Molecular Weight Analysis Service
- Protein and peptide mass fingerprinting
- Drug development and pharmacokinetics studies
- Quality control in pharmaceuticals
- Clinical diagnostics
Molecular weight analysis is a foundational tool across numerous fields, including proteomics, metabolomics, and biomedical, where precise molecular weight determination is essential for characterizing compounds and understanding their structural and functional attributes. Accurate molecular weight information aids in elucidating molecular structure, confirming compound identity, assessing purity, and monitoring structural modifications, which are all vital for research, product development, and quality control. As the complexity of biological molecules increases, the demand for reliable and high-throughput molecular weight determination methods has surged, necessitating advanced analytical techniques. At MtoZ Biolabs, we offer Molecular Weight Analysis Service, suitable for measuring the molecular weights of a wide range of biological samples, including antibodies, vaccines, protein therapeutics, peptides, nucleic acids, metabolites, and more.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (MS) Services Provider, provides advanced proteomics, metabolomics, and biopharmaceutical analysis services to researchers in biochemistry, biotechnology, and biopharmaceutical fields. Our ultimate aim is to provide more rapid, high-throughput, and cost-effective analysis, with exceptional data quality and minimal sample consumption. MtoZ Biolabs offers a comprehensive suite of molecular weight analysis methods tailored to meet diverse research and industry needs. Each technique provides unique insights, allowing for precise analysis across a wide range of samples.
1. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
SDS-PAGE is ideal for analyzing proteins and peptides. It is widely used in protein research to determine protein size, verify purification, and analyze the composition of protein complexes. SDS-PAGE is based on the principle of separating proteins by size. Proteins are treated with Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS), which binds to the proteins, denatures them, and imparts a uniform negative charge, eliminating their intrinsic charges. This allows proteins to migrate through a polyacrylamide gel solely based on their size under an applied electric field. Smaller proteins migrate faster, while larger proteins experience more resistance, creating a size-based separation pattern. By comparing the migration distances of sample proteins to those of molecular weight standards, the molecular weight of the proteins can be accurately estimated.
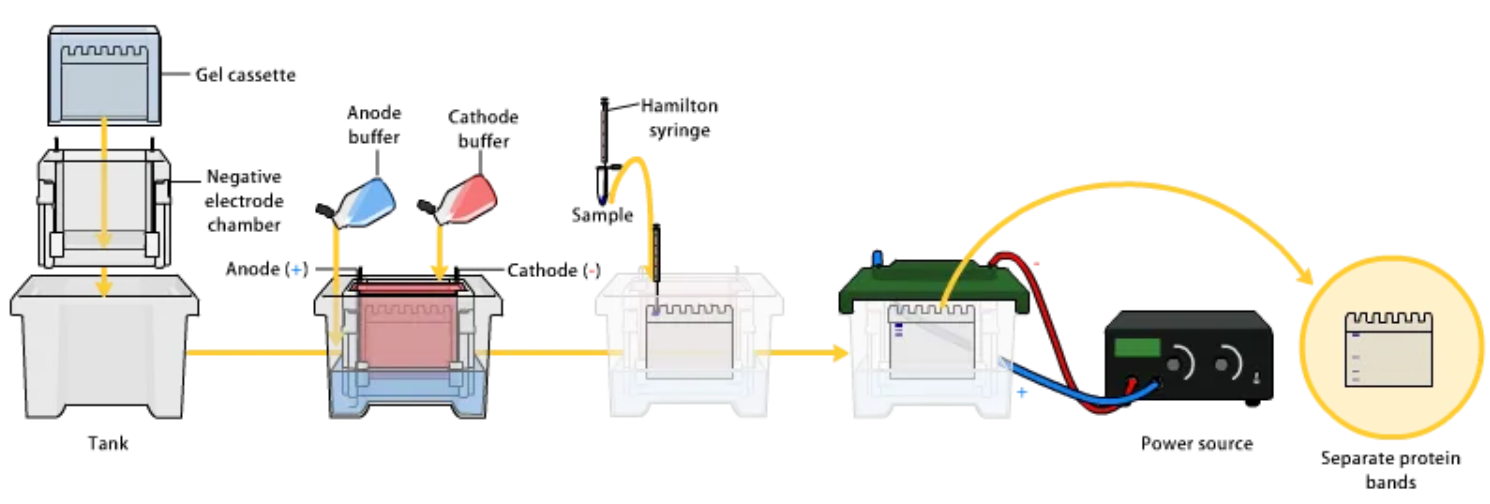
Figure 1. Molecular Weight Analysis Workflow Based on SDS-PAGE
2. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
SEC is a chromatographic technique used to separate molecules based on their size. In SEC, a sample is passed through a column packed with porous beads. Smaller molecules enter the pores of the beads and take longer to pass through the column, while larger molecules are excluded from the pores and elute more quickly. The result is a separation of the sample into different fractions based on molecular size. By comparing the elution times of sample molecules to those of molecular weight standards, the molecular weight of the sample can be estimated. SEC is particularly suitable for analyzing macromolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, and polymers, as well as protein complexes. It is commonly used for determining the molecular weight distribution and size heterogeneity of large biomolecules or synthetic polymers.
