Peptide Mapping Service
Peptide mapping service, through protein identification and characterization, can verify the integrity of a protein's amino acid sequence, detect post-translational modifications, and assess the purity and consistency of the protein, which is of significant importance for the development and quality control of biopharmaceuticals, including antibody, protein and peptides. The common peptide mapping process only uses trypsin for protein digestion, and the average coverage rate of identified protein is about 60%. In order to obtain the full sequence information of the targeted protein, MtoZ Biolabs uses up to 6 kinds of proteases for protein digestion (Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Asp-N, Glu-C, Lys-C and Lys-N). After protein digestion, sequences of peptide are mapped for full-length sequence of biopharmaceuticals. MtoZ Biolabs offers peptide mapping service based on LC-MS/MS, ensuring accurate peptide mapping analysis. This service can be used to analyze the sequence of biopharmaceuticals and confirm complete expression of recombinant protein. With well-established technology and professional expertise, we can guarantee 100% peptide coverage and accurate data analysis.
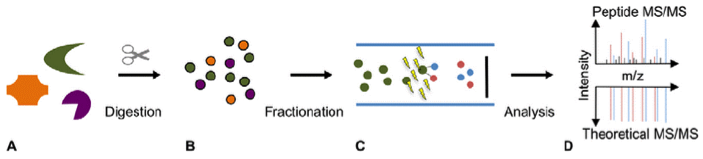
Bock, T. et al. Front. Biosci. 2012.
Figure 1. Peptide Mapping Analysis of Biopharmaceuticals
Analysis Workflow
1. Proper enzymes are selected for enzyme digestion and identification of target proteins.
2. Peptide analysis through LC-MS/MS or UV LC-MS/MS.
3. The total sequence of peptide coverage/peptide are mapped and compared with the theoretical sequence.
4. Delivery of report.
Service Advantages
1. Combination of specific and nonspecific proteases, achieving coverage of 100% of any protein (polypeptide).
2. Confirmation of each peptide is based on the MS/MS fingerprint of the sample, and is more accurate than MS analysis.
3. Protein sample 100% sequence validation service.
Sample Submission Requirements
1. Gel and solution samples are all acceptable for peptide mapping service, but special pretreatment is required for gel sample.
2. The required amount of protein sample: 10-20 μg.
3. Protein sample with purity of >80% is suggested.
Case Study
In the each and every experiment, we will try to improve identification efficiency and reduce the cost in accordance with the analytical principle. In this case, the customer sent us an in vitro expressed antibody for peptide mapping analysis and comparison with the theoretical sequence. After receiving the sample, we first selected 3 proteases for digestion and designed subsequent sequence analysis experiments based on the theoretical sequences provided by our customers. Part of the experimental data are shown below, which proved that the antibody obtained was consistent with the theoretical sequence.
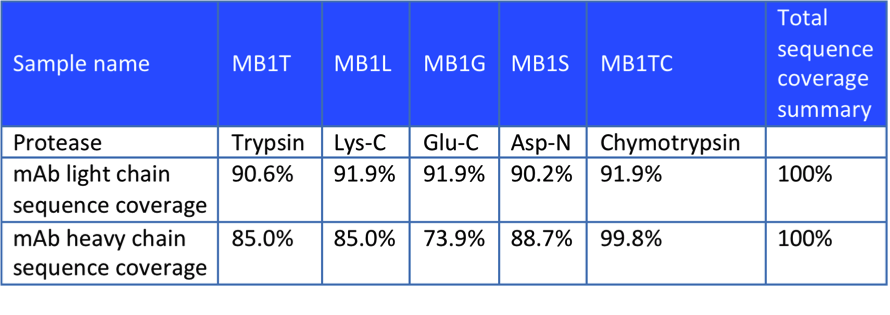
Figure 2. Enzyme Hydrolysis Results
In the final report, we will also provide detailed data on the coverage of the peptides as shown in the following graph.
