cIEF Protein Isoelectric Points Analysis Service
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
IEF Protein Isoelectric Points Analysis Service
Submit Inquiry
How to order?


Email:
info@MtoZ-Biolabs.comEmail:
info@MtoZ-Biolabs.comThe isoelectric point (pI) of a protein is closely related to its amino acid sequence and three-dimensional structure. The pI of a specific protein is fixed, thus allowing the study of structural and functional differences among different proteins by comparing their pIs. Accurate determination of the pI is an important aspect of characterizing the charge heterogeneity of bioproducts.
Based on the principle of capillary isoelectric focusing (cIEF) is the most commonly used method for protein pI analysis in biological products. The basic principle of this micro-separation technology involves applying a direct current voltage at both ends of a capillary, where amphoteric electrolytes inside the capillary generate a pH gradient within a certain range. Proteins move towards the anode or cathode depending on their charge until reaching a certain pH (i.e., pI) where the net charge becomes zero. Consequently, the proteins are focused into narrow segments, achieving separation and obtaining information on their pIs.
Protein pI detection based on cIEF offers advantages such as short analysis time, high resolution, good repeatability, high accuracy, and minimal sample requirement. It has become a key technology in the development and quality control of various bioproducts including amino acids, peptides, recombinant proteins, antibodies, and vaccines.