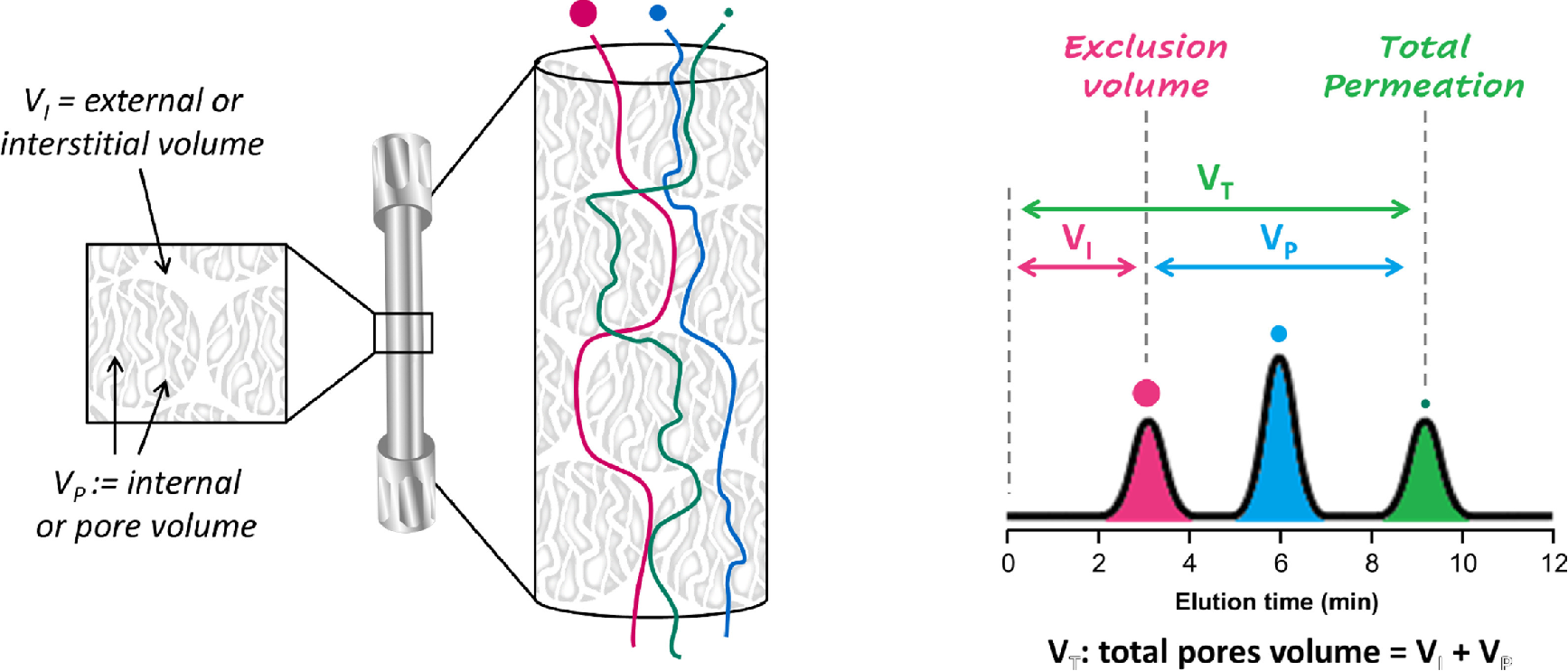
Figure 2. Schematic Diagram of a SEC Column and an Hypothetical Chromatogram
3. Viscosity Method
Viscosity Method is based on the measurement of a substance's intrinsic viscosity, which is related to its molecular weight. In this method, a solution of the analyte is prepared, and its flow behavior is measured using a viscometer. The viscosity of the solution increases with the size of the molecules; larger molecules experience more resistance to flow, resulting in higher viscosity. By correlating the viscosity with the molecular weight, an estimate of the molecular weight of the substance can be obtained. The viscosity method is particularly suitable for analyzing polymers and macromolecules, where the molecular weight is directly related to the viscosity of the solution. It is commonly used for characterizing large synthetic polymers and biopolymers, providing valuable information about molecular size and weight distribution in solution.
4. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-MS)
In MALDI-MS, the sample is mixed with a matrix material and applied to a solid surface. A laser is then used to ionize the sample, causing the matrix and the sample molecules to desorb and ionize into the gas phase. The ions are accelerated into the mass spectrometer, where they are detected based on their mass-to-charge ratio. The resulting data provides information on the molecular weight of the sample. This method is especially useful for characterizing the molecular weights of intact proteins and large polymers with high sensitivity and resolution.
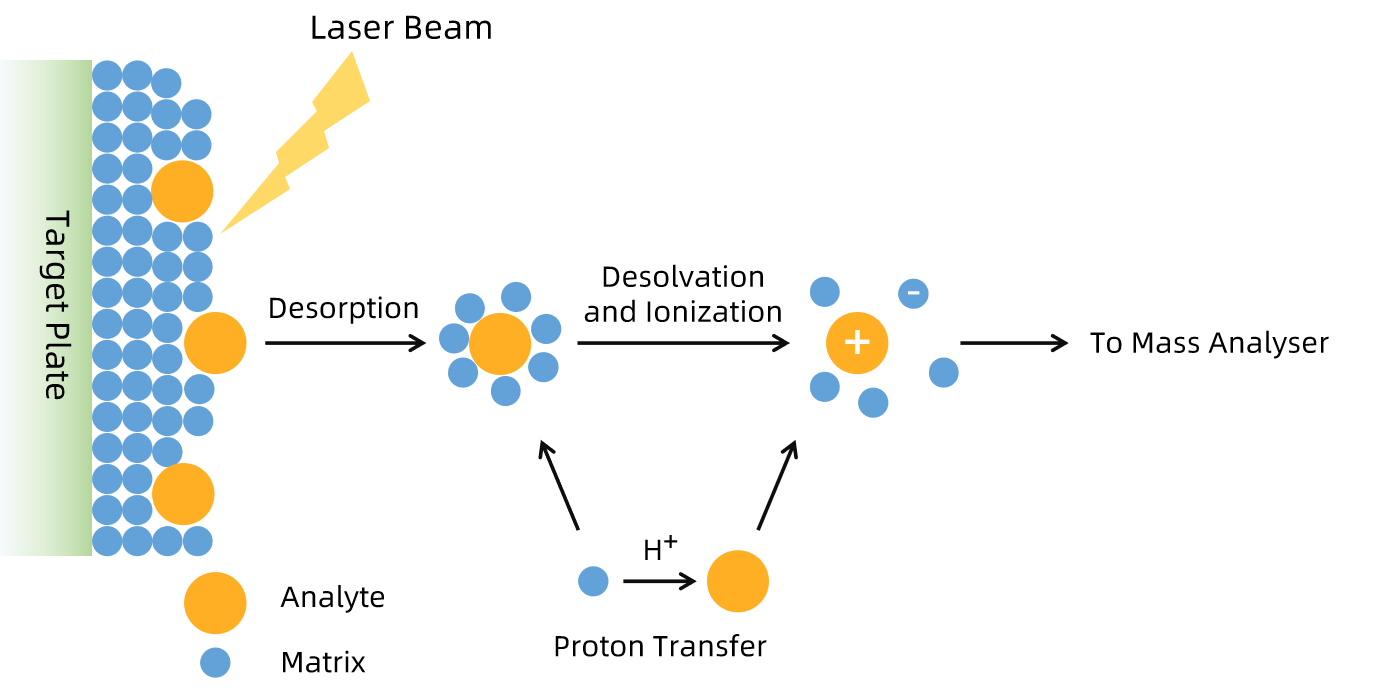
Figure 3. Ionization of Analytes by MALDI
5. Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (ESI-MS)
In ESI-MS, the sample is dissolved in a liquid solvent and passed through a charged needle, where it is subjected to a high voltage. This causes the sample to form charged droplets, which rapidly evaporate, leaving ions that enter the mass spectrometer. The ions are then separated based on their mass-to-charge ratio and detected, providing detailed molecular weight information. ESI-MS is particularly suited for analyzing biomolecules such as proteins, peptides, nucleic acids, and small molecules, especially those in solution. It is highly effective for studying complex mixtures, offering high sensitivity and the ability to analyze a wide range of molecular weights. ESI-MS is also ideal for analyzing protein complexes and non-covalent interactions.
