Molecular Weight Determination Service
Molecular weight is a basic physicochemical parameter of organic compounds, generally referring to the relative molecular mass, which is the sum of the relative atomic masses of each atom in the compound's chemical formula. The correctness of the molecular weight often represents whether the structure of the measured organic compound or biomacromolecule is accurate. Molecular weight is a primary parameter in the identification of peptides, proteins, etc., and is also one of the important data for the approval of genetic engineering products.
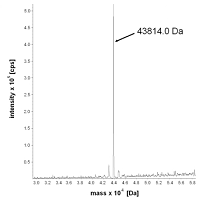
Figure 1. Molecular Weight Determination
There are many methods for determining the molecular weight of proteins, currently including viscosity method, gel permeation chromatography (GPC), SDS-PAGE, light scattering, mass spectrometry (MS), and among others. MS mainly includes electrospray ionization (ESI)-MS and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI)-MS. Compared to other methods, MS for protein molecular weight determination consumes less sample and has higher sensitivity, resolution, and accuracy, which is advantageous for analyzing complex mixture samples. In addition, MS can also determine the molecular weight of protein complexes and protein-small molecule complexes.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Protein Molecular Weight Determination Service
How to order?