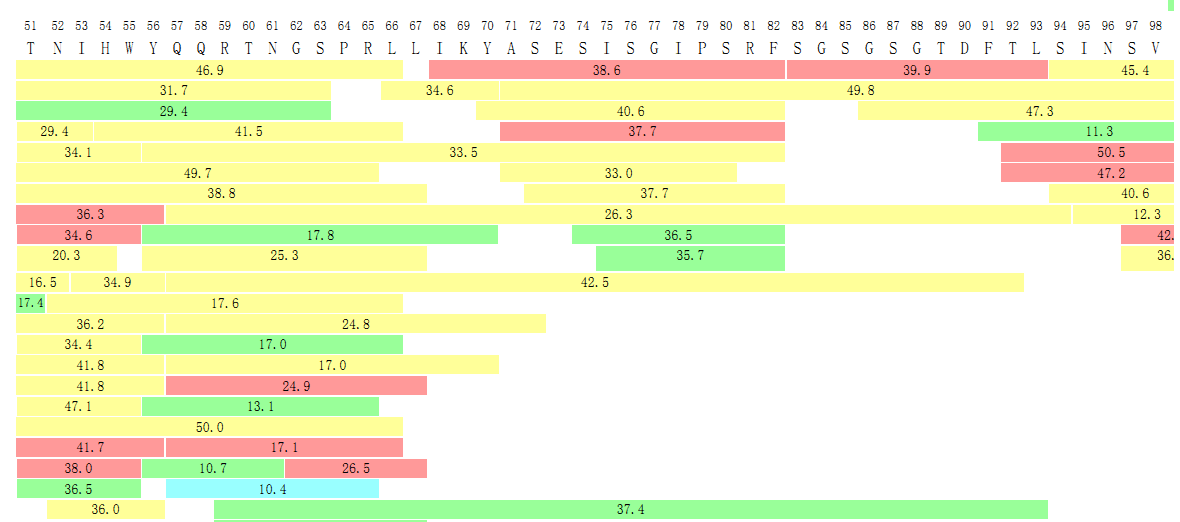
Figure 3. Peptide Mapping Results
Applications
1. Monitoring Quality Attribute of Biopharmaceutical
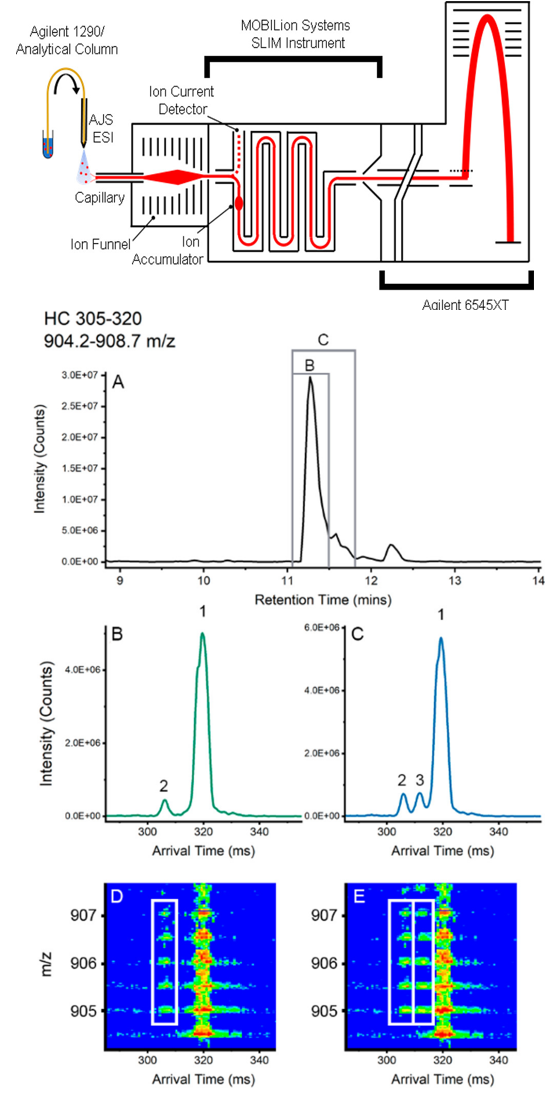
Arndt, JR. et al. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021.
Deliverables
1. Experiment Procedure
2. Parameters of Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometer
3. MS Raw Data Files
4. Peptide Mapping Results
5. Bioinformatics Analysis
Related Services
Identification of Biopharm
Variation Analysis
Purity Analysis
How to order?







