against known peptide sequences. The data is then processed using advanced bioinformatics tools to quantify and analyze the proteins present in the sample.
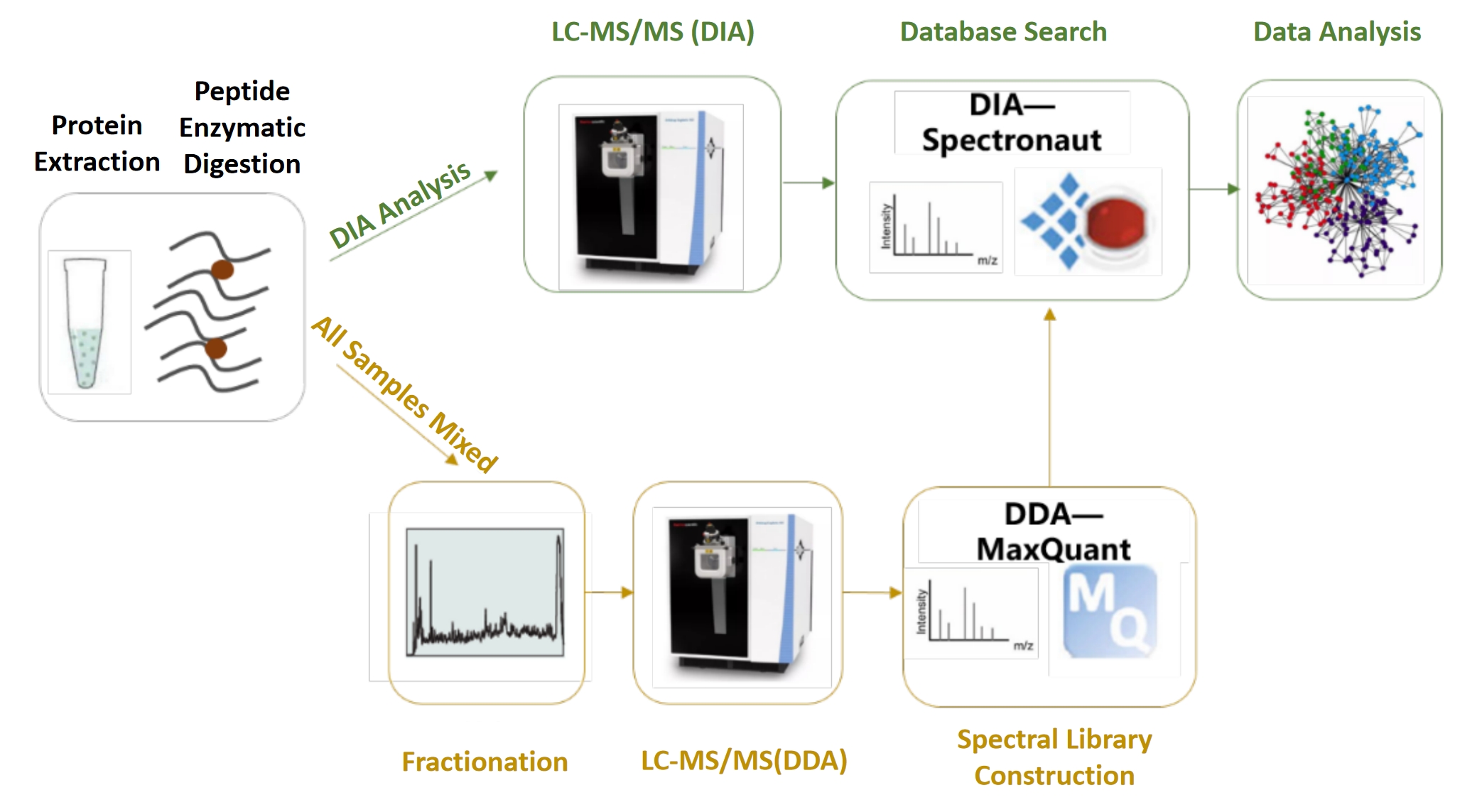
Applications of DIA Proteomics
DIA has wide-ranging applications across various fields:
1. Biomarker Discovery: DIA’s ability to analyze complex samples with high precision makes it a valuable tool for identifying novel biomarkers for diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
2. Comparative Protein Profiling: DIA is particularly suited for comparative studies, where researchers need to quantify protein expression levels across different conditions or time points.
3. Agricultural Research: DIA can be used to compare protein profiles in different crop varieties, helping to identify proteins that contribute to stress resistance, growth, and productivity.
Why Choose DIA at MtoZ Biolabs?
At MtoZ Biolabs, we utilize the latest advancements in DIA technology to offer cutting-edge proteomics services to our clients. Our DIA platform provides comprehensive and accurate data, enabling researchers to achieve deeper insights into their samples. Whether you are exploring new biomarkers, studying complex diseases, or conducting agricultural research, our DIA service offers unparalleled reproducibility, sensitivity, and quantification accuracy.
By leveraging our experience in proteomics and mass spectrometry, we deliver high-quality results that can help you accelerate your research and achieve your scientific goals. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing tailored solutions to meet the unique needs of your projects.
How to order?