MtoZ Biolabs has established a protein pI detection platform tailored for different categories of bioproducts. This platform enables precise determination of the pIs of proteins, antibodies, vaccines, peptides, recombinant collagen, and other bioproducts, and provides comprehensive services including method establishment, validation, and subsequent sample testing.
BECKMAN COULTER PA800+ Capillary Electrophoresis Instrument
cIEF offers advantages such as short analysis time, high resolution, good repeatability, high accuracy, and minimal sample requirement. This method has become one of the key technologies in the development and quality control of various bioproducts including amino acids, peptides, recombinant proteins, antibodies, and vaccines.
During the experiment, samples are mixed with ampholytes and 5 standard pI markers. Capillary electrophoresis is used for detection, focusing the samples in the capillary. Based on the retention times of the 5 internal standards, the pI of the test sample is calculated.
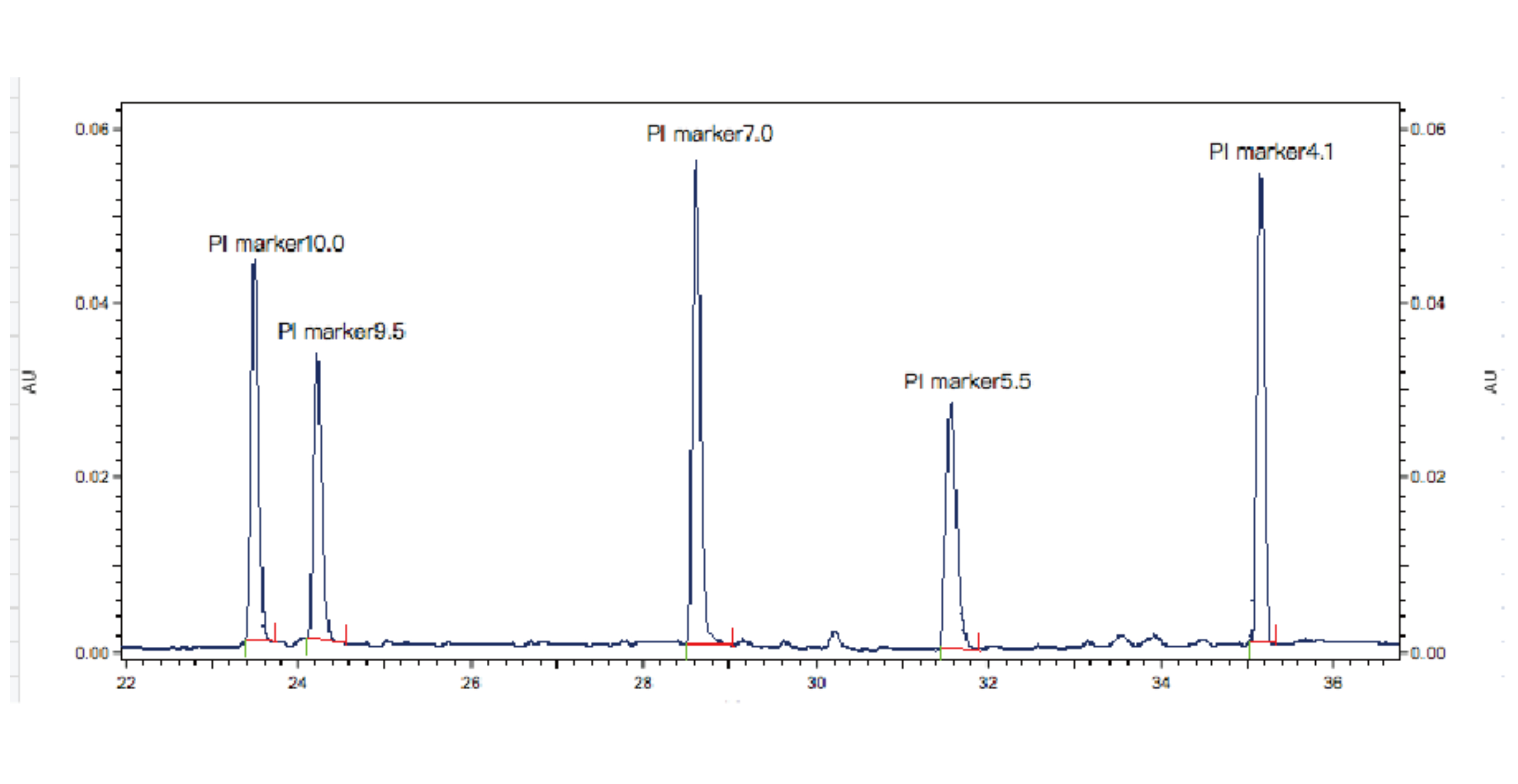
Figure 1. Results of PI Marker
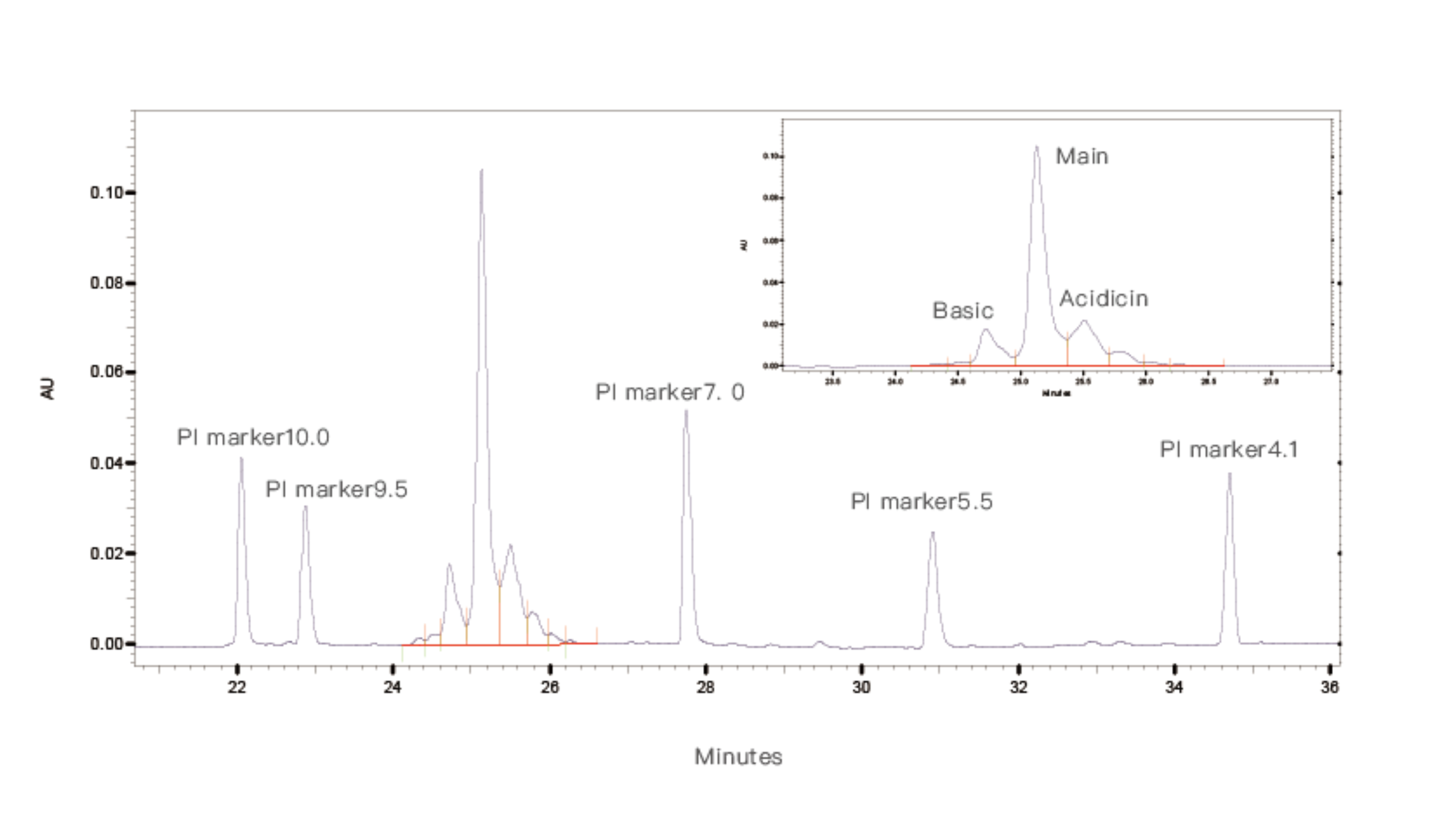
Figure 2. Detection Results of Monoclonal Antibody Samples
Proteins are composed of amino acids, and the pIs of most amino acids are below the pH of the human body (pH=7.4). Hence, the pIs of most proteins tend to be acidic, such as the pI of pepsin from goat, which is approximately 3.
There are proteins with alkaline pI. When proteins contain alkaline amino acids such as histidine, arginine, and lysine in significant amounts, their pIs tend to be alkaline, such as the pI of protamine, which is approximately 12.
PI detection based on cIEF requires samples to have a UV absorbance at 280 nm; for samples without UV absorbance at 280 nm (e.g., collagen), pI detection based on IEF is performed.
IEF Protein Isoelectric Points Analysis Service
How to order?


Submit Inquiry