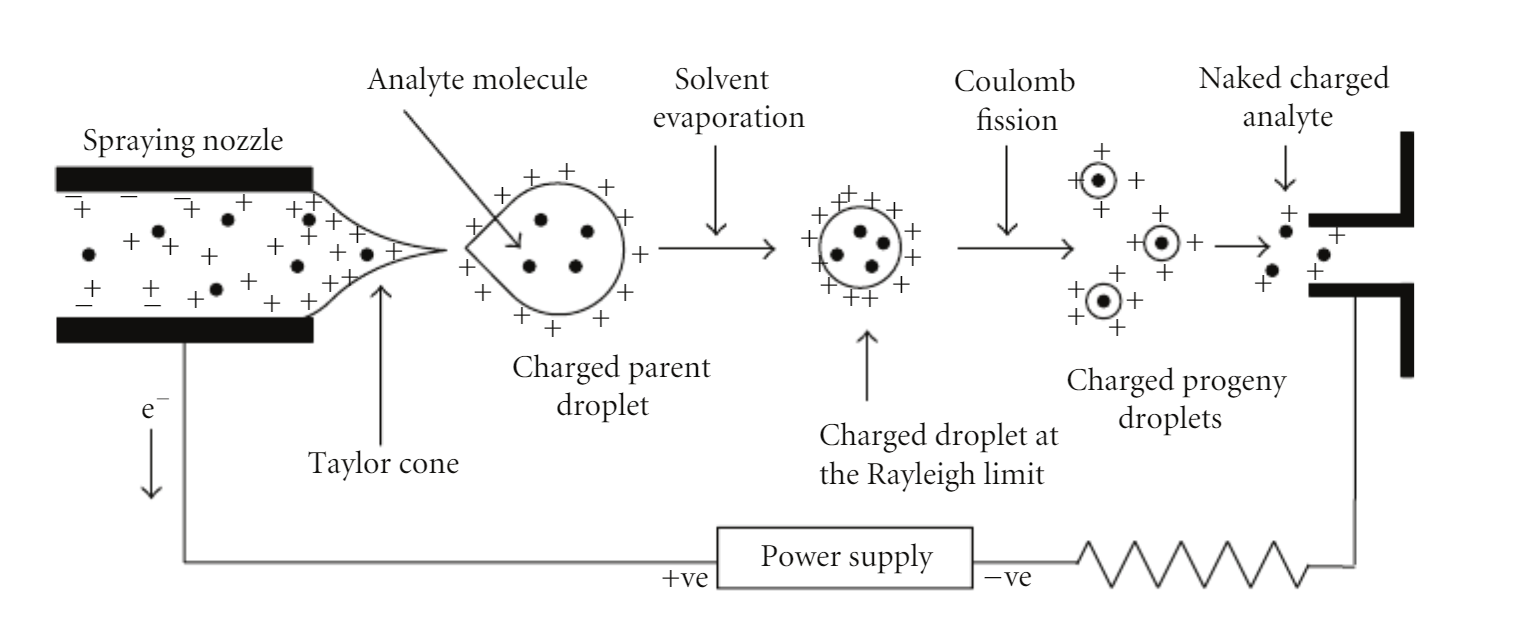
Banerjee, S. et al. Int J Anal Chem. 2012.
Figure 4. Schematic Representation of the Electrospray Ionization process
6. Liquid Chromatography with Mass Spectrometry Detection (LC-MS)
LC-MS combines the separation power of liquid chromatography with the sensitivity of mass spectrometry. In LC-MS, a sample is first separated using liquid chromatography, where it passes through a column that separates the compounds based on their interactions with the stationary phase. The separated components are then introduced into the mass spectrometer, where they are ionized and detected based on their mass-to-charge ratio. This technique provides both qualitative and quantitative analysis of complex mixtures and molecular weight determination. LC-MS is widely used in proteomics, metabolomics, and biomedical research.
Why Choose MtoZ Biolabs?
1. Advance Analysis Platform
MtoZ Biolabs established an advanced Molecular Weight Analysis Service platform, guaranteeing reliable, fast, and highly accurate analysis service.
2. One-Time-Charge
Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
3. High-Data-Quality
Deep data coverage with strict data quality control. AI-powered bioinformatics platform integrates all molecular weight analysis data providing clients with a comprehensive data report.
4. Rapid Turnaround Times
We understand the urgency of research projects, providing timely analysis without compromising quality, allowing you to move forward with your work quickly.
5. Customized Solutions
We recognize that each research project is unique. Our customized analytical solutions ensure that we address your specific requirements and challenges effectively.
Applications
At MtoZ Biolabs, we are committed to providing high-quality, reliable, and personalized analysis services. If you are interested in our Molecular Weight Analysis Service, please feel free to contact us.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Ultracentrifugation Molecular Weight Determination Service
How to order?







