Membrane proteins, such as receptors and ion channels, serve as crucial regulators of cellular function. Membrane proteins constitute two-thirds of known druggable targets, highlighting their significance in the biopharmaceutical industry.
Among them, G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) represent the largest and most widely studied class of membrane receptors. They represent the most significant targets for drug development, comprising over 50% of all human drug targets. These proteins serve as crucial therapeutic targets for a wide array of diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular ailments, metabolic disorders, central nervous system conditions, and inflammatory diseases.
Ion channels represent another important group of membrane protein drug targets, constituting 10% of currently marketed drugs. Nevertheless, producing a sufficient quantity of pure, correctly folded membrane receptors for drug development remains a major challenge.
Nan, L. et al. Lab on a chip. 2014.
Figure1. Membrane Protein Identification
Analysis Workflow
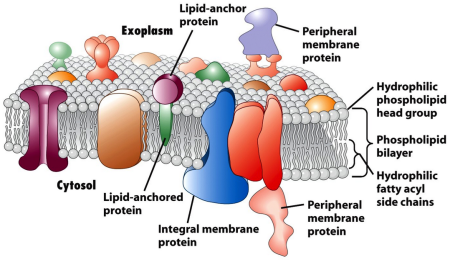
1. Purification of Membrane Proteins From Cytosol, Periplasm, or Cell Culture Supernatant
Proteins are purified from cytosol, (bacterial) periplasm, or cell culture supernatant depending on the expression host or expression vector used.
2. Buffer and Detergent Screening for Solubilization and Purification Enhancement
For soluble proteins and membrane proteins, conditions for optimal stability of buffer are determined using differential scanning fluorimetry (DSF). If applicable, established activity assays can be used to correlate stability with activity state. For membrane or membrane-associated proteins, detergent is required during protein extraction from bacterial or eukaryotic membranes. The use of detergents needs to be optimized for protein stability during extraction and purification steps. If the protein is expressed as inclusion bodies, after redissolution and refolding, optimization of optimal detergent and buffer conditions can be performed.
3. Affinity Purification Using His, Rho1D4, GST, or Strep Tags
Our high-quality affinity purification matrices can purify proteins fused with tags such as His, GST, or Strep tags. For membrane proteins, we recommend using the Rho1D4 system, although other tags can be used as per requirement. Our purification conditions are optimized and can be scaled up to milligram quantities depending on the target protein. The service can include optimization of buffers and detergents to provide proteins with optimal stability and activity. MtoZ Biolabs will provide detailed documentation for all steps, including data such as SDS-PAGE and Western Blot.
Further purification steps can be employed to prepare homogeneous protein fractions for crystallization. For proteins suitable for applications such as protein crystallization experiments or functional binding assays, a second or third purification step using techniques such as ion-exchange chromatography (IEC) or gel filtration can be utilized.








